中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (35): 5270-5276.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.35.015
• 脊柱损伤基础实验 basic experiments of spinal injury • 上一篇 下一篇
临床症状不同颈椎病患者颈椎间盘白细胞介素1β及白细胞介素6和环氧化酶2的表达
胡 炜1,马信龙2,袁建军1,张仁赞1,彭 兵1,张学利1
- 1天津市人民医院脊柱外科,天津市 300121;2天津医院骨科,天津市 300210
Expression of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and cyclooxygenase 2 in cervical intervertebral disc of cervical spondylosis patients with different clinical symptoms
Hu Wei1, Ma Xin-long2, Yuan Jian-jun1, Zhang Ren-zan1, Peng Bing1, Zhang Xue-li1
- 1Department of Spinal Surgery, Tianjin People’s Hospital, Tianjin 300121, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300210, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
白细胞介素:是由多种细胞产生并作用于多种细胞的一类细胞因子。由于最初是白细胞产生又在白细胞间发挥作用,所以由此得名,现仍一直沿用。白细胞介素interleukin 缩写为IL。关于免疫反应的表达和调节,有来源于淋巴细胞或巨噬细胞等许多因子参与。来源于淋巴细胞的有淋巴细胞活素,来源于巨噬细胞的总称为monokine,其中的各个因子的生物活性各有不同。现在是指一类分子结构和生物学功能已基本明确,具有重要调节作用而统一命名的细胞因子,它和血细胞生长因子同属细胞因子。两者相互协调,相互作用,共同完成造血和免疫调节功能。白细胞介素在传递信息,激活与调节免疫细胞,介导T、B细胞活化、增殖与分化及在炎症反应中起重要作用。
环氧化酶:又称前列腺素内氧化酶还原酶,是一种双功能酶,具有环氧化酶和过氧化氢酶活性,是催化花生四烯酸转化为前列腺素的关键酶。目前发现环氧化酶有两种环氧化酶1和环氧化酶2同工酶,前者为结构型,主要存在于血管、胃、肾等组织中,参与血管舒缩、血小板聚集、胃黏膜血流、胃黏液分泌及肾功能等的调节,其功能与保护胃肠黏膜、调节血小板聚集、调节外周血管的阻力和调节肾血流量分布有;后者为诱导型,各种损伤性化学、物理和生物因子激活磷脂酶A2水解细胞膜磷脂,生成花生四烯酸,后者经环氧化酶2催化加氧生成前列腺素。
摘要
背景:在颈椎的退变过程中,椎间盘细胞发生生物化学变化,此过程产生各种炎性细胞因子可能导致椎间盘突出。间盘突出后,反过来刺激周围毗邻组织产生各种炎性因子。
目的:探讨白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、环氧化酶2在不同临床症状的颈脊髓压迫患者中的表达及意义。
方法:颈前路间盘切除内固定患者的突出间盘或责任间盘,依据临床症状分为3组:髓型症状组,根性症状组,颈椎外伤组,对间盘进行苏木精-伊红染色及免疫组织化学染色进行形态学观察,对间盘免疫组织化学染色结果进行阳性细胞计数。
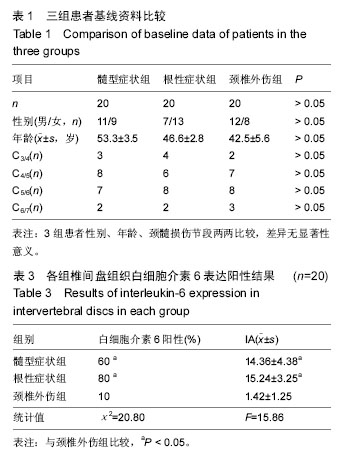
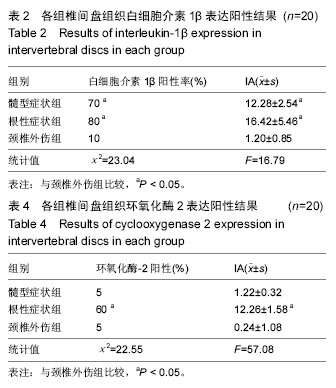
结果与结论:①髓型症状组和根性症状组苏木精-伊红染色在突出颈椎间盘周围的炎性肉芽组织中可见炎细胞浸润以及新生血管形成;颈椎外伤组未见明显炎细胞浸润以及新生血管形成;②免疫组织化学染色髓型症状组可见白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6表达阳性的细胞,其胞浆为棕黄色着色为主,环氧化酶2表达阳性的细胞稀少;根性症状组中可见白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、环氧化酶2表达阳性的细胞,数量明显多于髓型症状组;颈椎外伤组中免疫组织化学染色白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、环氧化酶2表达阳性细胞表达稀少;③髓型症状组及根性症状组中白细胞介素1β阳性表达率和IA值,白细胞介素6阳性表达率和IA值均显著高于颈椎外伤组(P < 0.05);根性症状组中环氧化酶2阳性表达率及IA值均显著高于颈椎外伤组。④结果说明,突出的颈椎间盘可发生白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、环氧化酶2细胞因子表达,并在颈椎间盘早期退变中发挥作用,不同临床症状的颈脊髓压迫患者这些炎症因子表达具有明显差异。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程ORCID: 0000-0002-8250-5103(胡炜)
中图分类号:

.jpg)