中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (44): 7209-7216.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.44.028
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇
重建钢板与克氏针置入内固定修复锁骨骨折的Meta分析
张谢卓,刘利国,哈斯鲁,徐 超,伊力哈木•托合提
- 新疆医科大学第二附属医院骨科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830063
Meta analysis of reconstruction plate and Kirschner wire fixation for the treatment of clavicle fractures
Zhang Xie-zhuo, Liu Li-guo, Ha Si-lu, Xu Chao, Yilihamu•Tuoheti
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830063, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
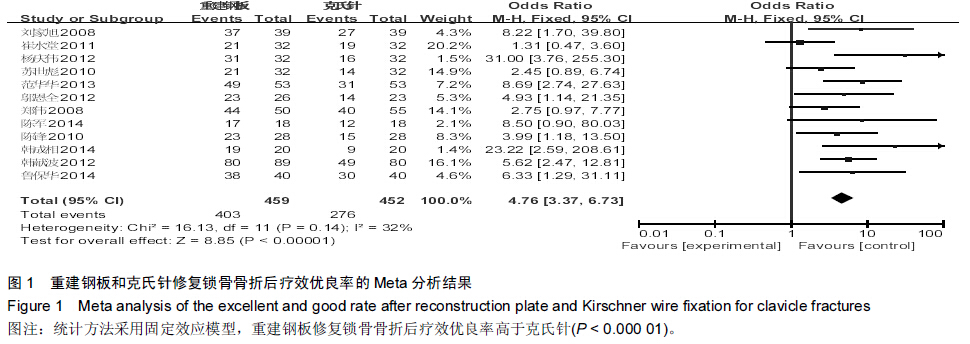
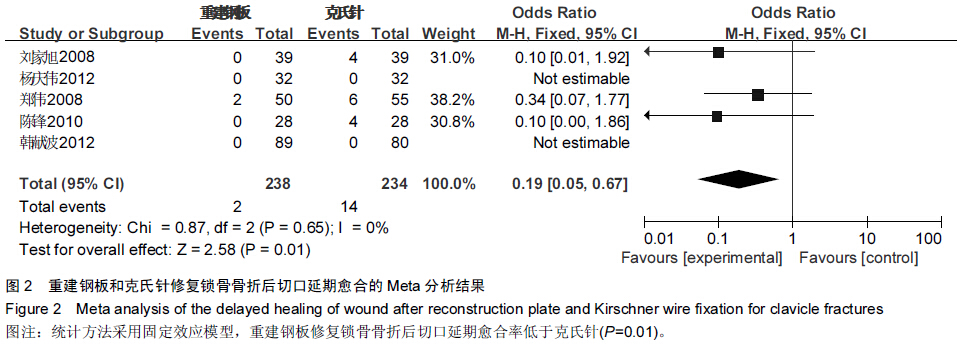
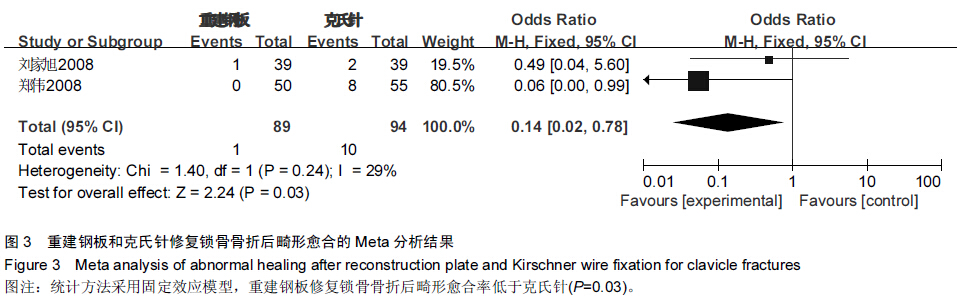
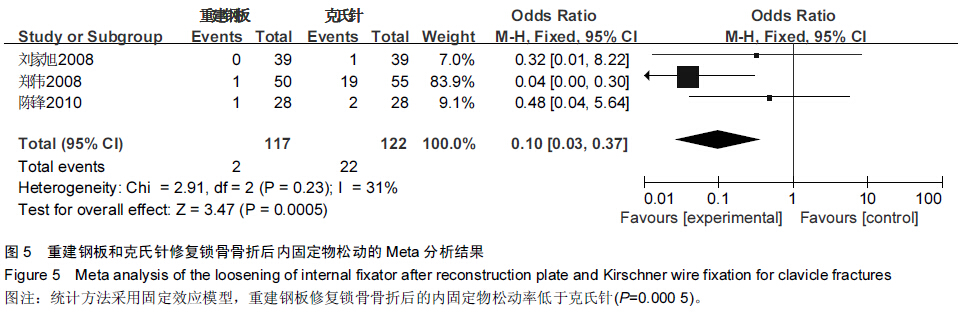
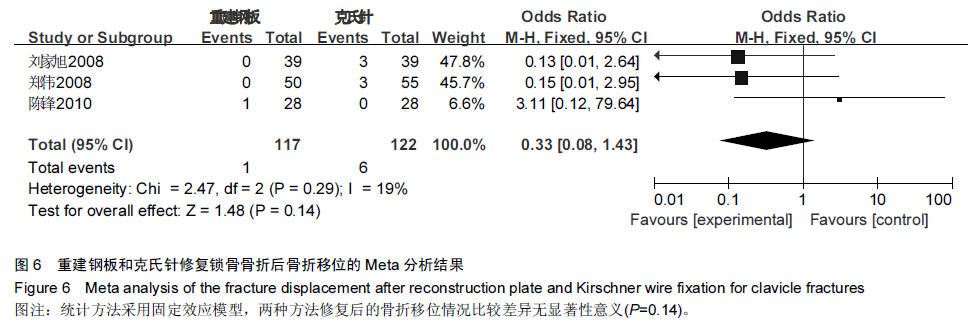
