中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (40): 5953-5958.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.40.004
• 脑及脊髓损伤动物模型 Animal models of brain and spinal cord injuries • 上一篇 下一篇
正交法筛选组穴对脑缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠细胞外信号调节激酶信号转导通路的影响
冯毅慧1,朱志华1,吴春晓2,周国平2
- 1广西中医药大学附属瑞康医院针灸科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530011;2南方医科大学,广东省广州市 510515
Effects of electroacupuncture at points selected by orthogonal experiment on the extracellular signal regulated kinase signal pathway in a rat model of cerebral ischenia-reperfusion injury
Feng Yi-hui1, Zhu Zhi-hua1, Wu Chun-xiao2, Zhou Guo-ping2
- 1Department of Acupuncture, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
缺血再灌注损伤:脑组织缺血所引起的组织损伤是致死性疾病的主要原因。缺血再灌注损伤时间越长,兴奋性递质含量越低,脑组织超微结构改变越明显:线粒体肿胀,有钙盐沉积,并可见线粒体嵴断裂、核染色质凝集、内质网高度肿胀,结构明显破坏、星形细胞肿胀,Nissl体完整性破坏、胶质细胞、血管内皮细胞肿胀,周围间隙增大并有淡红色水肿液、白质纤维间隙疏松,血管内由微血栓、髓鞘分层变性,呈现不可逆损伤。
信号转导通路:在细胞中,各种信号转导分子相互识别、相互作用,将信号进行转换和传递,构成信号转导通路。当外界环境变化时,单细胞生物可以直接做出反应,多细胞生物则通过复杂的信号传递系统来传递信息,从而调控机体活动。传导方式包括相邻细胞直接接触、细胞分泌各种化学物质来调节其他细胞代谢和功能。在脑缺血再灌注损伤中,信号通路是近年来研究的热点之一,丝裂原活化蛋白激酶级联反应是近年发现的细胞质和细胞核联系的枢纽,其在接受不同通路的上游信号后,激发即早基因和转录因子的表达和活化,并通过相应的靶基因、靶蛋白等的表达与合成来完成对各种胞外刺激的反应,在细胞凋亡的信号传导方面起着关键性的作用。
摘要
背景:既往电针治疗脑缺血再灌注损伤观察的针刺穴位搭配较少。
目的:探讨电针正交实验所选组穴对脑缺血再灌注损伤后细胞外信号调节激酶信号通路的影响。
方法:150只SD大鼠随机等分为5组,假手术组只暴露大脑中动脉;模型组及正交1,2,3号组建立脑缺血再灌注模型。正交1,2,3号组采用正交法筛选的穴位组合进行电针刺激。正交1号组为百会、曲池、足三里、尺泽,正交2号组为百会、足三里、尺泽、三阴交,正交3号组为合谷、足三里、尺泽、三阴交。
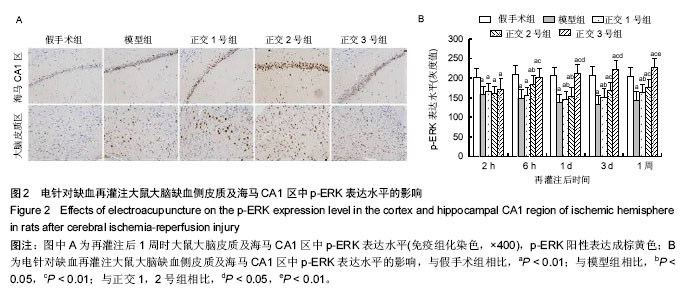
结果与结论:与模型组相比,正交1,2,3号组大鼠神经功能缺损评分降低,脑梗死面积缩小,脑缺血区微血管密度数量及缺血侧皮质和海马CA1区中磷酸化细胞外信号调节激酶表达水平增加,且正交3号组变化最为显著。提示电针经正交法筛选的合谷、足三里、尺泽、三阴交能有效减少脑缺血再灌注大鼠的梗死面积,且该效应可能与其调节受损脑组织中细胞外信号调节激酶信号通路密切相关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:肾移植;肝移植;移植;心脏移植;组织移植;皮肤移植;皮瓣移植;血管移植;器官移植;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-5496-3342(冯毅慧)
中图分类号:

.jpg)