中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (34): 5474-5480.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.34.011
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
细菌纳米纤维素与聚乙烯醇复合水凝胶管的生物相容性表征
唐敬玉1,包露涵1,李 雪1,陈 琳1,洪 枫1,2
- 1东华大学化学化工与生物工程学院微生物工程与工业生物技术研究组,上海市 201620;2纤维材料改性国家重点实验室(东华大学),上海市 201620
Biocompatibility of bacterial nanocellulose and bacterial nanocellulose/polyvinyl alcohol composite hydrogel tubes
Tang Jing-yu1, Bao Lu-han1, Li Xue1, Chen Lin1, Hong Feng1, 2
- 1Group of Microbiological Engineering and Industrial Biotechnology, College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China; 2State Key Laboratory for Modification of Chemical Fibers and Polymer Materials, Donghua University, Shanghai 201620, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
细菌纳米纤维素:是一种由微生物(如木葡糖酸醋杆菌等)分泌的多糖类高分子材料,具有与植物纤维素相同的化学组成,均为吡喃葡萄糖单体由β-1,4糖苷键构成的葡聚糖。与伴生半纤维素和木质素的植物纤维素相比,细菌纳米纤维素具有更高的化学纯度,独特的纳米纤维网络结构和更好的生物相容性,被广泛用于创伤敷料、人工皮肤和组织工程支架等。
聚乙烯醇:是一种水溶性的合成高分子,通过反复冻融的物理交联过程可制备成水凝胶材料,具有很好的弹性,与人体软组织的机械力学性能相近,被广泛研究用于医用敷料、人工血管和软骨组织工程支架等。研究证实,聚乙烯醇的高亲水特性可限制血浆蛋白在其表面的吸附,减少血小板的黏附,具有良好的血液相容性,然而这种特性同样限制了细胞在其表面的黏附,在应用于人工血管时不利于内皮层的形成。
背景:前期研究通过相分离技术制备了细菌纳米纤维素/聚乙烯醇复合管,显著改善了单纯细菌纳米纤维素管的机械力学性质,但对复合管生物相容性的研究并不充分。
目的:分析细菌纳米纤维素/聚乙烯醇复合管的生物相容性。
方法:通过单硅胶管和双硅胶管两种生物反应器,在线培育获得两种不同结构细菌纳米纤维素管,分别记为S-BNC和D-BNC;采用相分离方法将两种细菌纳米纤维素管分别与聚乙烯醇复合,制备细菌纳米纤维素/聚乙烯醇复合管;通过溶血率、血浆复钙、血小板黏附实验评价S-BNC、D-BNC、S-BNC/聚乙烯醇复合管及D-BNC/聚乙烯醇复合管材料的血液相容性。将4种管材料分别与猪髋骨内皮细胞(或人血管平滑肌细胞)共培养,3,7 d后,采用活死细胞染色观察细胞在材料表面生长情况。
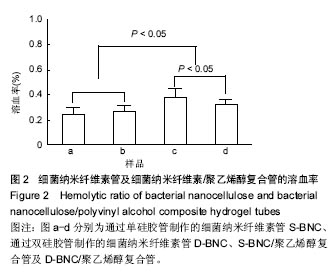
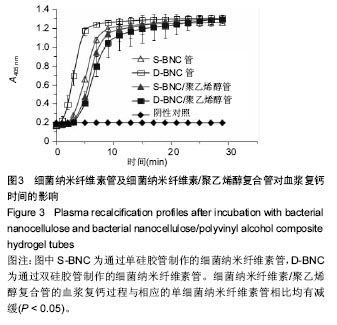
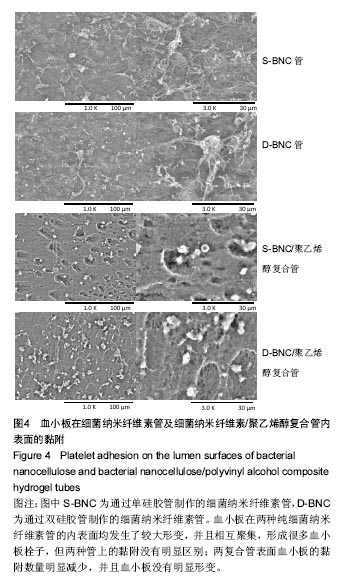
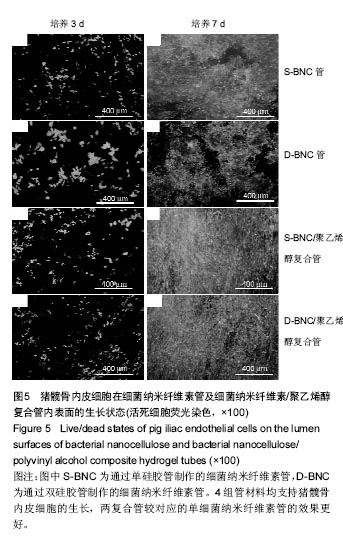
结果与结论:①血液相容性:4组管的溶血率均小于0.5%。D-BNC管的血浆复钙时间显著快于S-BNC管 (P < 0.05);两复合管的血浆复钙过程较相应的单细菌纳米纤维素管均有减缓(P < 0.05),两复合管血浆复钙时间无差异。血小板在两种纯细菌纳米纤维素管的内表面均发生了较大的形变,并且相互聚集,形成很多血小板栓子;两复合管的血小板黏附数量明显减少,且D-BNC/聚乙烯醇复合管血小板黏附量显著多于S-BNC/聚乙烯醇复合管;②细胞相容性:4组管材料均支持猪髋骨内皮细胞的生长,两复合管较对应的单细菌纳米纤维素管效果更好;4组管材料均支持人血管平滑肌细胞的生长,相对于单纯细菌纳米纤维素管,复合管可显著促进细胞的生长,其中以D-BNC/聚乙烯醇复合管的效果最好;③结果表明:细菌纳米纤维素/聚乙烯醇复合管具有良好的血液相容性与细胞相容性。
中图分类号:


.jpg)