| [1] Wang WZ, Baynosa RC, Zamboni WA. Therapeutic interventions against reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle. J Surg Res. 2011;171(1):175-182.
[2] Zhao ZQ, Corvera JS, Halkos ME, et al. Inhibition of myocardial injury by ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion: comparison with ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285(2):H579-588.
[3] McAllister SE, Ashrafpour H, Cahoon N, et al. Postconditioning for salvage of ischemic skeletal muscle from reperfusion injury: efficacy and mechanism. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;295(2):R681-689.
[4] Yan H, Zhang F, Kochevar AJ, et al. The effect of postconditioning on the muscle flap survival after ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Invest Surg. 2010;23(5):249-256.
[5] Park JW, Kang JW, Jeon WJ, et al. Postconditioning protects skeletal muscle from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Microsurgery. 2010;30(3):223-229.
[6] Guo XS, Li YZ, Liu XH, et al. Calcineurin mediates the protective effect of postconditioning on skeletal muscle. Shock. 2011;36(3):312-316.
[7] Lee JI, Wook Nha K, Suh JS, et al. Remote postconditioning attenuates ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat skeletal muscle through mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channel-dependent mechanism. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2013;29(9):571-578.
[8] 彭龙龙,阳富春,薄占东,等.不同缺血后调适方案对大鼠模型肢体骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(5):739-744.
[9] Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. New directions for protecting the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury: targeting the Reperfusion Injury Salvage Kinase (RISK)-pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;61(3): 448-460.
[10] Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. Reperfusion injury salvage kinase signalling: taking a RISK for cardioprotection. Heart Fail Rev. 2007;12(3-4):217-234.
[11] Heusch G. Treatment of Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Ischemic and Pharmacological Postconditioning. Compr Physiol. 2015;5(3):1123-1145.
[12] Lamas S, Marsden PA, Li GK, et al. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: molecular cloning and characterization of a distinct constitutive enzyme isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89(14):6348-6352.
[13] Fleming I, Busse R. Molecular mechanisms involved in the regulation of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003;284(1): R1-12.
[14] Chen CA, Wang TY, Varadharaj S, et al. S-glutathionylation uncouples eNOS and regulates its cellular and vascular function. Nature. 2010;468(7327): 1115-1118.
[15] Chen CA, Druhan LJ, Varadharaj S, et al. Phosphorylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase regulates superoxide generation from the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(40):27038-27047.
[16] Ozturk K, Ozyurt H, Somay A, et al. The effects of nitric oxide donor molsidomine on skeletal muscle damage in a rat hind limb model of ischemia-reperfusion. Eur Surg Res. 2009;42(2):71-77.
[17] Roberts BW, Mitchell J, Kilgannon JH, et al. Nitric oxide donor agents for the treatment of ischemia/reperfusion injury in human subjects: a systematic review. Shock. 2013;39(3):229-239.
[18] Talukder MA, Yang F, Shimokawa H, et al. eNOS is required for acute in vivo ischemic preconditioning of the heart: effects of ischemic duration and sex. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010;299(2):H437-445.
[19] Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore: its fundamental role in mediating cell death during ischaemia and reperfusion. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003;35(4):339-341.
[20] 贺永贵,李王芳,伊红丽,等.黄芪甲苷抑制GSK-3β活性介导大鼠心肌缺血/再灌注损伤作用的线粒体机制研究[J].中国药理学通报,2014,30(3):402-406.
[21] Miyauchi T, Miyata M, Ikeda Y, et al. Waon therapy upregulates Hsp90 and leads to angiogenesis through the Akt-endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathway in mouse hindlimb ischemia. Circ J. 2012;76(7): 1712-1721.
[22] Hernández-Reséndiz S, Palma-Flores C, De Los Santos S, et al. Reduction of no-reflow and reperfusion injury with the synthetic 17β-aminoestrogen compound Prolame is associated with PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling cascade. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015;110(2):1.
[23] Ming XF, Viswambharan H, Barandier C, et al. Rho GTPase/Rho kinase negatively regulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation through the inhibition of protein kinase B/Akt in human endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(24):8467-8477.
[24] Wolfrum S, Dendorfer A, Rikitake Y, et al. Inhibition of Rho-kinase leads to rapid activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase Akt and cardiovascular protection. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(10):1842-1847.
