中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (38): 5752-5757.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.38.019
• 生物材料学术探讨 biomaterial academic discussion • 上一篇 下一篇
动物源性再生型植入医疗器械社会合作网络分析:基于CNKI、万方、维普3大数据库中文文献研究
于舒洋,王红漫
- 北京大学医学人文研究院,北京市 100191
Social collaboration network analysis of animal-derived regenerative implantable medical devices: an overview based on Chinese literature from databases of CNKI, WANFANG DATA and VIP
Yu Shu-yang, Wang Hong-man
- Institute for Medical Humanities, Peking University, Beijing 100191, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
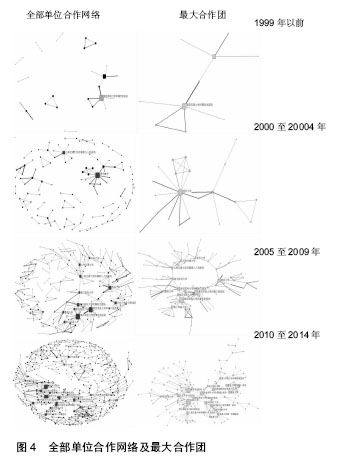
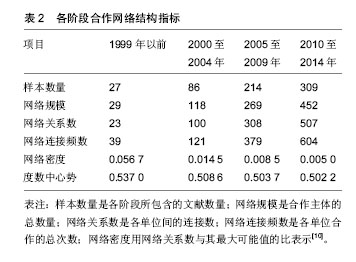
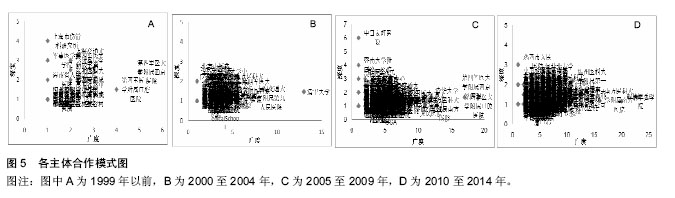
基于“广度-深度”的主体角色演变分析:利用度数和合作强度来分析各主体在不同阶段的角色演变。广度(度数)表示与某主体连接的其他主体个数,度数越高,表明该主体协调能力越强,合作广度越大。深度表示为联结次数与广度的比值。联结次数是某单位与其他单位合作的总次数。强度指标越大,表明该主体与其他主体合作越频繁,合作性越强。
网络密度:是用来反映合作网络各节点之间联系的紧密程度。密度越大,合作越紧密,利于信息的传递与交流;密度越小,合作越不紧密,不利于知识和信息在合作网络中的传播和共享。
背景:因组织工程涉及到生物学、材料学、医学、工程学等多种学科,随着相关科学技术的快速发展,不同研究部门之间的合作日益成为提高科研成果产出能力的重要因素。
目的:绘制以组织工程技术为基础的动物源性再生型植入医疗器械社会合作网络可视化图谱,阐述该领域合作网络演变过程和现状。
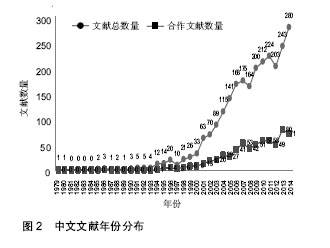
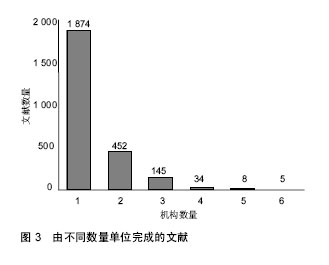
方法:采用社会网络分析方法,利用UCINET软件和北京大学自主著作权的文献信息统计分析软件SASI,对从CNKI、万方和维普数据库获取的2014年12月31日之前的,关于以组织工程技术为基础的动物源性再生型植入医疗器械的中文文献2 518篇进行分析。
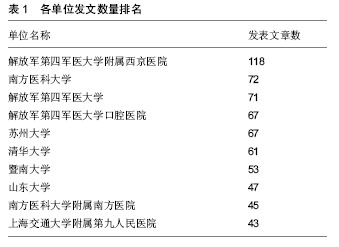
结果与结论:动物源性再生型植入医疗器械领域研究的合作网络进行了由松散型到单核主导、再到核心—边缘分布的演变;合作越来越多、越来越广;网络密度和中心势逐渐变小;2010至2014年核心结点单位为清华大学、解放军总医院和南方医科大学附属南方医院;存在大量的“边缘机构”。各单位的合作处于比较松散状态,边缘机构要扩大合作范围,核心机构要加强合作的持续性;应加强企业、科研机构与临床医院之间的合作,促进组织工程技术向临床的转化,加快产业化发展。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)