中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (15): 2225-2232.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.15.014
• 组织构建基础实验 basic experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
退变性腰椎侧凸发病中Hsa-let-7f调控白细胞介素10/STAT3信号通路的作用
王 磊1,李天旺1,刘建强2,刘晓宗3,王照国4,田 艳1,张永兴1,王 伟1
- 1解放军第252医院脊柱外科,河北省保定市 071000;2保定市骨科医院骨科,河北省保定市 071000;3保定市第一中心医院烧伤整形科,河北省保定市 071000;4保定市阜平县医院骨科,河北省保定市 073200
Downregulated Hsa-let-7f contributes to the loss of type II collagen by targeting interleukin-10/STAT3 signaling pathway in degenerative lumbar scoliosis
Wang Lei1, Li Tian-wang1, Liu Jian-qiang2, Liu Xiao-zong3, Wang Zhao-guo4, Tian Yan1, Zhang Yong-xing1, Wang Wei1
- 1Department of Spinal Surgery, the 252nd Hospital of PLA, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Baoding Orthopedics Hospital, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China; 3Department of Burn and Plastic Surgery, First Central Hospital of Baoding, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China; 4Department of Orthopedics, Hospital of Fuping County, Baoding 073200, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
非编码小RNA:非编码RNA(Non-coding RNA)是指不编码蛋白质的RNA。其中包括rRNA,tRNA,snRNA,snoRNA 和microRNA 等多种已知功能的 RNA,还包括未知功能的RNA。这些RNA的共同特点是都能从基因组上转录而来,但是不翻译成蛋白,在RNA 水平上就能行使各自的生物学功能了。非编码RNA分类:从长度上来划分可以分为3类:小于50 nt,包括microRNA,siRNA,piRNA;50-500 nt-包括rRNA,tRNA,snRNA,snoRNA,SLRNA,SRPRNA 等等;大于500 nt,包括长的mRNA-like 的非编码RNA,长的不带polyA 尾巴的非编码RNA等等。
背景:microRNAs(miRNAs)在多种疾病中扮演重要的角色,对退变性腰椎侧凸患者椎间盘中miRNAs表达谱的分析,有助于揭示其发病机制,为其治疗提供新的靶点。假设miRNA通过调控白细胞介素10/STAT3(椎间盘退变的一个潜在炎症通路)信号通路促使椎间盘退变。
目的:比较退变性腰椎侧凸患者与正常对照组椎间盘组织中miRNAs表达谱的差异,确定退变性腰椎侧凸特异性相关的miRNAs,并对其进行功能验证。
方法:对获取的退变性腰椎侧凸患者手术髓核组织和腰椎骨折患者正常髓核组织依次进行总RNA提取,其中,各取10例进行miRNA Solexa测序筛查,挑选表达有差异的microRNA。随后,采用qRT-PCR技术对其进行验证。对表达显著差异的miRNA进行探究。进一步对其进行功能验证,确定其与Ⅱ型胶原表达的关系。运用Western与荧光素酶报告系统进一步确定靶基因。
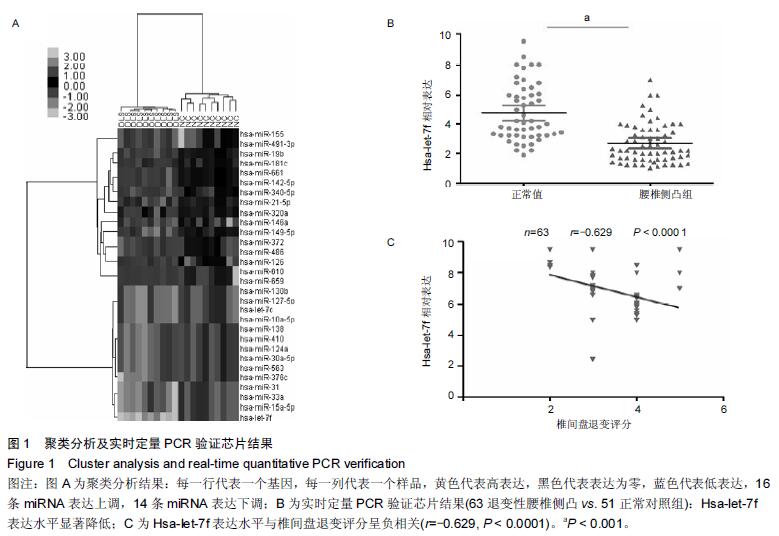
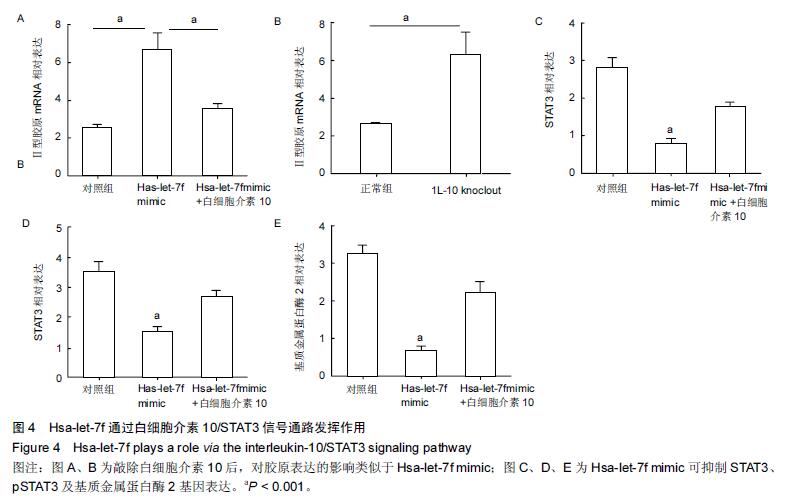
结果与结论:与正常对照相比,30条miRNA表达存在显著差异(16条表达上调和14条表达下调)。随后进行qRT-PCR验证,与正常对照相比,Hsa-let-7f在退变性腰椎侧凸患者椎间盘组织中,表达显著下调。此外,Hsa-let-7f表达水平与椎间盘退变评分密切相关。高表达Hsa-let-7f促进Ⅱ型胶原表达。敲除白细胞介素10后,对Ⅱ型胶原表达表达类似与过表达Hsa-let-7f。生物信息学软件证实,白细胞介素10为Hsa-let-7f理论上的靶基因。荧光素酶报告系统及western blot进一步证实Hsa-let-7f的靶基因为白细胞介素10。此外,Hsa-let-7f影响其下游基因STAT3及基质金属蛋白酶2基因表达。研究表明,下调的Hsa-let-7f通过调控白细胞介素10/STAT3信号通路,导致椎间盘组织中Ⅱ型胶原的丢失,进而引起椎间盘退变及退变性腰椎侧凸;Hsa-let-7f可成为治疗退变性腰椎侧凸的一个新的生物治疗靶点。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0002-2465-2017(王磊)


.jpg)