| [1] 陈小青,陈明珠,曾荣东.利塞膦酸钠治疗绝经后老年女性骨质疏松症临床研究[J]. 海峡药学, 2014, 26(2):97-99.
[2] Meschia M, Brincat M, Barbacini P, et al.A clinical trial on the effects of a combination of elcatonin (carbocalcitonin) and conjugated estrogens on vertebral bonemass in early postmenopausal women. Calcif Tissue Int. 1993;53(1):17-20.
[3] MellerI. Effects of salmon calcitonin in postmenopausal osteoporosis: a controlled double-blind study. Calcif Tissue Int. 1986;39(6):416-417.
[4] Muñoz-Torres M, Alonso G, Raya MP.Calcitonin therapy in osteoporosis. Treat Endocrinol. 2004;3(2):117-132.
[5] 刘强,孙佳,牛秀.依降钙素治疗老年骨质疏松症的临床疗效观察[J].中国实用医药, 2015, 10(1):6-7.
[6] Plosker GL,McTavish D.Intranasalsalcatonin (salmon calcitonin). A review of its pharmacological properties and role in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis.Drugs Aging. 1996;8(5):378-400.
[7] Fujita T, Ohue M, Nakajima M, et al.Comparison of the effects of elcatonin and risedronateonback and knee pain by electroalgometry using fall of skinimpedance and quality of life assessment using SF-36. J Bone Miner Metab. 2011;29(5):588-597.
[8] Knopp-Sihota JA, Newburn-Cook CV, Homik J, et al. Calcitonin for treating acute and chronicpain of recent and remote osteoporotic vertebral compressionfractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(1):17-38.
[9] Wells G, Cranney A, Peterson J, Boucher M, et al. Risedronate for the primary andsecondary prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausalwomen. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;23(1):CD004523.
[10] Takakuwa M, Iwamoto J. Elcatonin in combination withrisedronate is more effective than risedronate alone for relievingback pain in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(7): 1159-1165.
[11] 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 原发性骨质疏松诊治指南(2011年)[J]. 柳州医学, 2012, 25(3):188-199.
[12] Kumamoto K, Nakamura T, Suzuki T, et al.Validation of the Japanese Osteoporosis Quality of Life Questionnaire.J Bone Miner Metab. 2010;28(1):1-7.
[13] Miyakoshi N, Itoi E, Kobayashi M, et al. Impactofpostural deformities and spinal mobility on quality of life inpostmenopausal osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2003;14(12):1007-1012.
[14] Lyritis GP, TrovasG.Analgesic effects of calcitonin. Bone. 2002;30(5 Suppl):71S-74S.
[15] Abellan Perez M, Bayina Garcia FJ, Calabozo M, et al.Multicenter comparative study of synthetic salmon calcitoninadministered nasally in the treatment of establishedpostmenopausal osteoporosis. An Med Interna.1995;12(1):12-16.
[16] Wysowski DK, Chang JT.Alendronate and risedronate:reports of severe bone, joint, and muscle pain. Arch Intern Med.2005;165(3):346-347.
[17] Nakamura T, Osawa M, Itoh M, et al.The effect of risedronate (17.5 mg/week) treatment onquality of life in Japanese women with osteoporosis: a prospectiveobservational study. J Bone Miner Metab. 2012;30(6):715-721.
[18] Hadji P, Zanchetta JR, Russo L, et al.Theeffect of teriparatide compared with risedronate on reduction ofback pain in postmenopausal women with osteoporotic vertebralfractures. Osteoporos Int. 2012; 23(8):2141-2150.
[19] Papadokostakis G, Damilakis J, Mantzouranis E, et al.The effectiveness of calcitonin on chronicback pain and daily activities in postmenopausal women withosteoporosis. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(3):356-362.
[20] Pontiroli AE, Pajetta E, Scaglia L, et al. Analgesic effect of intranasal and intramuscular salmon calcitonin in post-menopausal osteoporosis: a double-blind, double-placebo study. Aging (Milano). 1994;6(6):459-463.
[21] Quinlan J, Acute pain management in patients with persistent pain[J]. CurrOpin Support Palliat Care. 2012, 6(2):188-193.
[22] Ito A,Kumamoto E, Takeda M, et al.Mechanisms for ovariectomy-induced hyperalgesiaandits relief by calcitonin: participation of 5-HT1A-like receptor onC-afferent terminals in substantiagelatinosa of the rat spinal cord.J Neurosci. 2000;20(16):6302-6308.
[23] Yoshimura M, Furue H,Ito A.Mechanism of antinociceptive action of calcitonin--involvement of descending serotonergic system.Nihon Rinsho. 2005; 63 Suppl 10:211-213.
[24] Ofluoglu D, Akyuz G, Unay O, et al.The effect ofcalcitonin on beta-endorphin levels in postmenopausal osteoporoticpatients with back pain. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26(1):44-49.
[25] Ringe JD, Farahmand P, Schacht E, et al.Superiorityof a combined treatment of Alendronate and Alfacalcidolcompared to the combination of Alendronate and plain vitamin DorAlfacalcidol alone in established postmenopausal or maleosteoporosis (AAC-Trial).Rheumatol Int. 2007;27(5):425-434.
[26] Itoh S, Sekino Y, Shinomiya K, et al.The effects ofrisedronate administered in combination with a proton pumpinhibitor for the treatment of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab.2013;31(2):206-211.
