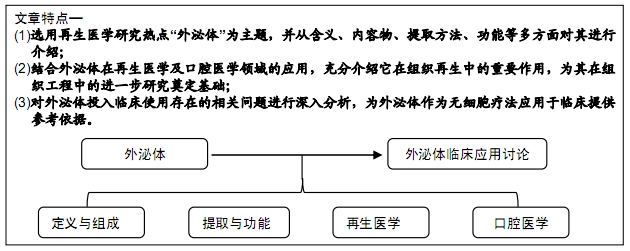
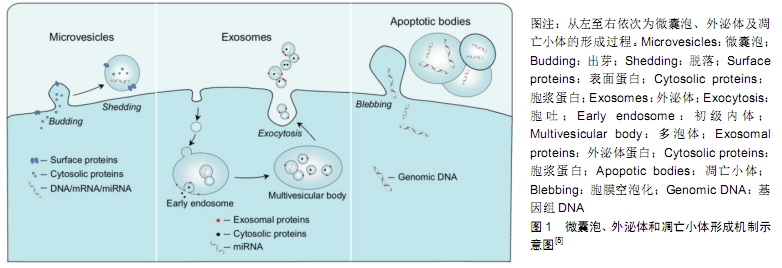
[1] 许怡薇,冯凯,石炳毅.干细胞在再生医学领域的临床应用现状及其前景[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(36): 7163-7166.
[2] LAI RC, YEO RW, LIM SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:82-88.
[3] 邓蓉蓉,谢伊旻,谢林.间充质干细胞归巢的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(19):2879-2888.
[4] HAN C, SUN X, LIU L, et al. Exosomes and Their Therapeutic Potentials of Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:7653489.
[5] LAWSON C, VICENCIO JM, YELLON DM, et al. Microvesicles and exosomes: new players in metabolic and cardiovascular disease. J Endocrinol. 2016;228(2):R57-71.
[6] ZHANG W, ZHOU X, ZHANG H, et al. Extracellular vesicles in diagnosis and therapy of kidney diseases. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016;311(5):F844-F851.
[7] EDGAR JR. Q&A: What are exosomes, exactly? BMC Biol. 2016;14:46.
[8] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420.
[9] YU S, CAO H, SHEN B, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes in cancer progression and treatment failure. Oncotarget. 2015; 6(35):37151-37168.
[10] ALENQUER M, AMORIM MJ. Exosome Biogenesis, Regulation, and Function in Viral Infection. Viruses. 2015; 7(9):5066-5083.
[11] LI XB, ZHANG ZR, SCHLUESENER HJ, et al. Role of exosomes in immune regulation. J Cell Mol Med. 2006;10(2): 364-375.
[12] THÉRY C, AMIGORENA S, RAPOSO G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3:Unit 3.22.
[13] LÄSSER C, ELDH M, LÖTVALL J. Isolation and characterization of RNA-containing exosomes. J Vis Exp. 2012;(59):e3037.
[14] SUBRA C, GRAND D, LAULAGNIER K, et al. Exosomes account for vesicle-mediated transcellular transport of activatable phospholipases and prostaglandins. J Lipid Res. 2010;51(8):2105-2120.
[15] MORELLI AE, LARREGINA AT, SHUFESKY WJ, et al. Endocytosis, intracellular sorting, and processing of exosomes by dendritic cells. Blood. 2004;104(10):3257-3266.
[16] BOON RA, VICKERS KC. Intercellular transport of microRNAs. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33(2):186-192.
[17] 孙晓燕,陈宁,谢臻蔚.外泌体在软组织损伤后修复中的研究进展[J].中国医药指南,2018,16(28):32-34.
[18] COLOMBO M, RAPOSO G, THÉRY C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30: 255-289.
[19] TAO SC, YUAN T, ZHANG YL, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics. 2017; 7(1):180-195.
[20] QIN Y, WANG L, GAO Z, et al. Bone marrow stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate osteoblast activity and differentiation in vitro and promote bone regeneration in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21961.
[21] KALLURI R. The biology and function of exosomes in cancer. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(4):1208-1215.
[22] GUPTA S, RAWAT S, ARORA V, et al. An improvised one-step sucrose cushion ultracentrifugation method for exosome isolation from culture supernatants of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):180.
[23] 缪着,卢福琼,马波,等.人间充质干细胞外泌体研究进展[J].中国医药生物技术,2019,14(4):361-365.
[24] LOBB RJ, BECKER M, WEN SW, et al. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27031.
[25] 高方园,焦丰龙,张养军,等.外泌体分离技术及其临床应用研究进展[J].色谱,2019,37(10):1071-1083.
[26] KALRA H, ADDA CG, LIEM M, et al. Comparative proteomics evaluation of plasma exosome isolation techniques and assessment of the stability of exosomes in normal human blood plasma. Proteomics. 2013;13(22): 3354-3364.
[27] KELLER S, RIDINGER J, RUPP AK, et al. Body fluid derived exosomes as a novel template for clinical diagnostics. J Transl Med. 2011;9:86.
[28] RUNZ S, KELLER S, RUPP C, et al. Malignant ascites-derived exosomes of ovarian carcinoma patients contain CD24 and EpCAM. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;107(3): 563-571.
[29] LAI RC, ARSLAN F, LEE MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214-222.
