| [1] Filardo G, Perdisa F, Roffi A, et al.Stem cells in articular cartilage regeneration. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11:42.[2] Harris JD, Siston RA, Brophy RH, et al.Failures, re-operations, and complications after autologous chondrocyte implantation--a systematic review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(7): 779-791.[3] Niemeyer P, Salzmann GM, Hirschmuller A, et al.[Factors that influence clinical outcome following autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage defects of the knee]. Z Orthop Unfall. 2012; 150(1):83-88.[4] Vasiliadis HS, Wasiak J, Salanti G.Autologous chondrocyte implantation for the treatment of cartilage lesions of the knee: a systematic review of randomized studies. Knee Surg. 2010; 18(12):1645-1655.[5] Nazempour A, Van Wie BJ. Chondrocytes, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, and Their Combination in Articular Cartilage Regenerative Medicine. Ann Biomed Eng. 2016; 44(5): 1325-1354.[6] Goers L, Freemont P, Polizzi KM.Co-culture systems and technologies: taking synthetic biology to the next level. J R Soc Interface. 2014;11(96). pii: 20140065. [7] Krinner A, Roeder I.Quantification and modeling of stem cell-niche interaction. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014; 844:11-36.[8] Lawrence TS, Beers WH, Gilula NB.Transmission of hormonal stimulation by cell-to-cell communication. Nature. 1978; 272(5653):501-506.[9] Gayathri L, Dhanasekaran D, Akbarsha MA.Scientific concepts and applications of integrated discrete multiple organ co-culture technology. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 2015;6(2):63-70.[10] Huang CP, Lu J, Seon H, et al. Engineering microscale cellular niches for three-dimensional multicellular co-cultures. Lab Chip. 2009; 9(12):1740-1748.[11] Li AP. In vitro evaluation of human xenobiotic toxicity: scientific concepts and the novel integrated discrete multiple cell co-culture (IdMOC) technology. Altex. 2008; 25(1):43-49.[12] Hendriks J, Riesle J, van Blitterswijk CA. Co-culture in cartilage tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Reg Med. 2007; 1(3):170-178.[13] Wu L, Leijten JC, Georgi N, et al.Trophic effects of mesenchymal stem cells increase chondrocyte proliferation and matrix formation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(9-10): 1425-1436.[14] Wu L, Prins HJ, Helder MN, et al.Trophic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in chondrocyte co-cultures are independent of culture conditions and cell sources. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(15-16):1542-1551.[15] Acharya C, Adesida A, Zajac P, et al.Enhanced chondrocyte proliferation and mesenchymal stromal cells chondrogenesis in coculture pellets mediate improved cartilage formation. J Cell Phys. 2012;227(1):88-97.[16] Windt TS, Hendriks JA, Zhao X, et al.Concise review: unraveling stem cell cocultures in regenerative medicine: which cell interactions steer cartilage regeneration and how? Stem Cells Trans Med. 2014;3(6):723-733.[17] Meretoja VV, Dahlin RL, Kasper FK, et al.Enhanced chondrogenesis in co-cultures with articular chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2012;33(27): 6362-6369.[18] Yang YH, Lee AJ, Barabino GA.Coculture-driven mesenchymal stem cell-differentiated articular chondrocyte-like cells support neocartilage development. Stem Cells Trans Med. 2012;1(11):843-854.