| [1] 贾玉磊, 人脂肪干细胞协同颗粒脂肪移植的实验研究[D].河北医科大学,2014.
[2] 周紫微,赵宇.脂肪干细胞研究进展与应用前景[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2013,(7): 846-849.
[3] 田霖,孙筱放,刘海波,等.人脂肪干细胞的分离培养与生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(32): 5946-5952.
[4] 徐婷,吴慧玲, 自体颗粒脂肪移植存活率的研究进展(综述)[C].2012年浙江省美容与整形学术年会暨私营美容机构行业论坛, 温州:2012.
[5] Sun W, Ni X, Sun S, et al.Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Alleviate Radiation-Induced Muscular Fibrosis by Suppressing the Expression of TGF-beta1. Stem Cells Int. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:5638204.
[6] Heo JS, Choi Y, Kim HS,et al.Comparison of molecular profiles of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta and adipose tissue. Int J Mol Med.2016; 37(1):115-125.
[7] Ozpur MA, Guneren E, Canter HI,et al.Generation of Skin Tissue Using Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells. Plast Reconstr Surg.2016;137(1): 134-143.
[8] Zhang J, Bai X, Zhao B, et al.Allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells promote survival of fat grafts in immunocompetent diabetic rats. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;364(2):357-367.
[9] 冯有支,雷岳崇,谭赵云,等.自体颗粒脂肪移植在合并多种畸形的重睑修复中的应用[J].中国美容医学, 2012,21(11): 1470-1471.
[10] 黄金龙,徐妍,闻可,等.脂肪干细胞辅助颗粒脂肪移植在隆乳术中的应用[C]. 2012全国中西医结合医学美容学术交流大会,成都. 2012.
[11] Petersen GF, Hilbert BJ, Trope GD,et al.Direct Conversion of Equine Adipose-Derived Stem Cells into Induced Neuronal Cells Is Enhanced in Three-Dimensional Culture. Cell Reprogram. 2015; 17(6):419-426.
[12] Sheykhhasan M, Qomi RT, Ghiasi M. Fibrin Scaffolds Designing in order to Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation to Chondrocytes in the Presence of TGF-beta3. Int J Stem Cells.2015;8(2): 219-227.
[13] Mehrabani D, Babazadeh M, Tanideh N, et al.The Healing Effect of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Full-thickness Femoral Articular Cartilage Defects of Rabbit. Int J Organ Transplant Med. 2015; 6(4):165-175.
[14] Tang XB, Dong PL, Wang J, et al.Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on the chondrogenic differentiation of rabbit adipose-derived stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 2015;10(2):477-483.
[15] Yao W, Hu Q, Ma Y, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells repair cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through antiapoptotic pathways. Exp Ther Med. 2015;10(2):468-476.
[16] Mohammadpour H, Pourfathollah AA, Nikougoftar Zarif M, et al.Increasing proliferation of murine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells by TNF-alpha plus IFN-gamma. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2016;38(2):68-76.
[17] Razavi S, Khosravizadeh Z, Bahramian H, et al. Changes of neural markers expression during late neurogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Adv Biomed Res. 2015;4:209.
[18] Horikoshi-Ishihara H, Tobita M, Tajima S, et al. Coadministration of adipose-derived stem cells and control-released basic fibroblast growth factor facilitates angiogenesis in a murine ischemic hind limb model. J Vasc Surg. 2015 Nov 17. pii: S0741-5214(15)02013-3.
[19] 孙哲.脂肪干细胞与碱性成纤维细胞生长因子在颗粒脂肪移植中应用的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2012,18(15): 2401-2403.
[20] 刘世宇,陆伟,张晓军,等.脂肪干细胞和纤维蛋白胶快速构建人工皮肤修复创面的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2009, 5(6):769-773.
[21] 王克明,栾杰,穆兰花,等.提高自体颗粒脂肪移植成活率的研究进展[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2007,3(6): 353-355.
[22] 雷华,李青峰.脂肪干细胞的研究进展[J].中华整形外科杂志,2003,19(6): 64-65.
[23] Razavi S, Razavi MR, Ahmadi N, et al.Estrogen treatment enhances neurogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells in vitro. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(8):799-804.
[24] Ha KY, Park H, Park SH, et al.The Relationship of a Combination of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells and Frozen Fat with the Survival Rate of Transplanted Fat. Arch Plast Surg.2015;42(6): 677-685.
[25] 李晶.湿性脂肪干细胞辅助自体颗粒脂肪移植填充颜面部凹陷的疗效观察[D]. 重庆医科大学,2013.
[26] 闫俊灵,狄国虎,丁红,等.脂肪干细胞介导的自体脂肪移植隆胸[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(5): 878-885.