[30] ABRAMOWICZ A, WIDLAK P, PIETROWSKA M. Proteomic analysis of exosomal cargo: the challenge of high purity vesicle isolation. Mol Biosyst. 2016;12(5):1407-1419.
[31] 郭莹,王秀伟,牛玉虎,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体提取方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(9):1382-1388.
[32] KIM J, SHIN H, KIM J, et al. Isolation of High-Purity Extracellular Vesicles by Extracting Proteins Using Aqueous Two-Phase System. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0129760.
[33] ZAROVNI N, CORRADO A, GUAZZI P, et al. Integrated isolation and quantitative analysis of exosome shuttled proteins and nucleic acids using immunocapture approaches. Methods. 2015;87:46-58.
[34] 卢婉,杨人强,王伶.外泌体的研究进展[J].生命的化学, 2013, 33(4):438-442.
[35] JANSEN FH, KRIJGSVELD J, VAN RIJSWIJK A, et al. Exosomal secretion of cytoplasmic prostate cancer xenograft-derived proteins. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009;8(6): 1192-1205.
[36] GÉMINARD C, DE GASSART A, BLANC L, et al. Degradation of AP2 during reticulocyte maturation enhances binding of hsc70 and Alix to a common site on TFR for sorting into exosomes. Traffic. 2004;5(3):181-193.
[37] WANG M, ALTINOGLU S, TAKEDA YS, et al. Integrating Protein Engineering and Bioorthogonal Click Conjugation for Extracellular Vesicle Modulation and Intracellular Delivery. PLoS One. 2015;10(11):e0141860.
[38] PÊCHE H, HESLAN M, USAL C, et al. Presentation of donor major histocompatibility complex antigens by bone marrow dendritic cell-derived exosomes modulates allograft rejection. Transplantation. 2003;76(10):1503-1510.
[39] PASCUCCI L, COCCÈ V, BONOMI A, et al. Paclitaxel is incorporated by mesenchymal stromal cells and released in exosomes that inhibit in vitro tumor growth: a new approach for drug delivery. J Control Release. 2014;192:262-270.
[40] TIAN Y, LI S, SONG J, et al. A doxorubicin delivery platform using engineered natural membrane vesicle exosomes for targeted tumor therapy. Biomaterials. 2014;35(7):2383-2390.
[41] YU B, ZHANG X, LI X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4142-4157.
[42] LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346.
[43] KATSUDA T, KOSAKA N, TAKESHITA F, et al. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Proteomics. 2013;13(10-11): 1637-1653.
[44] MERINO-GONZÁLEZ C, ZUÑIGA FA, ESCUDERO C, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Angiogenesis: Potencial Clinical Application. Front Physiol. 2016;7:24.
[45] FANG S, XU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(10): 1425-1439.
[46] ZHANG B, WANG M, GONG A, et al. HucMSC-Exosome Mediated-Wnt4 Signaling Is Required for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Stem Cells. 2015;33(7):2158-2168.
[47] HU L, WANG J, ZHOU X, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32993.
[48] ZHANG W, BAI X, ZHAO B, et al. Cell-free therapy based on adipose tissue stem cell-derived exosomes promotes wound healing via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2018;370(2):333-342.
[49] DING J, WANG X, CHEN B, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stimulated by Deferoxamine Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Promoting Angiogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019: 9742765.
[50] ZHANG S, CHUAH SJ, LAI RC, et al. MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials. 2018;156:16-27.
[51] ZHOU J, LIU HX, LI SH, et al. Effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on fracture healing in rats through the Wnt signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(11):4954-4960.
[52] LI R, CHEN C, ZHENG RQ, et al. Influences of hucMSC-exosomes on VEGF and BMP-2 expression in SNFH rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(7): 2935-2943.
[53] CHEN S, TANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-375-overexpressing human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(5): e12669.
[54] LI W, LIU Y, ZHANG P, et al. Tissue-Engineered Bone Immobilized with Human Adipose Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Promotes Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(6):5240-5254.
[55] FURUTA T, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Fracture Healing in a Mouse Model. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(12):1620-1630.
[56] BIAN S, ZHANG L, DUAN L, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis in a rat myocardial infarction model. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014;92(4):387-397.
[57] MA J, ZHAO Y, SUN L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Akt-Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Cardiac Regeneration and Promote Angiogenesis via Activating Platelet-Derived Growth Factor D. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(1):51-59.
[58] 张静,易阳艳,阳水发,等.脂肪干细胞来源外泌体对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移及管样分化的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018, 32(10):1352-1357.
[59] WANG C, SONG W, CHEN B, et al. Exosomes Isolated From Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: A New Cell-Free Approach to Prevent the Muscle Degeneration Associated With Torn Rotator Cuffs. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(13):3247-3255.
[60] NAKAMURA Y, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Mesenchymal-stem-cell-derived exosomes accelerate skeletal muscle regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(11): 1257-1265.
[61] 朱斌,李楠,田自锋,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体促进牙周再生的体外研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2016,9(12):709-713.
[62] CHEW JRJ, CHUAH SJ, TEO KYW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes enhance periodontal ligament cell functions and promote periodontal regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019; 89:252-264.
[63] MOHAMMED E, KHALIL E, SABRY D. Effect of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Their Exo as Adjunctive Therapy to Nonsurgical Periodontal Treatment: A Histologic and Histomorphometric Study in Rats. Biomolecules. 2018; 8(4):E167.
|