| [1] McBeth J, Jones K.Epidemiology of chronic musculoskeletal pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2007;21(3):403-425.
[2] Dagenais S, Caro J, Haldeman S. A systematic review of low back pain cost of illness studies in the United States and Internationally.Spine J. 2008;8(1):8-20.
[3] 庄汝杰,陈冠军,庄伟,等. TNF-α、IL-6、IL-8在Modic I型改变腰椎终板与椎间盘髓核中的表达及关系研究[J]. 浙江医学, 2015,37(4): 295-299.
[4] Yang H, Cao C, Wu C, et al. TGF-betal suppresses inflammation in cell therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Sci Rep. 2015,5:13254.
[5] Cao C, Zou J, Liu X, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells slow intevertebral disc degeneration through the NF-kappaB pathway. Spine J. 2015;15(3): 530-538.
[6] 秦剑剑,闫伟娟,代新年,等.中药熏蒸疗法在椎间盘源性腰痛中的康复疗效[J]. 实用医药杂志, 2016,33(6): 513-514.
[7] 张延松,胡侦明,郝杰.椎间盘退变基因治疗进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(7): 927-930.
[8] 李文举,李亦梅.椎间盘退变机制研究现状及生物治疗展望[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2014,7(1): 66-69.
[9] 郭健行,黄桂成.椎间盘退变影响因素研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2008,29(1):46-48.
[10] 翁浩,刘旸,周昭文. McKenie技术治疗椎间盘源性下腰痛的临床效果[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2014,20(4): 374-377.
[11] 陈杰,鲁贵生,高晓鹏,等.中西医综合疗法治疗腰椎间盘突出症疗效观察[J].四川中医, 2015,33(12):151-152.
[12] 胡绪江,邵增务. 外源性肿瘤坏死因子-α对腰椎间盘退变影响的实验研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2006,16(7): 541-544.
[13] 钟锐,刘少喻. 腰椎间盘退变动物模型评价方法的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(11):1039-1043.
[14] 黄国付,汪伯毅,邹璟,等.夹脊电针对兔退变椎间盘组织中decorin蛋白表达的影响[J].中国康复, 2015,30(5): 327-330.
[15] 周逸驰,李景峰,董视师,等.干细胞治疗椎间盘退变性疾病: 现状与展望[J]. 国组织工程研究, 2015,19(10): 1635-1639.
[16] Best BA, Guilak F, Setton LA. et al. Compressive mechanical mechanical properties of human annlus fibrosus and their relationship to biochemical composion.Spine.1994;19: 212.
[17] 高智,徐宏光,张晓玲,等.中药胡椒碱在终板软骨细胞退变中的保护作用的研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2016, 21(6): 611-615.
[18] Hardingham TE, Fosang AJ. Proteoglycan: many forms and many Functions. FASEB.1992;6:861.
[19] Li Z, Kaplan KM, Wertzel A, et al. Biomimetic fibrin-hyaluronan hydrogels for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Regen Med. 2014;9(3): 309-326.
[20] Urban MR, Fairbank JC, Bibby SR, et al. Interverbral disc composition in neuromuscular scoliosis: changes in cell density and glycosaminoglycan concentration at the curve apex. Spine.2001; 26(6): 610-617.
[21] Best LA, Guilak F, Setton LA, et al. Compressive mechanical mechanical properties of human annlus fibrosus and their relationship to biochemical composion. Spine.1994;19(2):212-221.
[22] Xu HG, Zhang Q, Song JX, et al. Intermittent eyelicmechanical tension promotes endplate cartilage degeneration via canonical W nt signaling pathway and Ecadherin/beta-catenin complex cross -talk. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(1): 158-168.
[23] Mariani E, Pulsatelli L, Facchini A. Signaling pathways in cartilage repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(5): 8667-8698.
[24] Zhang M, Wang H, Zhang J, et al. Unilateral anterior crossbite induces aberrant mineral deposition in degenerative temporomandibular cartilage in rats. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(5): 921-931.
[25] Gunzburg R, Szpalski M, Gunnar B. Degenerative Disc Disease. Andersson Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2004: 336.
[26] 孟祥宇,夏建龙,杨挺,等.椎间盘退变的机制及修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(11):1768-1773.
[27] 刘强,张军,张慧,等.不同腰椎扳法对椎间盘内压的影响[J].中医正骨,2014,26(1):11-16.
[28] 胡松,罗兴燕,刘阳,等. 椎间盘退变细胞及分子疗法研究进展[J]. 成都医学院学报, 2015, 10(1): 105-108.
[29] Scott JE, Bosworth TR, Cribb AM,et al.The chemical morphology of age-related changes in human intervertebral disc glycosaminoglycans from cervical thoracic and lumbar nucleus pulposus and anulus fibrosus. Anat.1994;184: 73.
