中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (12): 1838-1842.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.12.006
• 神经组织构建 nerve tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
硫辛酸干预坐骨神经缺血再灌注损伤后的电生理变化
富 玲1,黄 波2,李易嶙3,宋 宁4,莫忆南4,马 宏5
- 沈阳医学院附属中心医院,1手外二科,4足踝外科,辽宁省沈阳市 110024;2中国医科大学肿瘤医院,辽宁省肿瘤医院病理科,辽宁省沈阳市 110042;3大连医科大学基础医学院病理教研室,辽宁省大连市 116044;5沈阳医学院,辽宁省沈阳市 110036
Lipoic acid effects on electrophysiological changes of the sciatic nerve following ischemia/reperfusion injury
Fu Ling1, Huang Bo2, Li Yi-lin3, Song Ning4, Mo Yi-nan4, Ma Hong5
- 1Second Department of Hand Surgery, 4Department of Foot-Ankle Surgery, Affiliated Central Hospital of Shenyang Medical University, Shenyang 110024, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Pathology, Cancer Hospital of China Medical University & Liaoning Cancer Hospital, Shenyang 110024, Liaoning Province, China; 3Department of Pathology, School of Basic Medicine of Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China; 5Shenyang Medical University, Shenyang 110036, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
再灌注损伤:有许多证据说明仅仅缺血还不足以导致组织损伤,而是在缺血一段时间后又突然恢复供血(即再灌注)时才出现损伤。在创伤性休克、外科手术、器官移植、烧伤、冻伤和血栓等血液循环障碍时,都会出现缺血后再灌注损伤。缺血组织再灌注时造成的微血管和实质器官的损伤主要是由活性氧自由基引起的,这已在多种器官中得到的证明。在缺血组织中具有清除自由基的抗氧化酶类合成能力发生障碍,从而加剧了自由基对缺血后再灌注组织的损伤。使用SOD清除自由基对缺血再灌流组织损伤有保护作用。
周围神经损伤:主要由于创伤、产伤、骨发育异常、铅和酒精中毒等引起受该神经支配的区域出现感觉障碍、运动障碍和营养障碍。周围神经是指中枢神经(脑和脊髓)以外的神经,它包括12对脑神经,31对脊神经和自主神经(交感神经、副交感神经)。
文题释义:
再灌注损伤:有许多证据说明仅仅缺血还不足以导致组织损伤,而是在缺血一段时间后又突然恢复供血(即再灌注)时才出现损伤。在创伤性休克、外科手术、器官移植、烧伤、冻伤和血栓等血液循环障碍时,都会出现缺血后再灌注损伤。缺血组织再灌注时造成的微血管和实质器官的损伤主要是由活性氧自由基引起的,这已在多种器官中得到的证明。在缺血组织中具有清除自由基的抗氧化酶类合成能力发生障碍,从而加剧了自由基对缺血后再灌注组织的损伤。使用SOD清除自由基对缺血再灌流组织损伤有保护作用。
周围神经损伤:主要由于创伤、产伤、骨发育异常、铅和酒精中毒等引起受该神经支配的区域出现感觉障碍、运动障碍和营养障碍。周围神经是指中枢神经(脑和脊髓)以外的神经,它包括12对脑神经,31对脊神经和自主神经(交感神经、副交感神经)。
.jpg) 文题释义:
再灌注损伤:有许多证据说明仅仅缺血还不足以导致组织损伤,而是在缺血一段时间后又突然恢复供血(即再灌注)时才出现损伤。在创伤性休克、外科手术、器官移植、烧伤、冻伤和血栓等血液循环障碍时,都会出现缺血后再灌注损伤。缺血组织再灌注时造成的微血管和实质器官的损伤主要是由活性氧自由基引起的,这已在多种器官中得到的证明。在缺血组织中具有清除自由基的抗氧化酶类合成能力发生障碍,从而加剧了自由基对缺血后再灌注组织的损伤。使用SOD清除自由基对缺血再灌流组织损伤有保护作用。