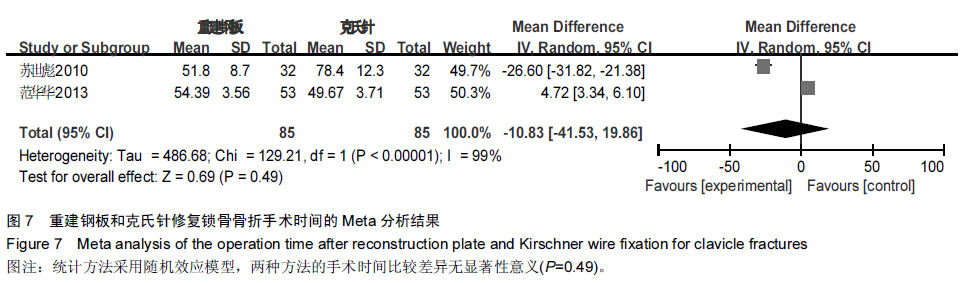
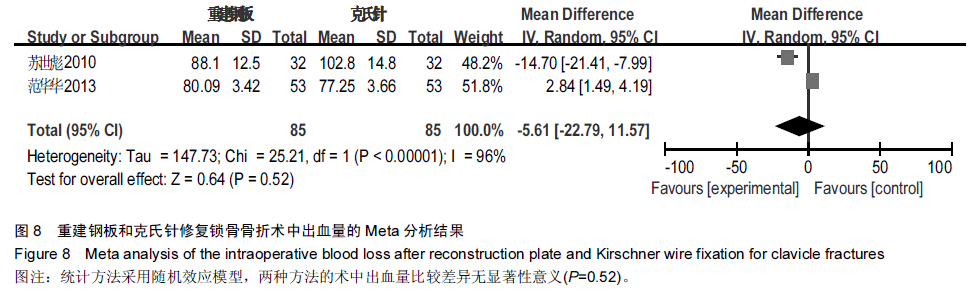
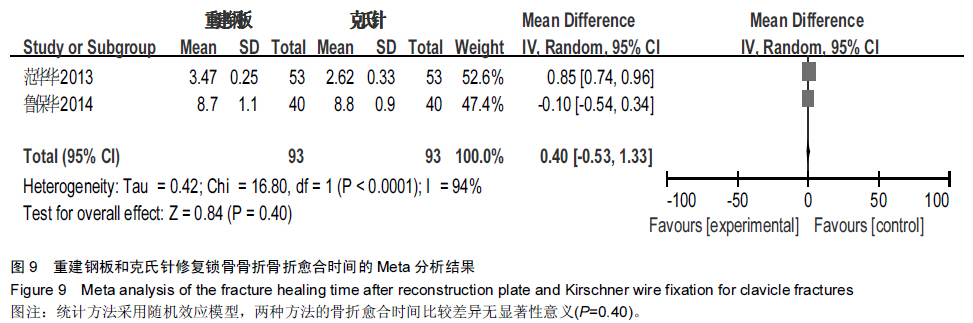
背景:目前已有大量研究证实,重建钢板相较于克氏针修复锁骨骨折具有较好的效果,但其具体优越性目前尚无确切报道,且临床上随机对照研究较少,缺乏系统性评价。 目的:采用Meta分析的方法对重建钢板和克氏针修复锁骨骨折的疗效和安全性进行系统评价。 方法:通过计算机检索2008至2015年MEDLINE、Embase、PubMed、Cochrane图书馆、CNKI、万方数据库、维普数据库,搜集有关重建钢板与克氏针修复锁骨骨折的对照研究,筛选出符合纳入标准的文献,对其进行严格的质量评价,选择疗效优良率、切口延期愈合、畸形愈合、术后感染、内固定物松动、术后骨折移位、手术时间、术中出血量、骨折愈合时间作为Meta分析的评价指标,利用Cochrane协作网提供的RevMan 5.2软件对纳入研究结果进行Meta分析。 结果与结论:最终纳入12篇文献,共911例患者,发表时间为2008至2014年,全部为中文文献。Meta分析结果显示,与克氏针相比,重建钢板修复锁骨骨折在提高疗效优良率、缩短切口延期愈合、减少畸形愈合、降低术后感染、防止内固定物松动、避免术后骨折移位方面具有一定的优越性,但两种方法修复锁骨骨折在手术时间、术中出血量、骨折愈合时间方面差异无显著性意义。提示与克氏针相比,重建钢板修复锁骨骨折具有较好的效果,在患者自身经济以及医院条件允许的情况下可优先选择重建钢板修复锁骨骨折。由于文章纳入病例有限,缺乏设计更为严格的多中心、大样本、长期的临床随机对照研究来进一步证实结论可信度。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程