中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (32): 5108-5114.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.32.005
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
整合性神经肌肉训练预防青少年女性运动性膝关节损伤
赵 响1,2,詹建国1,许 滨1
- (1北京体育大学,北京市 100084;2淮北师范大学,安徽省淮北市 235000)
-
收稿日期:2017-08-07出版日期:2017-11-18发布日期:2017-11-15 -
通讯作者:詹建国,教授,博士生导师,北京体育大学,北京市 100084 -
作者简介:赵响,男,1983年生,安徽省淮北市人,北京体育大学在读博士,讲师,主要从事青少年运动损伤预防的研究。 -
基金资助:国家社会科学基金教育学青年课题(CLA140161)
Integrative neuromuscular training protects juvenile female athletes from knee injury
Zhao Xiang1, 2, Zhan Jian-guo1, Xu Bin1
- (1Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China; 2Huaibei Normal University, Huaibei 235000, Anhui Province, China)
-
Received:2017-08-07Online:2017-11-18Published:2017-11-15 -
Contact:Zhan Jian-guo, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
About author:Zhao Xiang, Studying for doctorate, Lecturer, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China; Huaibei Normal University, Huaibei 235000, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:the Youth Education Project of National Social Science Foundation of China, No. CLA140161
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
整合性神经肌肉训练:是为了预防运动损伤和提高运动表现而设计的一般功能性动作训练与特定的力量、肌肉超等长、速度、灵敏、平衡训练相结合的综合性训练。
灵敏素质:是人体综合能力的反映,受遗传因素影响很大。为了提高灵敏素质,教练员应尽可能采取逐渐增加复杂程度的练习方式,也可以通过改变条件、器械、器材等方式增加技术动作的复杂性和难度。同时,还应着重培养和提高运动员掌握动作的能力、反应能力、平衡能力、观察能力、节奏感等。
文题释义:
整合性神经肌肉训练:是为了预防运动损伤和提高运动表现而设计的一般功能性动作训练与特定的力量、肌肉超等长、速度、灵敏、平衡训练相结合的综合性训练。
灵敏素质:是人体综合能力的反映,受遗传因素影响很大。为了提高灵敏素质,教练员应尽可能采取逐渐增加复杂程度的练习方式,也可以通过改变条件、器械、器材等方式增加技术动作的复杂性和难度。同时,还应着重培养和提高运动员掌握动作的能力、反应能力、平衡能力、观察能力、节奏感等。
中图分类号:
引用本文
赵 响,詹建国,许 滨. 整合性神经肌肉训练预防青少年女性运动性膝关节损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(32): 5108-5114.
Zhao Xiang1, 2, Zhan Jian-guo1, Xu Bin1. Integrative neuromuscular training protects juvenile female athletes from knee injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(32): 5108-5114.
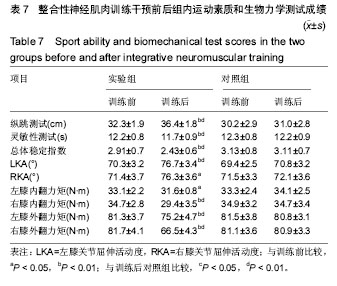
经过8周的整合性神经肌肉训练干预后,实验组的下肢生物力学有明显的变化,三维生物力学分析测试系统测出:①实验组的左膝关节屈伸度显著增加,右膝关节屈伸度显著增加(P < 0.05);对照组的左右膝关节屈伸度均无明显变化;②试验前后对受试者进行了左右膝内翻和外翻的力矩测试,实验前的实验组从箱子落地时膝内外翻力矩较大,经过8周的整合性神经肌肉训练干预后,左右膝内外翻力矩明显降低,左膝内翻力矩显著减小(P < 0.05);右膝内翻力矩显著减小(P < 0.01);左膝外翻力矩从显著减小(P < 0.05);右膝外翻力矩显著减小到(P < 0.05)。对照组的实验前后左右膝内外翻力矩均无明显变化。
2.4 不良事件 两组训练过程中均未发生与训练相关的不良事件。
| [1] Faigenbaum AD,Myer GD.Resistance training among young athletes:safety, efficacy and injury prevention effects. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(1):56-63.[2] Myer GD, Faigenbaum AD,Ford KR,et al.When to Initiate Integrative Neuromuscular Training to Reduce Sports-Related Injuries and Enhance Health in Youth.Current Sports Medicine Reports.2011;10(3):157-166.[3] Myer GD, Sugimoto D, Thomas S, et al. The Influence of Age on the Effectiveness of Neuromuscular Training to Reduce Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury in Female Athletes; A Meta-Analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(1):203-215. [4] Emery CA, Roy TO, Whittaker JL, et al. Neuromuscular training injury prevention strategies in youth sport: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Sports Med.2015;49(13):865-870.[5] Fort VA, Romero RD, Lloyd RS, et al.Integrative Neuromuscular Training in Youth Athletes.Part II:Strategies to Prevent Injuries and Improve Performance.Strength Condition J.2016;38(4):9-27.[6] Kraemer WJ,Hakkinen K,Triplett NT, et al. Physiological changes with periodized resistance training in women tennis players. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2003;35(5):889.[7] Jatin PA, Lindsey MM, Shane VC,et al.Relationships between core endurance, hip strength, and balance in collegiate female athletes.Int J Sports Phys Ther.2014; 9(5):604-616. [8] Mendiguchia J, Martinez R E, Morin JB, et al. Effects of hamstring-emphasized neuromuscular training on strength and sprinting mechanics in football players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;25(6):e621-629.[9] Ford KR, Shapiro R, Myer GD, et al. Longitudinal sex differences during landing in knee abduction in young athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2010;42(10):1923-1931.[10] Hewett TE, Myer GD, Ford KR.Decrease in Neuromuscular Control About the Knee with Maturation in Female Athletes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(8):1601-1608.[11] Schmitz RJ, Shultz SJ, Nguyen A.Dynamic valgus alignment and functional strength in males and females during maturation. J Athl Train. 2009;44(1):26-32.[12] Yu B,McClure SB,Onate JA,et al.Age and Gender Effects on Lower Extremity Kinematics of Youth Soccer Players in a Stop-Jump Task. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(9):1356-1364.[13] Yaniv M, Becker T, Goldwirt M, et al. Prevalence of Bowlegs Among Child and Adolescent Soccer Players. Clin J Sport Med. 2006 ;16(5):392-396.[14] Myer GD, Ford KR, Palumbo JP, et al. Neuromuscular training improves performance and lower-extremity biomechanics in female athletes. J Strength Cond Res. 2005;19(1):51-60.[15] Naclerio F,Faigenbaum A.Integrative neuromuscular training for youth.Revista Kronos.2011;10(1):49-56.[16] Tran ST, Thomas S, DiCesare C, et al.A pilot study of biomechanical assessment before and after an integrative training program for adolescents with juvenile fibromyalgia.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J.2016;14(1):43.[17] Wiggins AJ, Grandhi RK, Schneider DK, et al. Risk of Secondary Injury in Younger Athletes After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Am J Sports Med.2016;l44(7):1861-1876.[18] Faigenbaum AD, Farrell A, Fabiano M, et al. Effects of integrative neuromuscular training on fitness performance in children. Pediatr Exerc Sci. 2011 ;23(4):573-584.[19] Faigenbaum AD, Myer GD, Farrell A, et al.Integrative neuromuscular training and sex-specific fitness performance in 7-year-old children: an exploratory investigation. J Athl Train. 2014;49(2):145-153.[20] Myer GD, Faigenbaum AD. Exercise is sports medicine in youth: Integrative neuromuscular training to optimize motor development and reduce risk of sports related injury.Revista Kronos.2011;10(1): 39-48.[21] Pfile KR, Gribble PA, Buskirk GE, et al.Sustained Improvements in Dynamic Balance and Landing Mechanics After a 6-Week Neuromuscular Training Program in College Women's Basketball Players. J Sport Rehabil. 2016;25(3):233-240.[22] Stockbrugger BA, Haennel RG. Validity and reliability of a medicine ball explosive power test. J Strength Cond Res. 2001;15(4):431-438.[23] Martha RH. Factors Affecting Reliability of the Biodex Balance System: A Summary of Four Studies.J Sport Rehabil.2000;9(3):240. [24] Raya MA. Comparison of three agility tests with male servicemembers: Edgren Side Step Test, T-Test, and Illinois Agility Test. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2013;50(7):951-960.[25] Winter DA. Biomechanics and Motor Control of Human Movement.Hoboken:JOHN WILEY & SONS,2009. [26] 王安利.运动损伤预防的功能训练[M].