[25] Fleming I, Fisslthaler B, Dimmeler S, et al. Phosphorylation of Thr(495) regulates Ca(2+)/ calmodulin-dependent endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity. Circ Res. 2001;88(11):E68-75.
[26] Goligorsky MS, Li H, Brodsky S, et al. Relationships between caveolae and eNOS: everything in proximity and the proximity of everything. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2002;283(1):F1-10.
[27] Sugimoto M, Nakayama M, Goto TM, et al. Rho-kinase phosphorylates eNOS at threonine 495 in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;361(2): 462-467.
[28] Michell BJ, Chen Zp, Tiganis T, et al. Coordinated control of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation by protein kinase C and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276(21):17625-17628.
[29] Javadov S, Karmazyn M. Mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening as an endpoint to initiate cell death and as a putative target for cardioprotection. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2007;20(1-4):1-22.
[30] Shahzad T, Kasseckert SA, Iraqi W, et al. Mechanisms involved in postconditioning protection of cardiomyocytes against acute reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013;58:209-216.
[31] Juhaszova M, Zorov DB, Kim SH, et al. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta mediates convergence of protection signaling to inhibit the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. J Clin Invest. 2004;113(11): 1535-1549.
[32] Bopassa JC, Ferrera R, Gateau-Roesch O, et al. PI 3-kinase regulates the mitochondrial transition pore in controlled reperfusion and postconditioning. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;69(1):178-185.
[33] Cohen MV, Yang XM, Downey JM. The pH hypothesis of postconditioning: staccato reperfusion reintroduces oxygen and perpetuates myocardial acidosis. Circulation. 2007;115(14):1895-1903. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
