中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (17): 2540-2545.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.17.015
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
胫骨远端骨折有限元模型的建立及稳定性分析
杨志刚1,甘 霖2,叶俊星1
- 1南通大学第三附属医院,无锡市第三人民医院,无锡市中西医结合医院骨科,江苏省无锡市 214000;2南京医科大学附属无锡市第二医院,江苏省无锡市 214000
Construction and stability of finite element models of distal tibial fractures
Yang Zhi-gang1, Gan Lin2, Ye Jun-xing1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Wuxi Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine Hospital, Wuxi Third People’s Hospital, Third Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2the Second Hospital of Wuxi City Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
踝关节有限元模型:参照既往相关研究方法,试验建立了可靠、有效的踝关节有限元模型,对于骨骼的模拟应对皮质骨、松质骨、骨髓腔分别赋予材料参数,但实际操作中却给单元网格的划分增加了难度,为了简化计算在准静态载荷下,骨及软骨可定义为均一、各向同性材料。足踝部韧带及腱膜在关节稳定及平衡中起了重要作用,大多将其看成线弹性、各向同性材料,以杆单元模拟连接骨骼端起止点。
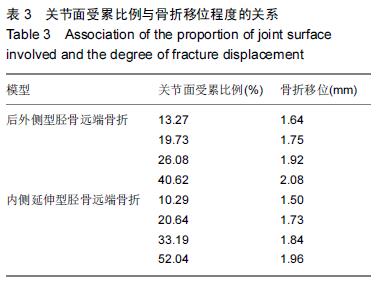
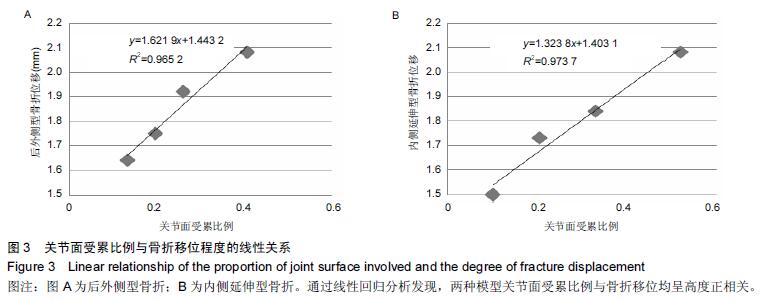
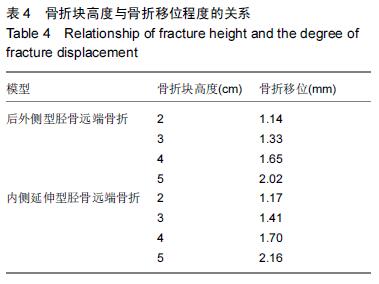
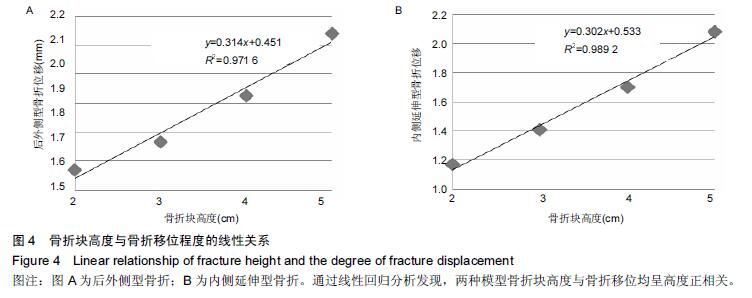
胫骨远端骨折有限元模型:胫骨远端骨折较重,多出现骨折移位,关节面多受累。试验在踝关节有限元模型基础上,对不同种类胫骨远端骨折(Pilon骨折)进行模拟,分析不同关节面受累比例及骨折块高度与骨折移位程度的关系。
背景:传统足踝部生物力学研究具有局限性,由于踝关节结构极为复杂、活动度大,故对于踝关节有限元模型的建立及不同骨折类型的分析也极为困难。
目的:建立胫骨远端骨折模型并进行稳定性分析。
方法:收集成年人正常足踝CT数据,采用Minics软件对志愿者右足踝部关节进行三维重建,并进行有效性验证。通过Solidwork软件假设不同关节面受累比例及骨折块高度,并制作出相应的胫骨远端骨折模型。通过ANSYS软件应用有限元法进行骨折稳定性分析。
结果与结论:胫骨远端骨折模型符合相关文献数据,可进一步行有限元分析,关节面受累比例与骨折块高度与骨折移位呈显著正相关,即与骨折稳定性呈负相关。提示踝关节及胫骨远端骨折三维有限元模型建立成功、有效,胫骨远端骨折稳定性与关节面受累比例及骨折高度相关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID:0000-0002-2453-8126(杨志刚)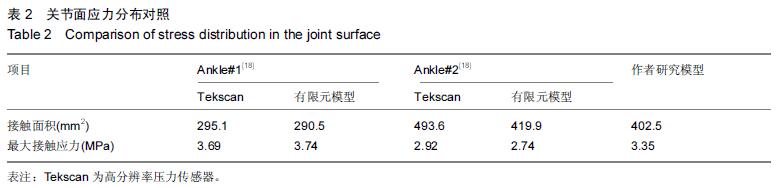
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)