| [1] Gilpin DA, Weidenbecher MS, Dennis JE. Scaffold-free tissue-engineered cartilage implants for laryngotracheal reconstruction. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(3):612-617.
[2] 冷晔.聚羟基丁酸己酸酯及其在组织工程中的应用[J].生物医学工程学进展,2011,32(4):213-218.
[3] 孙安科,李万同,孟庆延,等.带蒂肌筋膜瓣充填与包裹构建喉支架形态组织工程软骨[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2011,46(12): 1019-1023.
[4] 刘清宇,王富友,杨柳.关节软骨组织工程支架的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(10):1247-1250.
[5] Delawi D, Kruyt MC, Huipin Y, et al. Comparing autograft, allograft, and tricalcium phosphate ceramic in a goat instrumented posterolateral fusion model. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013;19(11):821-828.
[6] Dupont KM, Boerckel JD, Stevens HY, et al. Synthetic scaffold coating with adeno-associated virus encoding BMP2 to promote endogenous bone repair. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;347(3):575-588.
[7] Park SH, Tofighi A, Wang X, et al. Calcium phosphate combination biomaterials as human mesenchymal stem cell delivery vehicles for bone repair. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2011;97(2):235-244.
[8] Che JH, Zhang ZR, Li GZ, et al. Application of tissue-engineered cartilage with BMP-7 gene to repair knee joint cartilage injury in rabbits. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(4):496-503.
[9] Wang H, Zhang LC, Shi T, et al. Properties evaluation of collagen-hydroxyapatite-chondroitin sulfate-bone morphogenetic protein bone substitute material. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 20118;43(5):730-734.
[10] 江汕,刘勇,王秋实,等.组织工程骨神经化构建及其修复兔大段骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(5):599-605.
[11] 李亮,张鑫鑫,姜晓锐,等.雪旺细胞促进组织工程骨修复大鼠股骨损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(2):148-152.
[12] 邱耿韬.磷酸钙骨水泥在骨组织再生修复应用中的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(14):1406-1408.
[13] 胡金龙.组织工程学技术治疗骨缺损的最新研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(2):150-152.
[14] 刘阳,曹延林,朱立新,等.新型可注射性nHA/CS骨修复材料修复兔股骨髁骨缺损的X线评估[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(17): 1472-1475.
[15] 王岩松,刘丹平,张元和,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺 66 骨填充材料与自体骨修复良性骨肿瘤术后骨缺损的对比研究[J].军医进修学院学报,2011,32(4):373-374.
[16] 聂鹏飞,陈少文,应小洲,等.诱导膜技术治疗大段骨缺损的研究进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(5):439-440.
[17] Villemagne T, Bonnard C, Accadbled F, et al. Intercalary segmental reconstruction of long bones after malignant bone tumor resection using primary methyl methacrylate cement spacer interposition and secondary bone grafting: the induced membrane technique. J Pediatr Orthop. 2011;31(5):570-576.
[18] 李广恒,金丹,郑波,等.骨骼肌来源的细胞在骨和软骨组织修复与再生中的应用[J]中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(3):266-268.
[19] Blum AL, BongioVanni JC, Morgan SJ, et al. Complications associated with distraction osteogenesis for infected nonunion of the femoral shaft in the presence of a bone defect: a retrospective series. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(4):565-570.
[20] 金绍林,佘迪,王辉,等.指端缺损的5种同指皮瓣修复方法[J].安徽医学,2010,31(10):1174 -1176.
[21] 陈伟盛.急诊应用 V-Y 皮瓣治疗软组织缺损病例分析[J].中国现代药物应用,2010,4(16):104 -105.
[22] 范大礼,钟小明.带血管神经蒂的食指近节背侧岛状皮瓣修复拇指皮肤缺损18例[J].重庆医学,2008,37(10):1044-1045.
[23] Tan HL, Tan DY, Zhao JK. Treatment of thumb soft-tissue defects using a bipedicle island flap of the index finger: anatomical basis and clinical application. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(5):721-728.
[24] Greene EL, Houghton O, Collinsworth G, et al. 5-HT(2A) receptors stimulate mitogen-activated protein kinase via H(2)O(2) generation in rat renal mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2000;278(4):F650-658.
[25] Grewal JS, Mukhin YV, Garnovskaya MN, et al. Serotonin 5-HT2A receptor induces TGF-beta1 expression in mesangial cells via ERK: proliferative and fibrotic signals. Am J Physiol. 1999;276(6 Pt 2):F922-930.
[26] Banes A, Florian JA, Watts SW. Mechanisms of 5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) receptor activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999;291(3):1179-1187.