周围神经损伤:主要由于创伤、产伤、骨发育异常、铅和酒精中毒等引起受该神经支配的区域出现感觉障碍、运动障碍和营养障碍。周围神经是指中枢神经(脑和脊髓)以外的神经,它包括12对脑神经,31对脊神经和自主神经(交感神经、副交感神经)。
文题释义:
再灌注损伤:有许多证据说明仅仅缺血还不足以导致组织损伤,而是在缺血一段时间后又突然恢复供血(即再灌注)时才出现损伤。在创伤性休克、外科手术、器官移植、烧伤、冻伤和血栓等血液循环障碍时,都会出现缺血后再灌注损伤。缺血组织再灌注时造成的微血管和实质器官的损伤主要是由活性氧自由基引起的,这已在多种器官中得到的证明。在缺血组织中具有清除自由基的抗氧化酶类合成能力发生障碍,从而加剧了自由基对缺血后再灌注组织的损伤。使用SOD清除自由基对缺血再灌流组织损伤有保护作用。
周围神经损伤:主要由于创伤、产伤、骨发育异常、铅和酒精中毒等引起受该神经支配的区域出现感觉障碍、运动障碍和营养障碍。周围神经是指中枢神经(脑和脊髓)以外的神经,它包括12对脑神经,31对脊神经和自主神经(交感神经、副交感神经)。摘要
背景:硫辛酸具有由硫、碳原子所构成的封闭环状结构,具有强大的抗氧化能力,现已被广泛用于氧化应激、糖尿病性白内障、糖尿病多发性神经病及心血管损伤等糖尿病并发症等疾病的预防和治疗。
目的:探究硫辛酸在周围神经缺血再灌注损伤中对周围神经功能的保护作用。
方法:建立家兔周围神经缺血再灌注损伤模型,依据是否进行再灌注分为处理组与未处理组(不进行再灌注处理),处理组依据缺血时间1,3,6 h和再灌注前是否使用硫辛酸,于每个时间点又分别分为实验组与对照组,电镜观察各组实验动物坐骨神经超微结构的变化,并使用诱发电位仪检测坐骨神经电生理指标的变化。
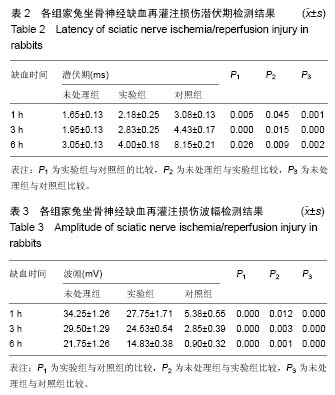
结果与结论:①随着缺血时间延长,轴突内空泡逐渐增多,轴突发生萎缩,轴突内微丝结构发生聚集并出现了明显的沃勒变性,而髓鞘则出现了增厚紊乱以及溶解现象。超微结构的破坏在缺血6 h时最为严重,沃勒变性及髓鞘溶解现象明显增加。对比实验组与对照组,硫辛酸的应用减少坐骨神经轴突中空泡数量,减轻了轴突的萎缩、沃勒变性以及脱髓鞘现象的产生;②随着缺血时间延长,各组实验动物坐骨神经的潜伏期显著增加,而波幅显著降低。潜伏期在缺血6 h达到最大值,而波幅在缺血6 h达到了最小值。对比未使用硫辛酸的对照组,实验组坐骨神经潜伏期明显下降而波幅明显增加;③结果说明,硫辛酸能够改善缺血再灌注造成的周围神经功能损伤。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-1920-3476(宋宁)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
再灌注损伤:有许多证据说明仅仅缺血还不足以导致组织损伤,而是在缺血一段时间后又突然恢复供血(即再灌注)时才出现损伤。在创伤性休克、外科手术、器官移植、烧伤、冻伤和血栓等血液循环障碍时,都会出现缺血后再灌注损伤。缺血组织再灌注时造成的微血管和实质器官的损伤主要是由活性氧自由基引起的,这已在多种器官中得到的证明。在缺血组织中具有清除自由基的抗氧化酶类合成能力发生障碍,从而加剧了自由基对缺血后再灌注组织的损伤。使用SOD清除自由基对缺血再灌流组织损伤有保护作用。
周围神经损伤:主要由于创伤、产伤、骨发育异常、铅和酒精中毒等引起受该神经支配的区域出现感觉障碍、运动障碍和营养障碍。周围神经是指中枢神经(脑和脊髓)以外的神经,它包括12对脑神经,31对脊神经和自主神经(交感神经、副交感神经)。
文题释义:
再灌注损伤:有许多证据说明仅仅缺血还不足以导致组织损伤,而是在缺血一段时间后又突然恢复供血(即再灌注)时才出现损伤。在创伤性休克、外科手术、器官移植、烧伤、冻伤和血栓等血液循环障碍时,都会出现缺血后再灌注损伤。缺血组织再灌注时造成的微血管和实质器官的损伤主要是由活性氧自由基引起的,这已在多种器官中得到的证明。在缺血组织中具有清除自由基的抗氧化酶类合成能力发生障碍,从而加剧了自由基对缺血后再灌注组织的损伤。使用SOD清除自由基对缺血再灌流组织损伤有保护作用。
周围神经损伤:主要由于创伤、产伤、骨发育异常、铅和酒精中毒等引起受该神经支配的区域出现感觉障碍、运动障碍和营养障碍。周围神经是指中枢神经(脑和脊髓)以外的神经,它包括12对脑神经,31对脊神经和自主神经(交感神经、副交感神经)。