[30] 谭炳毅,张佐伦,袁泽农,等.颈椎间盘纤维及髓核生化成分的分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2000,7(7):642.
[31] Urban JP, Mcmullin JF. Swelling pressure of the lumbar intervertebral discs:influence of age, spinal level, composition and Degeneration. Spine. 1988;13: 179-187.
[32] Frobin W, Brinckmann P,Kramaer M, et al. Height of lumbar discs measured from radiographs compared with degeneration and height classified from MR images. Eur Radiol. 2001;11:263-269.
[33] 汪巍,李广松,曹赫基,等.经皮穿刺射频热凝术与后路椎管减压突出髓核摘除术治疗椎间孔型腰椎间盘突出症临床疗效比较[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2014,35(6): 405-408.
[34] 宋瑞军,董莉莉,刘畅.独活寄生汤辅助经皮射频热凝术治疗腰椎间盘源性腰痛的疗效观察[J].中药材, 2015, 38(9): 2006-2008.
[35] 张辉,倪青,任艳,等.腰痛酸软与糖尿病肾虚症状的相关性[J].中医杂志2010;(51)5: 409-11
[36] 刘献强,张学利.椎间盘突出症中医药治疗进展[J].中华临床医学杂志,2008, 9(6):46-48.
[37] 林一峰,张震,刘海全,等.补肾壮督方预防腰椎间盘退变的实验研究[J]. 中国临床研究, 2016,8(13): 16-18.
[38] 刘才俊, 秦丰伟, 原超, 等. 益肾活血方对椎间盘退变患者IL-1β、TNF-α及远期功能恢复的影响[J]. 深圳中西医结合杂志, 2016,26(12):28-30.
[39] 权学民.益气化瘀中药结合BMSCs移植干预腰椎间盘退变的实验研究[D].北京中医药大学,2011.
[40] 张华.补肾活血舒筋方影响颈椎间盘退变的初步研究[J] 南京中医药大学,2012.
[41] 翟献斌.补肾活血方延缓腰椎间盘退变的实验研究[J].中医正骨,2009,21(5):18-22.
[42] 赵武述,张玉琴,李洁,等.山茱萸成分的免疫活性研究[J]. 中草药,1990,21(3):113-116.
[43] 段晓丽.六味地黄丸的药理作用与临床应用[J]. 山西医药杂志, 2009,38(12):1156-1157.
[44] 王秋娟,厚德晖,季慧芳,等.六味地黄汤及其租房对小鼠血糖和肝糖元的影响[J].中国中药杂志,1991,18(7): 437-438.
[45] 钱祝民.金匮肾气丸和六味地黄丸交替久服治疗慢性腰痛体会[J].山东中医杂志,2006,25(9):609. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
椎间盘退变:椎间盘退变所引起的椎间盘源性腰痛已成为社会上常见的多发病,并常常引起复杂的腰椎病变。目前临床上针对治疗椎间盘退变的治疗方法尚存在局限性,且疗效并不尽如人意。因此利用中医中药治疗不良反应小、成本低、疗效高的特点,治疗椎间盘退变的已越来越体现其自身特点及优势,具有积极的临床意义。