缺血后调适:又名缺血后处理或缺血后适应,是指在组织缺血后立即施予几个短时程的再灌注/缺血操作,可以引发内源性保护组织缺血再灌注损伤的现象。研究认为,缺血后调适能介导和激活一系列信号级联反应,从而减轻由缺血再灌注引起的细胞凋亡与坏死,发挥其保护作用。
缺血后调适方案可降低骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤:再灌注挽救激酶信号通路主要由PI3K-Akt和MEK1/ 2-Erk1/2两条重要信号通路组成,再灌注挽救激酶信号通路在缺血预调适和后调适过程中激活了对组织缺血再灌注损伤保护机制的关键环节。
文题释义:
缺血后调适:又名缺血后处理或缺血后适应,是指在组织缺血后立即施予几个短时程的再灌注/缺血操作,可以引发内源性保护组织缺血再灌注损伤的现象。研究认为,缺血后调适能介导和激活一系列信号级联反应,从而减轻由缺血再灌注引起的细胞凋亡与坏死,发挥其保护作用。
缺血后调适方案可降低骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤:再灌注挽救激酶信号通路主要由PI3K-Akt和MEK1/ 2-Erk1/2两条重要信号通路组成,再灌注挽救激酶信号通路在缺血预调适和后调适过程中激活了对组织缺血再灌注损伤保护机制的关键环节。.jpg) 文题释义:
缺血后调适:又名缺血后处理或缺血后适应,是指在组织缺血后立即施予几个短时程的再灌注/缺血操作,可以引发内源性保护组织缺血再灌注损伤的现象。研究认为,缺血后调适能介导和激活一系列信号级联反应,从而减轻由缺血再灌注引起的细胞凋亡与坏死,发挥其保护作用。
缺血后调适方案可降低骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤:再灌注挽救激酶信号通路主要由PI3K-Akt和MEK1/ 2-Erk1/2两条重要信号通路组成,再灌注挽救激酶信号通路在缺血预调适和后调适过程中激活了对组织缺血再灌注损伤保护机制的关键环节。
文题释义:
缺血后调适:又名缺血后处理或缺血后适应,是指在组织缺血后立即施予几个短时程的再灌注/缺血操作,可以引发内源性保护组织缺血再灌注损伤的现象。研究认为,缺血后调适能介导和激活一系列信号级联反应,从而减轻由缺血再灌注引起的细胞凋亡与坏死,发挥其保护作用。
缺血后调适方案可降低骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤:再灌注挽救激酶信号通路主要由PI3K-Akt和MEK1/ 2-Erk1/2两条重要信号通路组成,再灌注挽救激酶信号通路在缺血预调适和后调适过程中激活了对组织缺血再灌注损伤保护机制的关键环节。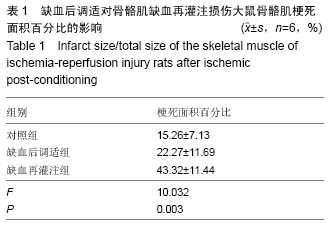
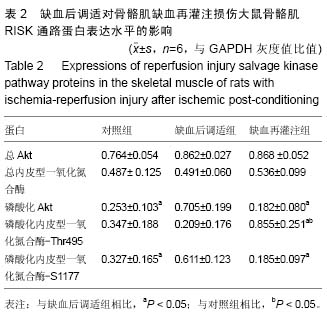
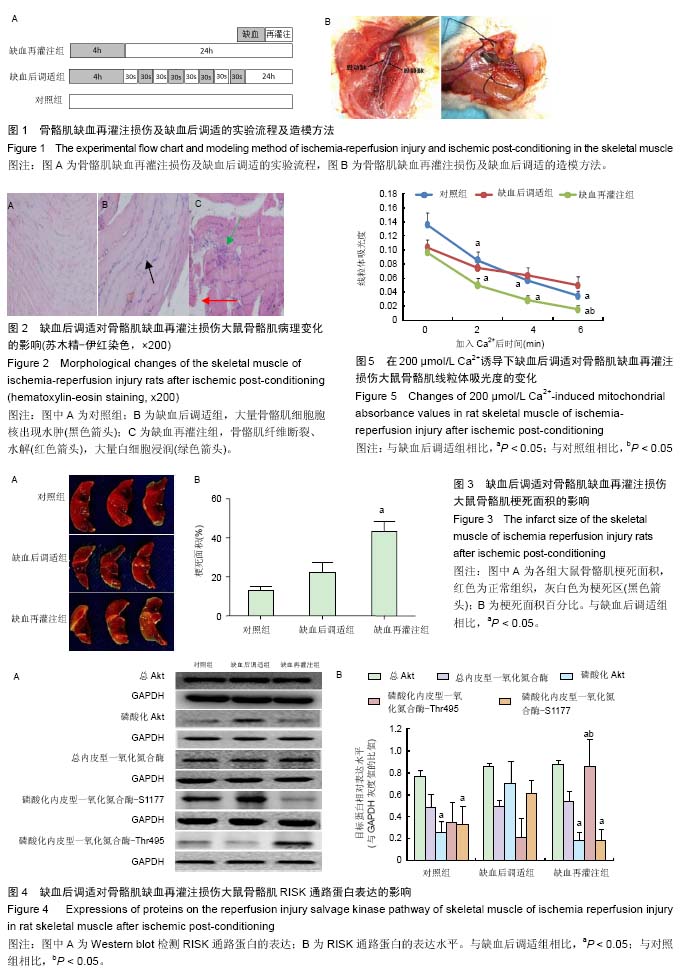
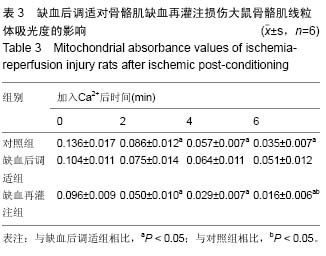
.jpg) 文题释义:
缺血后调适:又名缺血后处理或缺血后适应,是指在组织缺血后立即施予几个短时程的再灌注/缺血操作,可以引发内源性保护组织缺血再灌注损伤的现象。研究认为,缺血后调适能介导和激活一系列信号级联反应,从而减轻由缺血再灌注引起的细胞凋亡与坏死,发挥其保护作用。
缺血后调适方案可降低骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤:再灌注挽救激酶信号通路主要由PI3K-Akt和MEK1/ 2-Erk1/2两条重要信号通路组成,再灌注挽救激酶信号通路在缺血预调适和后调适过程中激活了对组织缺血再灌注损伤保护机制的关键环节。
文题释义:
缺血后调适:又名缺血后处理或缺血后适应,是指在组织缺血后立即施予几个短时程的再灌注/缺血操作,可以引发内源性保护组织缺血再灌注损伤的现象。研究认为,缺血后调适能介导和激活一系列信号级联反应,从而减轻由缺血再灌注引起的细胞凋亡与坏死,发挥其保护作用。
缺血后调适方案可降低骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤:再灌注挽救激酶信号通路主要由PI3K-Akt和MEK1/ 2-Erk1/2两条重要信号通路组成,再灌注挽救激酶信号通路在缺血预调适和后调适过程中激活了对组织缺血再灌注损伤保护机制的关键环节。