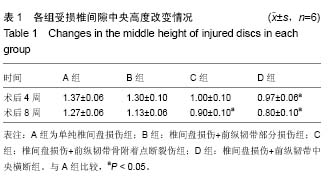
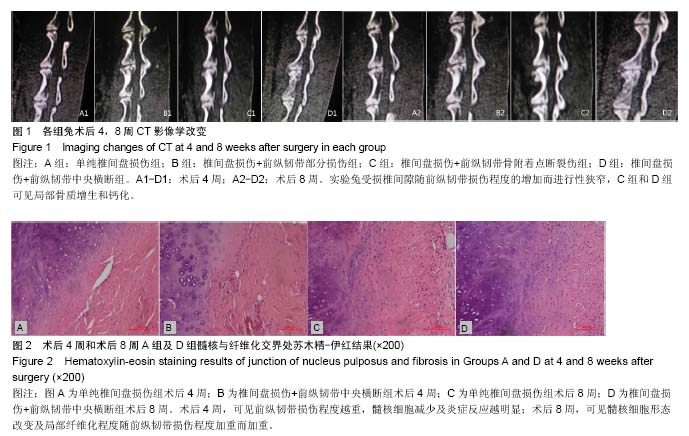
| [1] Yoganandan N, Cusick J, Pintar FA, et al. Whiplash injury determination with conventional spine imaging and cryomicrotomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2001; 26(22): 2443-2448.[2] 黄宗强,刘尚礼,郑召民.椎间失稳诱发椎间盘退变的病理学观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(5): 376-379.[3] 叶添,陈雄生,贾连顺,等.颈椎前纵韧带损伤的诊断与治疗[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(7): 643-636.[4] 吉立新,谢文贵,高鹏飞, 等.颈椎前纵韧带及椎间盘损伤的影像学诊断[J].中国骨与关节外科,2009, 2(1): 30-34.[5] 程杰平,马洪顺,褚怀德.人颈椎前纵韧带生物力学特性实验研究[J].医用生物力学.2004,19(4):221-223.[6] Rizzolo SJ, Vaccaro AR,Cotler JM. Cervical spine trauma. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19 (20):2228-2298.[7] Lifeso RM, Colucci MA. Anterior fusion for rotationally unstable cervical spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25(16): 2028-2034.[8] Stemper BD, Yoganandan N, Pintar FA, et al. Anterior longitudinal ligament injuries in whiplash may lead to cervical instability. Med Eng Phys. 2006; 28(6): 515-524.[9] Maeda T, Ueta T, Mori E, et al. Soft-tissue damage and segmental instability in adult patients with cervical spinal cord injury without major bone injury. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 37(25): E1560-1566.[10] Michalek AJ, Iatridis JC. Height and torsional stiffness are most sensitive to annular injury in large animal intervertebral discs. Spine J. 2012; 12(5): 425-432.[11] Takeuchi T, Abumi K, Shono Y, et al. Biomechanical role of the intervertebral disc and costovertebral joint in stability of the thoracic spine. A canine model study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24(14): 1414-1420.[12] Lipson SJ, Muir H. Proteoglycans in experimental intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1981; 6(3): 194-210.[13] Sobajima S, Kompel JF, Kim JS, et al. A slowly progressive and reproducible animal model of intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by MRI, X-ray, and histology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(1):15-24.[14] Kim KS, Yoon ST, Li J, et al. Disc degeneration in the rabbit: a biochemical and radiological comparison between four disc injury models. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(1): 33-37.[15] Chan DD, Khan SN, Ye X, et al. Mechanical deformation and glycosaminoglycan content changes in a rabbit annular puncture disc degeneration model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(18):1438-1445.[16] Mwale F, Ciobanu I, Giannitsios D, et al. Effect of oxygen levels on proteoglycan synthesis by intervertebral disc cells. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36(2): E131-138.[17] Adams MA, Freeman BJ,Morrison HP,et al.Mechanical initiation of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 5(13):1625-1636.[18] 林鸿宽,叶君健.纤维环损伤诱导兔椎间盘退变模型[J].解剖学杂志,2008, 31(5): 699-702.[19] 崔运能,李绍林,周荣平,等. CT引导下经皮纤维环穿刺建立兔腰椎间盘退变模型[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014, 24(3): 234-243.[20] Moon CH, Jacobs L, Kim JH, et al. Quantitative proton T2 and sodium magnetic resonance imaging to assess intervertebral disc degeneration in a rabbit model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 37(18): E1113-1119.[21] Zhou RP, Zhang ZM, Wang L, et al. Establishing a disc degeneration model using computed tomography-guided percutaneous puncture technique in the rabbit. J Surg Res. 2013; 181(2): e65-74.[22] Xin L, Zhang C, Zhong F, et al. Minimal invasive annulotomy for induction of disc degeneration and implantation of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) plugs for annular repair in a rabbit model. Eur J Med Res. 2016; 21: 7.[23] 黄宗强,刘尚礼,郑召民.关节突关节失稳致兔椎间盘退变的分子生物学评价[J].基础医学与临床, 2007, 27(9): 970-974.[24] 林曦,叶君健.骨形态发生蛋白2对退变椎间盘组织学和Ⅰ,Ⅱ型胶原的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(43): 7501-7506.[25] 黄宗强,刘尚礼,郑召民.椎间失稳诱发椎间盘退变的超微结构改变[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2008, 26(2): 185-188.[26] 黄河,李宁宁,胡朝晖,等.纤维环穿刺法与腰椎失稳法建立椎问盘退变模型[J].中国现代医生, 2011,49(16): 22-24.[27] 戴力扬. 颈椎椎间盘退行性改变与颈椎不稳[J]. 中华外科杂志, 1999,37(3): 180-182.[28] 金文杰,陶海荣,刘兴振,等.无骨折脱位颈椎外伤后迟发性神经损伤的诊治[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014,29(5): 417-419. |
.jpg)
.jpg)