北京:北京体育大学出版社,2013.[27] Fischer DV. Neuromuscular Training to Prevent Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury in the Female Athlete.Strength Condition J. 2006;28(5):44.[28] Faigenbaum AD, Kraemer WJ, Blimkie CJ, et al. Youth resistance training:updated position statement paper from the national strength and conditioning association. J Strength Cond Res. 2009;23(5 Suppl):S60-79. [29] Mayhew JL, Johnson BD, LaMonte MJ, et al.Accuracy of prediction equations for determining one repetition maximum bench press in women before and after resistance training. J Strength Cond Res. 2008;22(5):1570-1577.[30] DiStefano LJ, Padua DA, Blackburn JT, et al. Integrated Injury Prevention Program Improves Balance and Vertical Jump Height in Children.Psychiatric Hospital.2010;24(2):332-342. [31] Kent A, John PO, Katie LO, et al.The Effect of Six Weeks of Squat, Plyometric and Squat Plyometric Training on Power Production.The Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research.1992;6(1):36.[32] Mathisen G,Pettersen SA. Anthropometric factors related to sprint and agility performance in young male soccer players.Open Access J Sports Med.2015;10(12):337-342.[33] Bauer T,Thayer RE,Baras G.Comparison of training modalities for power development in the lower extremity.J Applied Sport Sci Res. 1990;4(4):115-121.[34] Mathisen G,Pettersen SA. Effect of high-intensity training on speed and agility performance in 10-year-old soccer players.J Sports Med Phys Fitness.2015;55(1-2):25-29.[35] Sarabon N, Panjan A, Rosker J, et al. Functional and neuromuscular changes in the hamstrings after drop jumps and leg curls.J Sports Sci Med.2013;12(3):431-438.[36] Michaelidis M, Koumantakis GA.Effects of knee injury primary prevention programs on anterior cruciate ligament injury rates in female athletes in different sports: a systematic review. Phys Ther Sport. 2014;15(3):200-210.[37] Timothy EH, Amanda LS, Thomas AN, et al. Plyometric training in female athletes: Decreased impact forces and increased hamstring torques. Am J Sports Med. 1996;24(6):765-773.[38] Marloes HP,Joan MD,Anne B,et al.Effect of Interventions on Potential, Modifiable Risk Factors for Knee Injury in Team Ball Sports:A Systematic Review.Sports Medi.2014;44(10):1403-1426.[39] Borghuis J, Hof AL, Lemmink KA.The importance of sensory-motor control in providing core stability: implications for measurement and training.Sports Med.2008;38(11):893-916. [40] Fitzgerald GK, Piva SR, Gil AB, et al.Agility and Perturbation Training Techniques in Exercise Therapy for Reducing Pain and Improving Function in People With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Physical Therapy.2011; 91(4):452-469.[41] Jae HY, Bee OL, Mina H,et al.A meta-analysis of the effect of neuromuscular training on the prevention of the anterior cruciate ligament injury in female athletes. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2010;18(6):824-830. |
| [1] | 王建平, 张晓辉, 余进伟, 魏绍亮, 张新民, 许幸新, 曲海军. 三维图像配准及坐标变换膝关节运动分析在机构学中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | 张玉芳, 吕 蒙, 梅 钊. 青少年脊柱侧弯全脊柱生物力学模型的构建及验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [3] | 张吉超, 董跃福, 牟志芳, 张 震, 李冰言, 徐祥钧, 李佳意, 任 梦, 董万鹏. 骨关节炎患者在不同步态角度下膝关节内部生物力学变化的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [4] | 白子兴, 曹旭含, 孙承颐, 杨艳军, 陈 思, 温建民, 林新晓, 孙卫东. 步态周期中踝关节有限元模型的构建及生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1362-1366. |
| [5] | 刘 峰, 冯 毅. 步态周期下不同克氏针张力带治疗髌骨横行骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1367-1371. |