[19] Ouyang X, Wei B, Mao F, et al.Uncultured bone marrow mononuclear cells delay the dedifferentiation of unexpanded chondrocytes in pellet culture. Cell Tissue Res. 2015;361(3): 811-821.[20] Zhang F, Su K, Fang Y, et al.A mixed co-culture of mesenchymal stem cells and transgenic chondrocytes in alginate hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(1):77-84.[21] Vats A, Bielby RC, Tolley N, et al.Chondrogenic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells: the effect of the micro-environment. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(6):1687-1697.[22] Pereira RC, Costa-Pinto AR, Frias AM, et al.In vitro chondrogenic commitment of human Wharton's jelly stem cells by co-culture with human articular chondrocytes. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015.[23] Zheng P, Ju L, Jiang B, et al.Chondrogenic differentiation of human umbilical cord bloodderived mesenchymal stem cells by coculture with rabbit chondrocytes. Mol Med Reports. 2013; 8(4):1169-1182.[24] Wang L, Ott L, Seshareddy K, et al.Musculoskeletal tissue engineering with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells. Regen Med. 2011;6(1):95-109.[25] Chai DH, Arner EC, Griggs DW, et al.Alphav and beta1 integrins regulate dynamic compression-induced proteoglycan synthesis in 3D gel culture by distinct complementary pathways. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18(2): 249-256.[26] Diaz-Romero J, Gaillard JP, Grogan SP, et al.Immunophenotypic analysis of human articular chondrocytes: changes in surface markers associated with cell expansion in monolayer culture. J Cell Physiol. 2005; 202(3):731-742.[27] Kisiday JD, Jin M, DiMicco MA, et al.Effects of dynamic compressive loading on chondrocyte biosynthesis in self-assembling peptide scaffolds. J Biomech. 2004;37(5): 595-604.[28] Sabatino MA, Santoro R, Gueven S, et al. Cartilage graft engineering by co-culturing primary human articular chondrocytes with human bone marrow stromal cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(12):1394-1403.[29] Taylor DW, Ahmed N, Hayes AJ, et al.Hyaline cartilage tissue is formed through the co-culture of passaged human chondrocytes and primary bovine chondrocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 2012;60(8):576-587.[30] Lacombe-Gleize S, Gregoire M, Demignot S, et al.Implication of TGF beta 1 in co-culture of chondrocytes-osteoblasts. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1995;31(9): 649-652.[31] Schaefer D, Martin I, Shastri P, et al.In vitro generation of osteochondral composites. Biomaterials. 2000;21(24):2599- 2606.[32] Sanchez C, Deberg MA, Piccardi N, et al.Subchondral bone osteoblasts induce phenotypic changes in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005; 13(11):988-997.[33] Spalazzi JP, Dionisio KL, Jiang J, et al.Osteoblast and chondrocyte interactions during coculture on scaffolds. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 2003;22(5):27-34.[34] Jiang J, Nicoll SB, Lu HH.Co-culture of osteoblasts and chondrocytes modulates cellular differentiation in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;338(2):762-770.[35] Qing C, Wei-ding C, Wei-min F.Co-culture of chondrocytes and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro enhances the expression of cartilaginous extracellular matrix components. Brazil J Med Biol Res. 2011;44(4):303-310.