中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (37): 5524-5529.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.37.008
• 皮肤粘膜组织构建 skin and mucosal tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
血竭对组织工程皮肤移植模型大鼠创伤修复的影响
俞 琦,王文佳,王 平
- 贵阳中医学院基础医学院,贵州省贵阳市 550025
Effects of Sanguis draxonis on wound healing in rat models of tissue-engineered skin transplantation
Yu Qi, Wang Wen-jia, Wang Ping
- School of Basic Medicine, Guiyang University of Chinese Medicine, Guiyang 550025, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
血竭:又名麒麟竭,为棕榈科植物麒麟竭果实渗出的树脂经加工制成。具有活血定痛,止血,生肌敛疮的功效。主治跌打损伤、瘀血肿痛、金疮出血、溃疡不敛等。其药理活性表现为抗炎、止痛,以及活血与止血的双向调节作用等方面。
组织工程皮肤:是一种较为完善的组织工程化组织,是通过在体外大量培养和扩增功能细胞,将其与细胞外基质及支架材料互相作用,制成的具有生物活性的人工皮肤替代物。组织工程皮肤为皮肤创伤的修复、皮肤功能的重塑提供了新的策略。
文题释义:
血竭:又名麒麟竭,为棕榈科植物麒麟竭果实渗出的树脂经加工制成。具有活血定痛,止血,生肌敛疮的功效。主治跌打损伤、瘀血肿痛、金疮出血、溃疡不敛等。其药理活性表现为抗炎、止痛,以及活血与止血的双向调节作用等方面。
组织工程皮肤:是一种较为完善的组织工程化组织,是通过在体外大量培养和扩增功能细胞,将其与细胞外基质及支架材料互相作用,制成的具有生物活性的人工皮肤替代物。组织工程皮肤为皮肤创伤的修复、皮肤功能的重塑提供了新的策略。
.jpg) 文题释义:
血竭:又名麒麟竭,为棕榈科植物麒麟竭果实渗出的树脂经加工制成。具有活血定痛,止血,生肌敛疮的功效。主治跌打损伤、瘀血肿痛、金疮出血、溃疡不敛等。其药理活性表现为抗炎、止痛,以及活血与止血的双向调节作用等方面。
组织工程皮肤:是一种较为完善的组织工程化组织,是通过在体外大量培养和扩增功能细胞,将其与细胞外基质及支架材料互相作用,制成的具有生物活性的人工皮肤替代物。组织工程皮肤为皮肤创伤的修复、皮肤功能的重塑提供了新的策略。
文题释义:
血竭:又名麒麟竭,为棕榈科植物麒麟竭果实渗出的树脂经加工制成。具有活血定痛,止血,生肌敛疮的功效。主治跌打损伤、瘀血肿痛、金疮出血、溃疡不敛等。其药理活性表现为抗炎、止痛,以及活血与止血的双向调节作用等方面。
组织工程皮肤:是一种较为完善的组织工程化组织,是通过在体外大量培养和扩增功能细胞,将其与细胞外基质及支架材料互相作用,制成的具有生物活性的人工皮肤替代物。组织工程皮肤为皮肤创伤的修复、皮肤功能的重塑提供了新的策略。摘要
背景:研究显示,血竭治疗皮肤压疮、烧烫伤、溃疡等具有显著疗效。
目的:观察血竭对组织工程皮肤移植大鼠血管内皮细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子、神经肽P物质和羟脯氨酸的影响,验证血竭促进组织工程皮肤修复创面的作用。
方法:制备组织工程皮肤移植大鼠模型,将大鼠随机分为模型对照组、血竭外用组、血竭内服组、血竭外用加内服组,治疗组分别采用药物外敷、单纯口服[0.1 g/(kg•d)]、外敷加口服治疗,7 d后检测皮肤组织中血管内皮细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子、P物质和羟脯氨酸的表达。
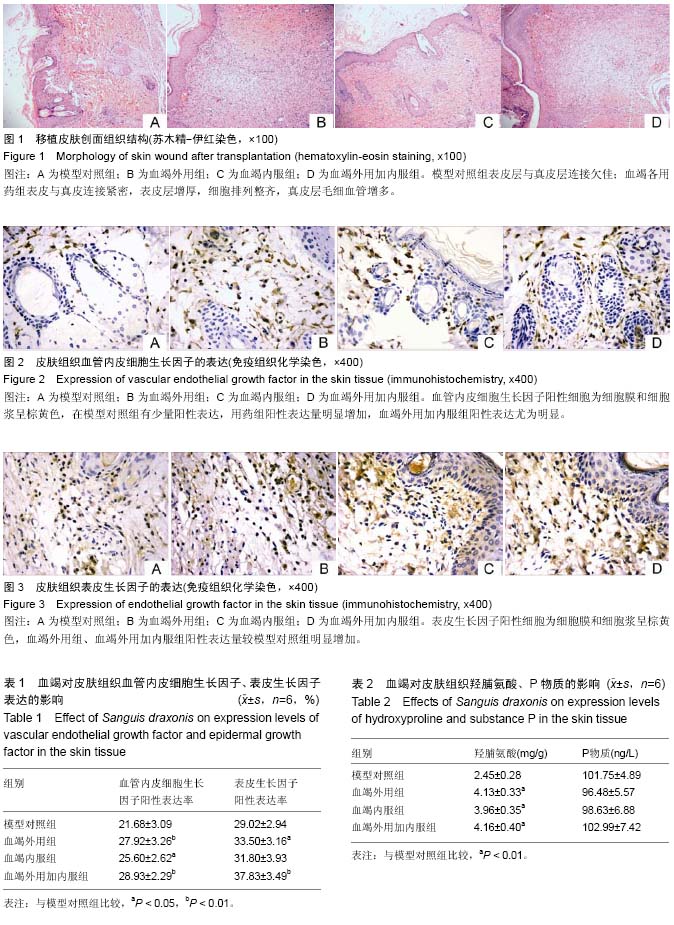
结果与结论:①与模型对照组比较,血竭治疗组皮肤组织中血管内皮细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子和羟脯氨酸表达水平显著提高(P < 0.01或P < 0.05),P物质含量无改变(P > 0.05)。②结果说明,血竭可通过上调组织工程皮肤移植模型大鼠血管内皮细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子和羟脯氨酸的表达,促进组织工程皮肤对创面的修复作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4723-3288(俞琦)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
血竭:又名麒麟竭,为棕榈科植物麒麟竭果实渗出的树脂经加工制成。具有活血定痛,止血,生肌敛疮的功效。主治跌打损伤、瘀血肿痛、金疮出血、溃疡不敛等。其药理活性表现为抗炎、止痛,以及活血与止血的双向调节作用等方面。
组织工程皮肤:是一种较为完善的组织工程化组织,是通过在体外大量培养和扩增功能细胞,将其与细胞外基质及支架材料互相作用,制成的具有生物活性的人工皮肤替代物。组织工程皮肤为皮肤创伤的修复、皮肤功能的重塑提供了新的策略。
文题释义:
血竭:又名麒麟竭,为棕榈科植物麒麟竭果实渗出的树脂经加工制成。具有活血定痛,止血,生肌敛疮的功效。主治跌打损伤、瘀血肿痛、金疮出血、溃疡不敛等。其药理活性表现为抗炎、止痛,以及活血与止血的双向调节作用等方面。
组织工程皮肤:是一种较为完善的组织工程化组织,是通过在体外大量培养和扩增功能细胞,将其与细胞外基质及支架材料互相作用,制成的具有生物活性的人工皮肤替代物。组织工程皮肤为皮肤创伤的修复、皮肤功能的重塑提供了新的策略。