蛋白多糖:蛋白多糖是维持椎间盘的正常结构、代谢及生物力学性能的基础结构。其中主要含量糖胺多糖反映了椎间盘的生物功能。糖胺多糖中含有硫酸软骨素、硫酸角质素、透明质酸,其含量的改变对椎间盘的结构和生物力学性能有着重要影响。
文题释义:
椎间盘退变:椎间盘退变所引起的椎间盘源性腰痛已成为社会上常见的多发病,并常常引起复杂的腰椎病变。目前临床上针对治疗椎间盘退变的治疗方法尚存在局限性,且疗效并不尽如人意。因此利用中医中药治疗不良反应小、成本低、疗效高的特点,治疗椎间盘退变的已越来越体现其自身特点及优势,具有积极的临床意义。
蛋白多糖:蛋白多糖是维持椎间盘的正常结构、代谢及生物力学性能的基础结构。其中主要含量糖胺多糖反映了椎间盘的生物功能。糖胺多糖中含有硫酸软骨素、硫酸角质素、透明质酸,其含量的改变对椎间盘的结构和生物力学性能有着重要影响。.jpg) 文题释义:
椎间盘退变:椎间盘退变所引起的椎间盘源性腰痛已成为社会上常见的多发病,并常常引起复杂的腰椎病变。目前临床上针对治疗椎间盘退变的治疗方法尚存在局限性,且疗效并不尽如人意。因此利用中医中药治疗不良反应小、成本低、疗效高的特点,治疗椎间盘退变的已越来越体现其自身特点及优势,具有积极的临床意义。
蛋白多糖:蛋白多糖是维持椎间盘的正常结构、代谢及生物力学性能的基础结构。其中主要含量糖胺多糖反映了椎间盘的生物功能。糖胺多糖中含有硫酸软骨素、硫酸角质素、透明质酸,其含量的改变对椎间盘的结构和生物力学性能有着重要影响。
文题释义:
椎间盘退变:椎间盘退变所引起的椎间盘源性腰痛已成为社会上常见的多发病,并常常引起复杂的腰椎病变。目前临床上针对治疗椎间盘退变的治疗方法尚存在局限性,且疗效并不尽如人意。因此利用中医中药治疗不良反应小、成本低、疗效高的特点,治疗椎间盘退变的已越来越体现其自身特点及优势,具有积极的临床意义。
蛋白多糖:蛋白多糖是维持椎间盘的正常结构、代谢及生物力学性能的基础结构。其中主要含量糖胺多糖反映了椎间盘的生物功能。糖胺多糖中含有硫酸软骨素、硫酸角质素、透明质酸,其含量的改变对椎间盘的结构和生物力学性能有着重要影响。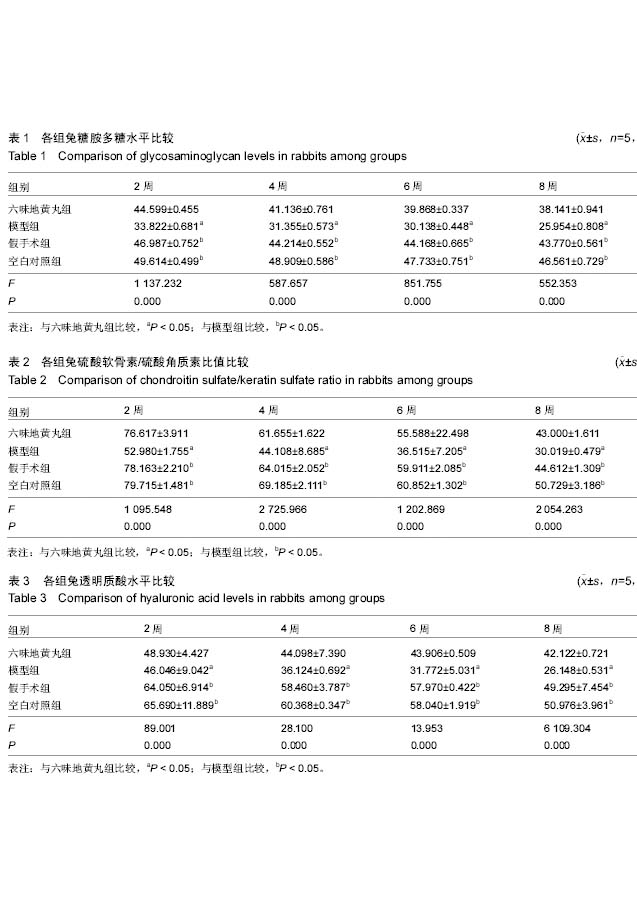
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
椎间盘退变:椎间盘退变所引起的椎间盘源性腰痛已成为社会上常见的多发病,并常常引起复杂的腰椎病变。目前临床上针对治疗椎间盘退变的治疗方法尚存在局限性,且疗效并不尽如人意。因此利用中医中药治疗不良反应小、成本低、疗效高的特点,治疗椎间盘退变的已越来越体现其自身特点及优势,具有积极的临床意义。
蛋白多糖:蛋白多糖是维持椎间盘的正常结构、代谢及生物力学性能的基础结构。其中主要含量糖胺多糖反映了椎间盘的生物功能。糖胺多糖中含有硫酸软骨素、硫酸角质素、透明质酸,其含量的改变对椎间盘的结构和生物力学性能有着重要影响。
文题释义:
椎间盘退变:椎间盘退变所引起的椎间盘源性腰痛已成为社会上常见的多发病,并常常引起复杂的腰椎病变。目前临床上针对治疗椎间盘退变的治疗方法尚存在局限性,且疗效并不尽如人意。因此利用中医中药治疗不良反应小、成本低、疗效高的特点,治疗椎间盘退变的已越来越体现其自身特点及优势,具有积极的临床意义。
蛋白多糖:蛋白多糖是维持椎间盘的正常结构、代谢及生物力学性能的基础结构。其中主要含量糖胺多糖反映了椎间盘的生物功能。糖胺多糖中含有硫酸软骨素、硫酸角质素、透明质酸,其含量的改变对椎间盘的结构和生物力学性能有着重要影响。