中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (39): 5873-5878.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.39.015
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
基于贝叶斯决策的髋关节自动分割方法
马安邦1,王 东1,2,吴慧慧1,戴尅戎1,2,顾冬云1,2
- 1上海交通大学生物医学工程学院,数字医学临床转化教育部工程研究中心,上海市 200030;2上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院骨科,上海市 200011
Automatic segmentation method for hip joint based on Bayesian Decision Theory
Ma An-bang1, Wang Dong1, 2, Wu Hui-hui1, Dai Ke-rong1, 2, Gu Dong-yun1, 2
- 1School of Biomedical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Engineering Research Center of the Ministry of Education for Clinical Transformation of Digital Medicine, Shanghai 200030, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Ninth People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200011, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
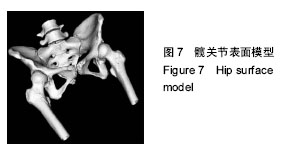
髋关节CT序列图像:不同于其他序列图像,股骨头与髋臼间隙小,而且股骨近端为松质骨,有天然的多孔结构,普通的CT图像分割算法无法准确提取序列中的所有股骨轮廓,股骨轮廓提取多是由手动提取,准确率低,效率低下。
CT图像阈值分割方法:是一种有效的分割骨组织与其他组织的方法,但是髋关节股骨近端骨间隙小,骨间界限不清晰,股骨近端为多孔结构,因此仅使用阈值分割算法很难有效分割髋关节股骨近端并提取骨轮廓。
摘要
背景:基于CT图像的髋关节分割技术已广泛应用于计算机辅助手术规划、假体设计和有限元分析。
目的:探讨基于贝叶斯决策的髋关节自动分割方法在计算机辅助髋关节手术中的应用效果。
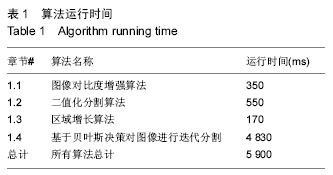
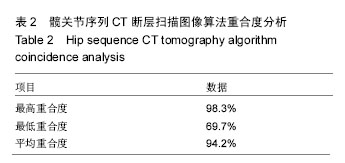
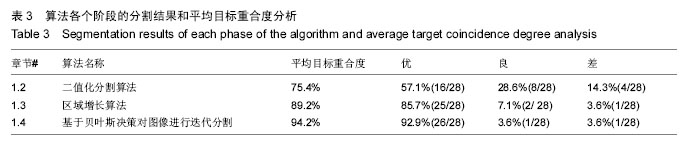
方法:针对髋关节序列CT图像中骨骼近端分割精度低,计算复杂度高,自动化程度低等问题,提出了一种自动分割算法,通过对比度增强、阈值分割和区域增长等算法提取股骨的初步轮廓,再根据贝叶斯决策论对股骨边缘进行再次分割。
结果与结论:基于贝叶斯决策的髋关节自动分割方法计算速度快,鲁棒性高,分割准确,在计算机辅助髋关节手术及假体设计等方面具有一定的实用价值。
ORCID: 0000-0002-7831-454X(马安邦)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)