[27] van Schoor NM, Smit JH, Twisk JW, et al. Impactofvertebral deformities, osteoarthritis, and other chronic diseases onquality of life: a population-based study.Osteoporos Int.2005; 16(7):749-756. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
降钙素:降钙素由甲状腺的滤泡旁细胞产生和分泌,它由32个肽组成。主要生理功能是低血浆中钙、磷浓度,抑制钙、磷的吸收。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松性疼痛及中、重度症状明显的畸形性骨炎。
双膦酸盐:双膦酸盐是抗骨吸收的一类新药,主要通过改变破骨细胞的形态学,从而抑制其功能。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松症、变形性骨炎、恶性肿瘤骨转移引起的高钙血症和骨痛症等。
文题释义:
降钙素:降钙素由甲状腺的滤泡旁细胞产生和分泌,它由32个肽组成。主要生理功能是低血浆中钙、磷浓度,抑制钙、磷的吸收。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松性疼痛及中、重度症状明显的畸形性骨炎。
双膦酸盐:双膦酸盐是抗骨吸收的一类新药,主要通过改变破骨细胞的形态学,从而抑制其功能。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松症、变形性骨炎、恶性肿瘤骨转移引起的高钙血症和骨痛症等。.jpg) 文题释义:
降钙素:降钙素由甲状腺的滤泡旁细胞产生和分泌,它由32个肽组成。主要生理功能是低血浆中钙、磷浓度,抑制钙、磷的吸收。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松性疼痛及中、重度症状明显的畸形性骨炎。
双膦酸盐:双膦酸盐是抗骨吸收的一类新药,主要通过改变破骨细胞的形态学,从而抑制其功能。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松症、变形性骨炎、恶性肿瘤骨转移引起的高钙血症和骨痛症等。
文题释义:
降钙素:降钙素由甲状腺的滤泡旁细胞产生和分泌,它由32个肽组成。主要生理功能是低血浆中钙、磷浓度,抑制钙、磷的吸收。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松性疼痛及中、重度症状明显的畸形性骨炎。
双膦酸盐:双膦酸盐是抗骨吸收的一类新药,主要通过改变破骨细胞的形态学,从而抑制其功能。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松症、变形性骨炎、恶性肿瘤骨转移引起的高钙血症和骨痛症等。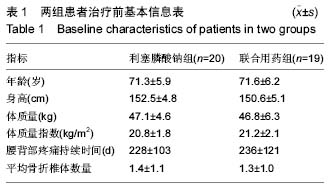
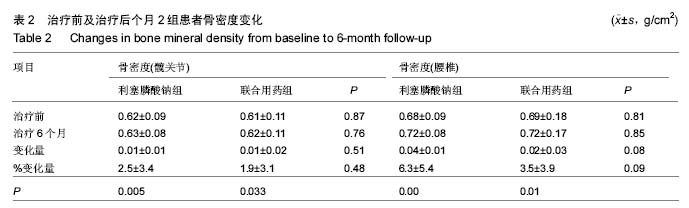
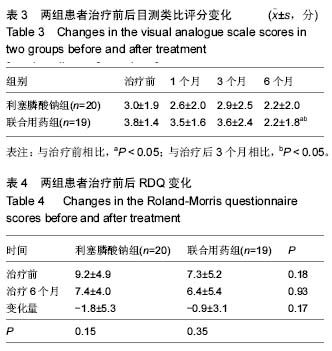
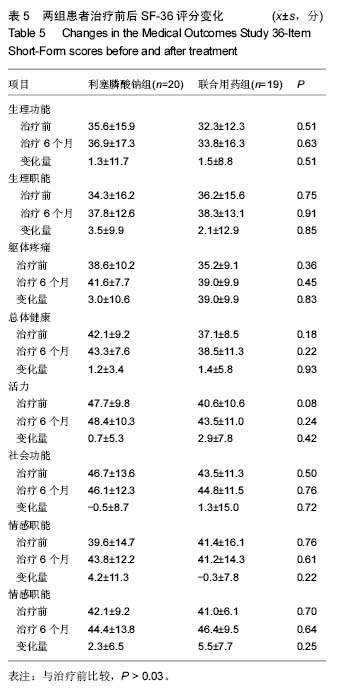
.jpg) 文题释义:
降钙素:降钙素由甲状腺的滤泡旁细胞产生和分泌,它由32个肽组成。主要生理功能是低血浆中钙、磷浓度,抑制钙、磷的吸收。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松性疼痛及中、重度症状明显的畸形性骨炎。
双膦酸盐:双膦酸盐是抗骨吸收的一类新药,主要通过改变破骨细胞的形态学,从而抑制其功能。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松症、变形性骨炎、恶性肿瘤骨转移引起的高钙血症和骨痛症等。
文题释义:
降钙素:降钙素由甲状腺的滤泡旁细胞产生和分泌,它由32个肽组成。主要生理功能是低血浆中钙、磷浓度,抑制钙、磷的吸收。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松性疼痛及中、重度症状明显的畸形性骨炎。
双膦酸盐:双膦酸盐是抗骨吸收的一类新药,主要通过改变破骨细胞的形态学,从而抑制其功能。临床上主要用于治疗骨质疏松症、变形性骨炎、恶性肿瘤骨转移引起的高钙血症和骨痛症等。