| [1]肖振宇.骨髓间充质干细胞与软骨细胞共同培养复合可注射性改良纤维蛋白凝胶支架修复兔膝关节软骨缺损的实验研究[D].成都:四川医科大学,2015.[2]吴岩,欧阳宏伟,毕龙,等.神经示踪技术在感觉神经化组织工程骨评价中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(5):444-448.[3]刘志刚,熊敏,曾云,等.DA-2006促进骨髓基质干细胞分化为成骨细胞效果及机制分析[J]. 现代仪器与医疗,2014,20(2):35-38.[4]李新江,方艳伟,张爱民,等.骨髓间充质干细胞-生物蛋白胶复合物修复兔膝关节软骨缺损[J].中华创伤杂志,2015,31(6): 563-567.[5]陈浩,张治金,赵德伟,等.羊膜衍生膜负载骨髓间充质干细胞修复软骨缺损的可行性研究[J]. 中华显微外科杂志, 2014,37(3): 254-257.[6]Teng SH,Liang MH,Wang P,et al.Biomimetic composite microspheres of collagen/chitosan/nano-hydroxyapatite: In-situ synthesis and characterization.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;58:610-613. [7]Hui DY,Li R,Sakuma NA,et al.Formation of proximal and anterior limb skeleton requires early function of Irx3 and Irx5 and is negatively regulated by Shh signaling. Dev Cell.2014; 29(2):233-240.[8]Song K,Rao NJ,Chen ML,et al.Enhanced bone regeneration with sequential delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor and sonic hedgehog.Injury.2011;42(8):796-802.[9]宋珂,石琦,青莹,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养及鉴定的相关研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2015,31(9):531-535.[10]Ejeian F,Baharvand H,Nasr-Esfahani MH.Hedgehog signalling is dispensable in the proliferation of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth.Cell Biol Int.2014;38(4): 480-487. [11]Jia Y,Wu D,Zhang R,et al.Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells expressing the Shh transgene promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats.Neurosci Lett.2014;573:46-51. [12]Balasundaram G,Storey DM,Webster TJ.Novel nano-rough polymers for cartilage tissue engineering.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;9:1845-1853.[13]Simberg Ying,Chao PP,Karmali R,et al.Direct recognition of superparamagnetic nanocrystals by macrophage scavenger receptor SR-AI.ACS Nano.2013;7(5):4289-4298.[14]任义德,张亚峰,尤武林,等.Foxc2基因修饰骨髓间充质干细胞修复实验性兔股骨头坏死[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(6): 834-840.[15]张雁儒,张辉,卡卡,等.血管内皮生长因子复合骨形态发生蛋白-2转染骨髓间充质干细胞修复兔股骨头坏死模型[J].解剖学杂志, 2015,38(2):157-161.[16]Cheng Y,Cheng P,Xue F,et al.Repair of ear cartilage defects with allogenic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rabbits.Cell Biochem Biophys.2014;70(2):1137-1143.[17]李巍,户小伟,冼呈,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植联合氯化锂治疗兔股骨头缺血坏死疗效[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(6): 868-875.[18]Frisch J,Venkatesan JK,Rey-Rico A,et al.Determination of the chondrogenic differentiation processes in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells genetically modified to overexpress transforming growth factor-β via recombinant adeno-associated viral vectors.Hum Gene Ther.2014;25(12): 1050-1060.[19]谭旭仪,李刚,高书图,等.股骨头坏死愈胶囊含药血清对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡的保护作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2015, 21(3):146-149.[20]蔡伟斌,范积平,吕扬阳,等.髓芯减压术、自体髂骨移植术与骨髓间充质干细胞移植术联合治疗战创伤致早期成人股骨头坏死[J].广东医学,2016,37(1):106-108.[21]Gao G,Yonezawa T,Hubbell K,et al.Inkjet-bioprinted acrylated peptides and PEG hydrogel with human mesenchymal stem cells promote robust bone and cartilage formation with minimal printhead clogging.Biotechnol J.2015;10(10): 1568-1577.[22]刘慧娟,胡若愚,戴王娟,等.绿色荧光蛋白转基因大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞培养及鉴定[J]. 中国医学科学院学报,2016,38(1):9-15.[23]莫峰波,杨述华,叶树楠,等.5'-氮杂胞苷对激素性股骨头坏死骨髓间充质干细胞分化作用的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(2):165-171.[24]Mehrabani D,Babazadeh M,Tanideh N,et al.The Healing Effect of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Full-thickness Femoral Articular Cartilage Defects of Rabbit.Int J Organ Transplant Med.2015;6(4):165-175.[25]李昂,王晓宇,许茜楠,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合骨髓间充质干细胞阻止股骨骨不连的形成[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(21):3080-3087.[26][ayton E,Purcell M,Smith JO,et al.The scale-up of a tissue engineered porous hydroxyapatite polymer composite scaffold for use in bone repair:An ovine femoral condyle defect study.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;103(4):1346-1356.[27]Khojasteh A,Dashti SG,Dehghan MM,et al.The osteoregenerative effects of platelet-derived growth factor BB cotransplanted with mesenchymal stem cells, loaded on freeze-dried mineral bone block: A pilot study in dog mandible.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2014;102(8): 1771-1778.[28]张波,韦冰丹,甘坤宁,等.富血小板血浆联合骨髓间充质干细胞对兔股骨头坏死BMP-2/Smads通路的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2016,22(2):131-134.[29]石正松,李强,宁寅宽,等.hBMP-2基因转染兔骨髓间充质干细胞体内移植后hBMP-2的活性检测[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015, 21(11):1333-1337. |
.jpg)
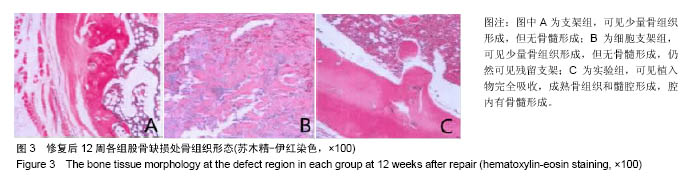
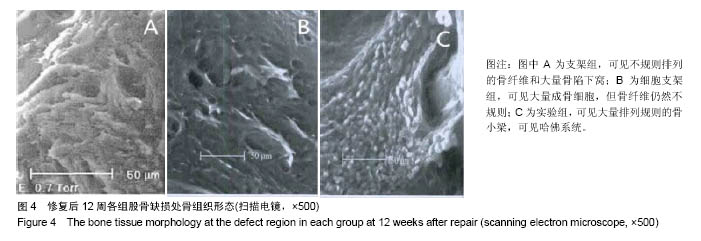
.jpg)
.jpg)