[27] Shum JK, Melendez JA, Jeffrey JJ. Serotonin-induced MMP-13 production is mediated via phospholipase C, protein kinase C, and ERK1/2 in rat uterine smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(45):42830-42840.
[28] Florian JA, Watts SW. Integration of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase activation in vascular 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptor signal transduction. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998; 284(1):346-355.
[29] Quinn JC, Johnson-Farley NN, Yoon J, et al. Activation of extracellular-regulated kinase by 5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) receptors in PC12 cells is protein kinase C-independent and requires calmodulin and tyrosine kinases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;303(2):746-752.
[30] Gorin Y, Ricono JM, Wagner B, et al. Angiotensin II-induced ERK1/ERK2 activation and protein synthesis are redox-dependent in glomerular mesangial cells. Biochem J. 2004;381(Pt 1):231-239.
[31] Yang CM, Yo YL, Hsieh JT, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in canine cultured tracheal smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1994; 111(3):777-786.
[32] Sellers LA, Simon J, Lundahl TS, et al. Adenosine nucleotides acting at the human P2Y1 receptor stimulate mitogen-activated protein kinases and induce apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(19):16379-16390.
[33] Labasque M, Meffre J, Carrat G, et al. Constitutive activity of serotonin 2C receptors at G protein-independent signaling: modulation by RNA editing and antidepressants. Mol Pharmacol. 2010;78(5):818-826.
[34] Song HJ, Lee TS, Jeong JH, et al. Hydrogen peroxide-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in cultured feline ileal smooth muscle cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;312(1):391-398.
[35] Goppelt-Struebe M, Stroebel M. Signaling pathways mediating induction of the early response genes prostaglandin G/H synthase-2 and egr-1 by serotonin via 5-HT2A receptors. J Cell Physiol. 1998;175(3):341-347.
[36] Goppelt-Struebe M, Fickel S, Reiser CO. The platelet-derived-growth-factor receptor, not the epidermal-growth-factor receptor, is used by lysophosphatidic acid to activate p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase and to induce prostaglandin G/H synthase-2 in mesangial cells. Biochem J. 2000;345 Pt 2:217-224.
[37] Breshnahan BA, Kelefiotis D, Stratidakis I, et al. PGF2alpha- induced signaling events in glomerular mesangial cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1996;212(2):165-173.
[38] Huwiler A, van Rossum G, Wartmann M, et al. Stimulation by extracellular ATP and UTP of the stress-activated protein kinase cascade in rat renal mesangial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1997;120(5):807-812.
[39] Watts SW, Yang P, Banes AK, et al. Activation of Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase proteins by vascular serotonin receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2001;38(4): 539-551.
[40] Errico M, Crozier RA, Plummer MR, et al. 5-HT(7) receptors activate the mitogen activated protein kinase extracellular signal related kinase in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience. 2001;102(2):361-367.
[41] Mukhin YV, Garnovskaya MN, Collinsworth G, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine1A receptor/Gibetagamma stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinase via NAD(P)H oxidase and reactive oxygen species upstream of src in chinese hamster ovary fibroblasts. Biochem J. 2000;347 Pt 1:61-67.
[42] 陈建良,黄冬梅.充气式硅橡胶赝复体修复单侧上颌骨缺损的研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2009,10(3):157-161
[43] 杜兵,陈巨峰,符志峰.计算机辅助设计与制作在磁性固位分体式上颌骨赝复体修复中的应用[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版), 2011,5(2):178-183.
[44] 毛恩亮,戴红莲,雷军,等.热致相分离/粒子滤出法制备多孔支架的研究[J].武汉理工大学学报,2010,(12):15-18.
[45] 魏学磊,董福慧.计算机辅助成型技术制备骨组织工程支架的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,(12):1508-1512.
[46] 范伟,刘亮,孙海钰,等.以Ⅰ型胶原缓释重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2复合新型多孔酸钙支架修复兔大段桡骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国药物与临床,2008,8(8):627-629.
[47] 刘冰,陈鹏,臧晓霞,等.活性纳米羟基磷灰石复合胶原/聚乳酸材料对拔牙创早期愈合及牙槽嵴吸收影响的实验研究[J].口腔医学,2010,30(1):38-41.
[48] 袁道英,杨佑成,张彬,等.VEGF在脱细胞骨基质复合富血小板血浆修复颅骨缺损中的表达[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2010,8(4): 347-351. |
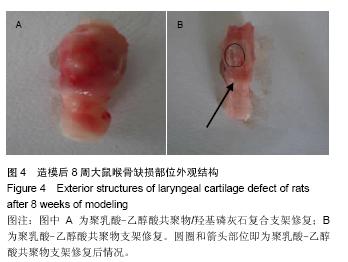
.jpg)