[36] Mo XT, Guo SC, Xie HQ, et al.Variations in the ratios of co-cultured mesenchymal stem cells and chondrocytes regulate the expression of cartilaginous and osseous phenotype in alginate constructs. Bone. 2009;45(1):42-51.[37] Heng BC, Cao T, Lee EH.Directing stem cell differentiation into the chondrogenic lineage in vitro. Stem cells (Dayton, Ohio). 2004;22(7):1152-1167.[38] Tan AR, Dong EY, Andry JP, et al.Coculture of engineered cartilage with primary chondrocytes induces expedited growth. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(10):2735-2743.[39] Ahmed N, Dreier R, Gopferich A, et al.Soluble signalling factors derived from differentiated cartilage tissue affect chondrogenic differentiation of rat adult marrow stromal cells. Cell Phys Biochem. 2007;20(5):665-678.[40] Fischer J, Dickhut A, Rickert M, et al.Human articular chondrocytes secrete parathyroid hormone-related protein and inhibit hypertrophy of mesenchymal stem cells in coculture during chondrogenesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(9):2696-2706.[41] Richardson SM, Walker RV, Parker S, et al.Intervertebral disc cell-mediated mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio). 2006;24(3):707-716.[42] Zuo Q, Cui W, Liu F, et al.Co-cultivated mesenchymal stem cells support chondrocytic differentiation of articular chondrocytes. Int Orthop. 2013;37(4):747-752.[43] Djouad F, Delorme B, Maurice M, et al.Microenvironmental changes during differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells towards chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(2):R33.[44] Varas L, Ohlsson LB, Honeth G, et al.Alpha10 integrin expression is up-regulated on fibroblast growth factor-2-treated mesenchymal stem cells with improved chondrogenic differentiation potential. Stem Cells Dev. 2007;16(6):965-978.[45] Bian L, Zhai DY, Mauck RL, et al. Coculture of human mesenchymal stem cells and articular chondrocytes reduces hypertrophy and enhances functional properties of engineered cartilage. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(7-8):1137-1145.[46] Battiston KG, Cheung JW, Jain D, et al.Biomaterials in co-culture systems: towards optimizing tissue integration and cell signaling within scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2014;35(15): 4465-4476.[47] Rowland CR, Colucci LA, Guilak F.Fabrication of anatomically-shaped cartilage constructs using decellularized cartilage-derived matrix scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2016;91: 57-72.[48] Shijun X, Junsheng M, Jianqun Z, et al. In vitro three-dimensional coculturing oly3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3- hydroxyhexanoate with mouse-induced pluripotent stem cells for myocardial patch application. J Biomater Appl. 2016;30(8): 1273-1282.[49] Kalpakci KN, Kim EJ, Athanasiou KA.Assessment of growth factor treatment on fibrochondrocyte and chondrocyte co-cultures for TMJ fibrocartilage engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(4):1710-1718.[50] He X, Feng B, Huang C, et al.Electrospun gelatin/polycaprolactone nanofibrous membranes combined with a coculture of bone marrow stromal cells and chondrocytes for cartilage engineering. Int J Nanomed. 2015; 10:2089-2099.[51] Levorson EJ, Santoro M, Kasper FK, et al.Direct and indirect co-culture of chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells for the generation of polymer/extracellular matrix hybrid constructs. