中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (52): 7851-7857.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.52.014
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
3D打印羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇支架、纳米级羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇支架、羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇无孔骨板的性能比较
周琦琪1,韩祥祯1,宋艳艳1,吕明凡2,胡 杨1,何惠宇1
- 1新疆医科大学第一附属医院口腔修复科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;2新疆财经大学金融学院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830012
Performance comparison of 3D printing sheep vertebral bone meal/polyvinyl alcohol scaffold, nano-hydroxyapatite/polyvinyl alcohol scaffold and sheep vertebral bone meal/polyvinyl alcohol nonporous bone plate
Zhou Qi-Qi1, Han Xiang-zhen1, Song Yan-yan1, Lv Ming-fan2, Hu Yang1, He Hui-yu1
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Financial institute, Xinjiang University of Finance & Economics, Urumqi 830012, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇支架:羊椎骨粉作为天然的骨质材料,具有其他无机材料所不可比拟的生物相容性和骨传导特性。聚乙烯醇水凝胶是一种在组织工程中应用广泛的高分子材料,作为黏结剂无毒且易降解,机械性能良好,吸水量大,生物相容性好。实验以天然绵羊脊柱松质骨为原料,通过选择化学试剂浸泡法、物理高温煅烧法处理,去除羊松质骨中易引起免疫反应的各种异种抗原成分,制成骨粉,以备与聚乙烯醇水凝胶混合,制成羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇组织工程骨支架。
支架微孔结构:支架材料是否能良好发挥其材料性能,合适的微孔结构关是键。孔隙过大易造成支架力学性不良,难以应用于例如牙槽骨等力学要求较高的功能区域;孔径过小会导致新生细胞及组织难以长入。已有研究证实,最小孔径为100-150 µm,即可满足组织再生,并发现支架材料的孔径在300-600 μm间,最有利于新骨长成。
背景:随着3D打印技术的推广,3D打印组织工程骨支架成为颌骨缺损修复的新方向。
目的:对比3D打印羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇支架、纳米级羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇支架、羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇无孔骨板的理化与生物性能。
方法:利用3D打印技术,分别打印出羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇支架、纳米级羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇支架、羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇无孔骨板,进行孔隙率、扫描电镜、吸水率及压缩力学性能测定;将3种支架分别与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养1,4,7 d,采用CCK-8法检测细胞增殖。
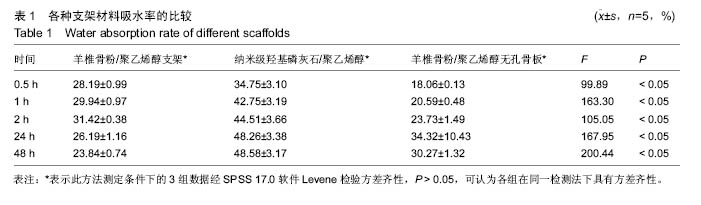
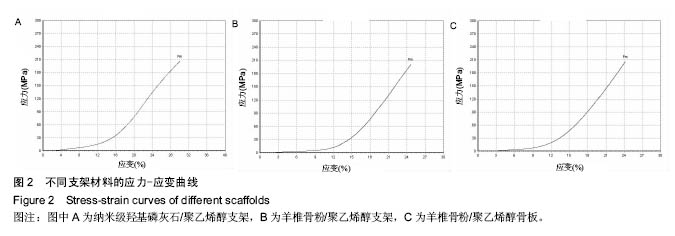
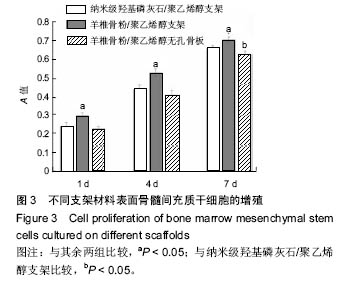
结果与结论:①扫描电镜观察:纳米级羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇支架、羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇支架孔隙规则,网状结构清晰,孔隙间存在广泛交通,连续性好;羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇无孔骨板没有明显孔隙,但表面有大小不一微孔,材料致密,分布均匀;②孔隙率:纳米级羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇支架孔隙率低于羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇支架(P < 0.05);③吸水率:在不同时间点,纳米级羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇支架>羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇支架>羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇无孔骨板(P < 0.05);④压缩力学性能:羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇支架的韧性高于纳米级羟基磷灰石/聚乙烯醇支架,低于羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇无孔骨板;⑤细胞毒性:羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇支架的细胞增殖活性高于其余两组支架(P < 0.05);⑥结果表明:3D打印羊椎骨粉/聚乙烯醇支架具有良好的物理及化学性能。
中图分类号:

.jpg)