| [6] | 姚晓玲, 彭建城, 许岳荣, 杨志东, 张顺聪. 可变角度零切迹前路椎间融合内固定系统治疗脊髓型颈椎病:30个月随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [7] | 肖 豪, 刘 静, 周 君. 脉冲电磁场治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [8] | 安维政, 何 萧, 任 帅, 刘建宇. 肌源干细胞在周围神经再生中的潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [9] | 张璟琳, 冷 敏, 朱博恒, 汪 虹. 干细胞源外泌体促进糖尿病创面愈合的机制及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [10] | 温明韬, 梁学振, 李嘉程, 许 波, 李 刚 . 两种方式固定Sanders Ⅱ型跟骨骨折后的力学稳定性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(6): 838-842. |
| [11] | 黄 浩, 洪 嵩, 瓦庆德. 全膝关节置换过程中股骨假体旋转对髌股关节接触压影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [12] | 郑永泽, 郑利钦, 何兴鹏, 陈心敏, 李木生, 李鹏飞, 林梓凌. 基于ABAQUS软件股骨颈骨折的扩展有限元建模分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(6): 853-857. |
| [13] | 刘宇航, 周建强, 徐雪彬, 曲星月, 李梓瑜, 李 琨, 王 星, 李志军, 李筱贺, 张少杰. 6岁儿童下颈椎有限元模型建立及有效性验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(6): 870-874. |
| [14] | 段 超, 尚晓强, 段祥林, 杨 平, 陶圣祥. 聚髌爪固定与袢钢板结合聚髌爪固定治疗髌骨下极粉碎性骨折的稳定性对比[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(6): 934-937. |
| [15] | 何云影, 李玲婕, 张舒淇, 李雨舟, 杨 生, 季 平. 聚丙烯酸/琼脂糖三维培养构建细胞球的方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(4): 553-559. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
|
表1 本项研究受试者的基本情况 (x±s,n=9)
Table 1 Basic information of the subjects
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
表2 整合性神经肌肉训练安排
Table 2 Integrative neuromuscular training arrangement
|
|
表注:训练内容参照前人的研究改编[18-21]。
|
|
|
表3 速度素质训练安排
Table 3 Speed training arrangement
|
|
|
表4 耐力素质训练安排
Table 4 Endurance training arrangement
|
|
|
表5 灵敏素质训练安排
Table 5 Agility training arrangement
|
|
|
表6 传统体能训练安排
Table 6 Traditional physical fitness training arrangement
|
|
(3)灵敏素质测试:灵敏性测试(T-test)(图1)包含了前后左右各个方向的加速、减速以及迅速变向的能力。灵敏性测试的评判间信度(interrater reliability)的组内相关系数(ICC)是0.98,重测信度(test-retest)的组内相关系数(ICC)是0.83,均达到了较高的水平[24]。测试前,受试者先进行 15 min的慢跑和动态肌肉拉伸。然后进行2次全程试走,以熟悉测试路线,这样做不会因运动员体力下降影响测试准确性。全程由一名测试员来记录时间。听到“开始”的口令后,受试者从起点处出发,用最快的速度向前跑10 m到中间的标志物,然后向右跑动5 m到达最右侧的标志物,接着向左跑动10 m到达最左侧的标志物,再向右跑动5 m到达中间的标志物,最后向后跑到终点处(注:全程身体面相前方,脚尖朝前,不能使用交叉步)。用秒表记录2次按本试验要求通过全程的最快时间,2次测试的时间间隔为5 min。
.jpg)
1.4.4 运动生物力学测试 用于本研究的三维生物力学分析测试仪器包括一个具有8个摄像头、频率控制在 200 Hz的高速摄像机(Vicon Motion Analysis Inc.,Oxford,UK)和三维测力平台(1 000 Hz,Kistler Instruments AG Corp.,Winterthur,Switzerland),分别进行三维运动捕捉和采集起跳过程中地面的反作用力信息。测试前,提前24 h对测力台进行开机预热,防止开机后的零点漂移现象。三维测力台的频率控制在1 000 Hz,保持和三维运动分析系统在时间上的同步性。在进行下落纵跳测试前,对受试者进行了marker的标记(包括:左髂后上棘、两侧大转子左右大腿中部、膝盖的内侧和外侧、小腿的中部、脚踝的中部和外侧、脚背第2和第3跖骨的中间)并且进行了静态建模。向受试者讲清楚测试的内容、目的、动作过程、具体做法和注意事项,然后进行15 min慢跑和韧带牵拉,每人进行3次试跳,以便掌握动作要领。在正式测试时,受试者双手插腰,从30 cm高的测试箱上以站立姿势准备开始跳下箱子,然后进行一个最大纵跳,记录下每位受试者成功的3次纵跳数据。使用12 Hz的低通滤波器和直接线性转换法对marker的轨迹进行评 估[25],同时记录下左右侧膝关节的屈伸角度,最终通过动作和力的逆动力学原理来计算出膝关节内外翻的扭矩。
1.6 统计学分析 用SPSS 17.0对实验组和对照组的前测、后测成绩进行配对t 检验分析。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
.jpg)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
.jpg) 文题释义:
整合性神经肌肉训练:是为了预防运动损伤和提高运动表现而设计的一般功能性动作训练与特定的力量、肌肉超等长、速度、灵敏、平衡训练相结合的综合性训练。
灵敏素质:是人体综合能力的反映,受遗传因素影响很大。为了提高灵敏素质,教练员应尽可能采取逐渐增加复杂程度的练习方式,也可以通过改变条件、器械、器材等方式增加技术动作的复杂性和难度。同时,还应着重培养和提高运动员掌握动作的能力、反应能力、平衡能力、观察能力、节奏感等。
文题释义:
整合性神经肌肉训练:是为了预防运动损伤和提高运动表现而设计的一般功能性动作训练与特定的力量、肌肉超等长、速度、灵敏、平衡训练相结合的综合性训练。
灵敏素质:是人体综合能力的反映,受遗传因素影响很大。为了提高灵敏素质,教练员应尽可能采取逐渐增加复杂程度的练习方式,也可以通过改变条件、器械、器材等方式增加技术动作的复杂性和难度。同时,还应着重培养和提高运动员掌握动作的能力、反应能力、平衡能力、观察能力、节奏感等。对运动员进行符合生物力学特征的动作模式进行反复的强化教育,也是预防运动损伤的重要因素。通过反复练习正确的双脚垫步跳、单脚跳及快速变向技术,可以强化和改善下肢在做跳跃动作时的生物力学动作模式,最终,人体可以自动化地做出正确的动作模式。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||