[27] 李越, 梁杰,张培华.自体颗粒脂肪移植在矫治面部老化中的应用[J]. 广东医学院学报, 2012,30(1):28-30.
[28] 刘乃军,黄金井, 脂肪干细胞辅助自体颗粒脂肪移植术研究进展[J].中国美容医学, 2012,21(9): 1451-1454.
[29] Koh YG, Kwon OR, Kim YS, et al.Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells With Microfracture Versus Microfracture Alone: 2-Year Follow-up of a Prospective Randomized Trial. Arthroscopy. 2016;32(1):97-109.
[30] Aboul-Fotouh GI, Zickri MB, Metwally HG, et al. Therapeutic Effect of Adipose Derived Stem Cells versus Atorvastatin on Amiodarone Induced Lung Injury in Male Rat. Int J Stem Cells.2015;8(2):170-180.
[31] Chen Y, Dahai H, Zhao Z, et al.[Effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells over-expressing glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor on electrically injured sciatic nerve of rats]. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi.2015;31(3):199-204.
[32] Weimin P, Zheng C, Shuaijun J, et al.Synergistic enhancement of bone regeneration by LMP-1 and HIF-1alpha delivered by adipose derived stem cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2016;38(3):377-384.
[33] Yun SP, Lee MY, Ryu JM, et al.Role of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation by 17beta-estradiol: involvement of PKC, PI3K/Akt, and MAPKs. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2009;296(2): C317-26.
[34] Gu A, Tsark W, Holmes KV, et al.Role of Ceacam1 in VEGF induced vasculogenesis of murine embryonic stem cell-derived embryoid bodies in 3D culture. Exp Cell Res. 2009; 315(10):1668-1682.
[35] Das H, George JC, Joseph M, et al. Stem cell therapy with overexpressed VEGF and PDGF genes improves cardiac function in a rat infarct model. PLoS One.2009; 4(10):e7325.
[36] Zisa D, Shabbir A, Suzuki G,et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) as a key therapeutic trophic factor in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-mediated cardiac repair. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2009;390(3):834-838.
[37] Guo X, Lian R, Guo Y, et al. bFGF and Activin A function to promote survival and proliferation of single iPS cells in conditioned half-exchange mTeSR1 medium. Hum Cell.2015;28(3):122-132.
[38] An SS, Jin HL, Kim KN,et al.Neuroprotective effect of combined hypoxia-induced VEGF and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment. Childs Nerv Syst.2010; 26(3): 323-331.
[39] Sun J, Sha B, Zhou W, et al.VEGF-mediated angiogenesis stimulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation in the premature brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2010;394(1):146-152.
[40] Lee YB, Polio S, Lee W, et al.Bio-printing of collagen and VEGF-releasing fibrin gel scaffolds for neural stem cell culture. Exp Neurol.2010;223(2):645-652.
[41] Deng ZG, B Li, Zu C.[The effect of allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation on tumor recurrence and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy and the relationship with presence of AFP mRNA and VEGF-C mRNA in peripheral blood]. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.2010;41(2): 256-260.
[42] Xie JX, Feng Y, Yuan JM, et al.Positive effects of bFGF modified rat amniotic epithelial cells transplantation on transected rat optic nerve. PLoS One.2015; 10(3): e0119119.
[43] Yujuan T, Shaoquan C, Zaizhong Z, et al.[Effect of propranolol gel on plasma VEGF, bFGF and MMP-9 in proliferating infantile hemangiomas of superficial type]. Zhonghua Zheng Xing Wai Ke Za Zhi.2015; 31(4): 268-273.
[44] Huat TJ, Khan AA, Abdullah JM, et al.MicroRNA expression profile of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived neural progenitor by microarray under the influence of EGF, bFGF and IGF-1. Genom Data.2015; 5:201-205.
[45] Zhengcai-Lou, Zihan-Lou, Yongmei-Tang. Comparative study on the effects of EGF and bFGF on the healing of human large traumatic perforations of the tympanic membrane. Laryngoscope. 2016;126(1): E23-28. |
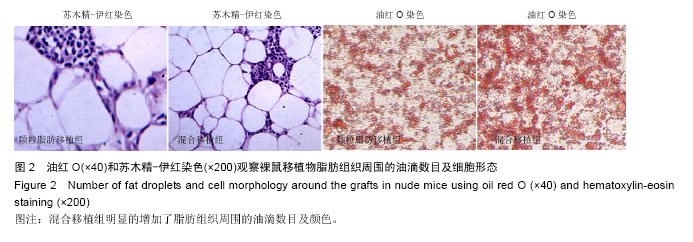
.jpg)

.jpg)