中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (52): 7773-7780.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.52.003
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
结合3D打印技术构建聚己内酯-骨细胞外基质复合支架及体外骨诱导性能
杨 鹏,李淳德
- 北京大学第一医院骨科,北京市 100034
Construction of a polycaprolactone/bone extracellular matrix scaffold with three-dimensional printing technology and its osteoinductivity in vitro
Yang Peng, Li Chun-de
- Department of Orthopaedics, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
聚己内酯:具有良好的生物相容性、生物降解性、力学性能、药物通过性及易加工等特点,并且该材料在体内降解之后的产物对机体没有毒害作用,已被广泛应用于组织工程生物材料领域,但由于聚己内酯表面缺乏细胞亲和位点且降解速度较慢,因此其临床应用受到一定限制。
骨细胞外基质:是由骨细胞合成并分泌到胞外,形成分布于细胞表面和细胞之间的复杂网状结构,它支撑并连接了骨骼的整体结构,并是动物体内骨细胞生长、分化、代谢的场所。
背景:骨组织工程学者们仍在寻找理想的骨组织工程支架,3D打印技术为支架的构建提供了新的方法,同时骨细胞外基质在成骨诱导中的作用也越来越受到关注。
目的:采用3D细胞-支架共培养的方式获取聚己内酯-骨细胞外基质复合支架,检测其成骨性能。
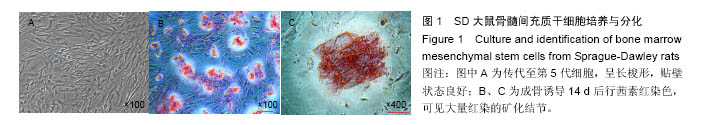
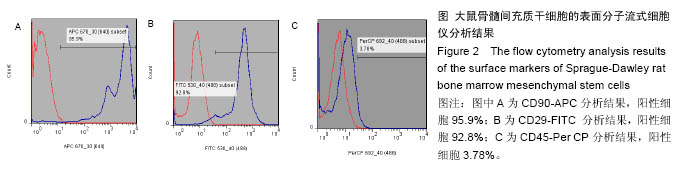
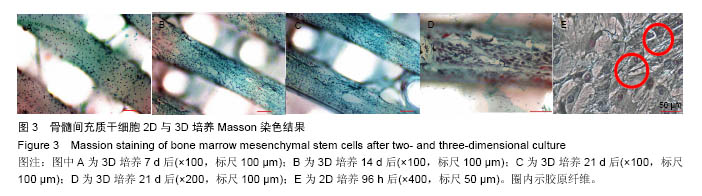
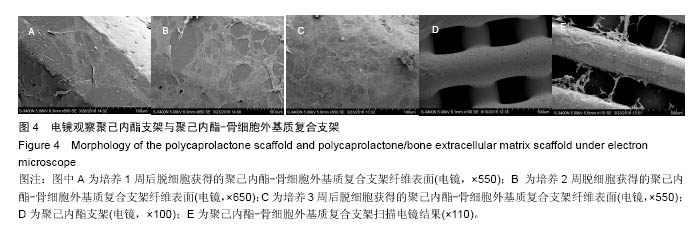
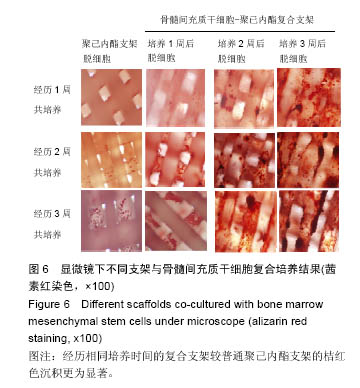
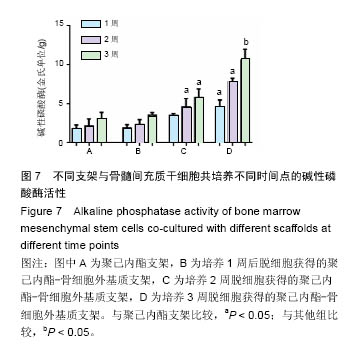
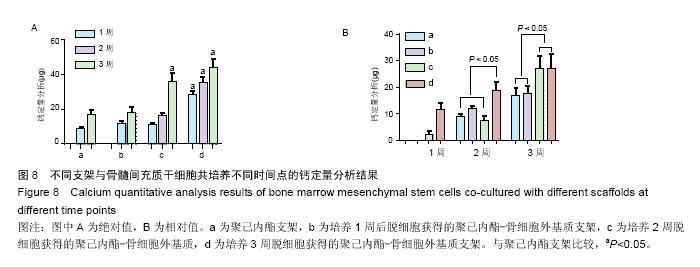
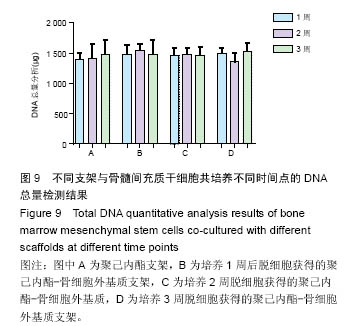
方法:将216枚3D打印聚己内酯支架分为A组(与96孔板匹配,n=72)、B组(与48孔板匹配,n=144)。①第1轮三维培养:将第5代SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分别接种于两组支架上,接种1,2,3周,A组进行茜素红染色、Masson染色,B组进行胶原、糖胺多糖检测;②第2轮三维培养:将第1轮三维培养1,2,3周的支架进行脱细胞处理,分别记为AE1、AE2、AE3、BE1、BE2、BE3,将第5代SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞再次接种于6组支架上,接种1,2,3周,AE1、AE2、AE3组进行茜素红染色,BE1、BE2、BE3组进行钙定量、碱性磷酸酶活性及DNA定量分分析。
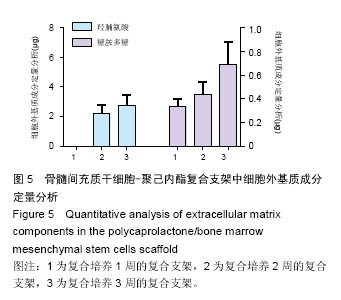
结果与结论:①Masson染色及糖胺多糖、羟脯氨酸定量分析结果提示,随着培养时间延长,复合支架表面的细胞外基质成分逐渐增加;②碱性磷酸酶活性检测结果提示,聚己内酯-骨细胞外基质复合支架的细胞成骨分化程度显著高于普通聚己内酯支架(P < 0.05);③茜素红染色分析及钙定量分析结果提示,复合支架的矿化程度显著高于普通聚己内酯支架(P < 0.05),复合支架的DNA总量相对于普通样本并没有显著升高;④结果表明,通过3D细胞-支架共培养的方式可以获得带有细胞外基质的复合支架,该复合支架具备更好的成骨诱导性能。
中图分类号:
.jpg)