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):1824-1835.[52] Benya PD, Shaffer JD.Dedifferentiated chondrocytes reexpress the differentiated collagen phenotype when cultured in agarose gels. Cell. 1982;30(1):215-224.[53] Darling EM, Athanasiou KA.Rapid phenotypic changes in passaged articular chondrocyte subpopulations. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(2):425-432.[54] Mata-Miranda MM, Martinez-Martinez CM, Noriega-Gonzalez JE, et al.Morphological, genetic and phenotypic comparison between human articular chondrocytes and cultured chondrocytes. Histoch Cell Biol. 2016;146(2):183-189.[55] Kubosch EJ, Heidt E, Bernstein A, et al.The trans-well coculture of human synovial mesenchymal stem cells with chondrocytes leads to self-organization, chondrogenic differentiation, and secretion of TGFbeta. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):64.[56] Cooke ME, Allon AA, Cheng T, et al.Structured three-dimensional co-culture of mesenchymal stem cells with chondrocytes promotes chondrogenic differentiation without hypertrophy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(10):1210-1218.[57] Fong CY, Subramanian A, Gauthaman K, et al.Human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly stem cells undergo enhanced chondrogenic differentiation when grown on nanofibrous scaffolds and in a sequential two-stage culture medium environment. Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8(1): 195-209.[58] Armstrong JP, Shakur R, Horne JP, et al.Artificial membrane-binding proteins stimulate oxygenation of stem cells during engineering of large cartilage tissue. Naturecommunications. 2015;6:7405.[59] Kalpakci KN, Kim KJ, Athanasiou KA. Assessment of Growth Factor Treatment on Fibrochondrocyte,Chondrocyte Co-Cultures for TMJ Fibrocartilage Engineering. Acta Biomater. 2011; 7(4): 1710-1718.[60] 张勇,赵建宁,韩宁波.不同培养条件下脂肪干细胞与软骨细胞共培养的研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(10):782-785. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
共培养:模拟机体内生理条件,将两种(可来自同一组织或不同的组织)及以上的细胞混合共同培养,从而体外再次仿生构建体内微环境,促进其中一种或多种细胞的形态和功能维持在机体内的稳定表达状态,并持续较长久的时间。
组织工程:应用生命科学与工程科学的原理和技术,在正确认识生物体有机体的正常及病理状态下的组织结构与功能关系的基础上,应用生物支架、活细胞及细胞因子等构建组织工程组织,用于修复和促进机体各种组织或器官损伤后的功能与形态的再生。
文题释义:
共培养:模拟机体内生理条件,将两种(可来自同一组织或不同的组织)及以上的细胞混合共同培养,从而体外再次仿生构建体内微环境,促进其中一种或多种细胞的形态和功能维持在机体内的稳定表达状态,并持续较长久的时间。
组织工程:应用生命科学与工程科学的原理和技术,在正确认识生物体有机体的正常及病理状态下的组织结构与功能关系的基础上,应用生物支架、活细胞及细胞因子等构建组织工程组织,用于修复和促进机体各种组织或器官损伤后的功能与形态的再生。.jpg) 文题释义:
共培养:模拟机体内生理条件,将两种(可来自同一组织或不同的组织)及以上的细胞混合共同培养,从而体外再次仿生构建体内微环境,促进其中一种或多种细胞的形态和功能维持在机体内的稳定表达状态,并持续较长久的时间。
组织工程:应用生命科学与工程科学的原理和技术,在正确认识生物体有机体的正常及病理状态下的组织结构与功能关系的基础上,应用生物支架、活细胞及细胞因子等构建组织工程组织,用于修复和促进机体各种组织或器官损伤后的功能与形态的再生。
文题释义:
共培养:模拟机体内生理条件,将两种(可来自同一组织或不同的组织)及以上的细胞混合共同培养,从而体外再次仿生构建体内微环境,促进其中一种或多种细胞的形态和功能维持在机体内的稳定表达状态,并持续较长久的时间。
组织工程:应用生命科学与工程科学的原理和技术,在正确认识生物体有机体的正常及病理状态下的组织结构与功能关系的基础上,应用生物支架、活细胞及细胞因子等构建组织工程组织,用于修复和促进机体各种组织或器官损伤后的功能与形态的再生。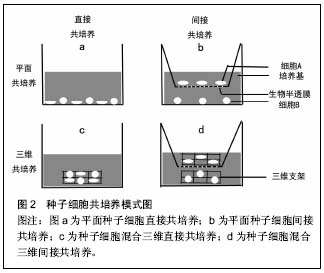
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
共培养:模拟机体内生理条件,将两种(可来自同一组织或不同的组织)及以上的细胞混合共同培养,从而体外再次仿生构建体内微环境,促进其中一种或多种细胞的形态和功能维持在机体内的稳定表达状态,并持续较长久的时间。
组织工程:应用生命科学与工程科学的原理和技术,在正确认识生物体有机体的正常及病理状态下的组织结构与功能关系的基础上,应用生物支架、活细胞及细胞因子等构建组织工程组织,用于修复和促进机体各种组织或器官损伤后的功能与形态的再生。
文题释义:
共培养:模拟机体内生理条件,将两种(可来自同一组织或不同的组织)及以上的细胞混合共同培养,从而体外再次仿生构建体内微环境,促进其中一种或多种细胞的形态和功能维持在机体内的稳定表达状态,并持续较长久的时间。
组织工程:应用生命科学与工程科学的原理和技术,在正确认识生物体有机体的正常及病理状态下的组织结构与功能关系的基础上,应用生物支架、活细胞及细胞因子等构建组织工程组织,用于修复和促进机体各种组织或器官损伤后的功能与形态的再生。