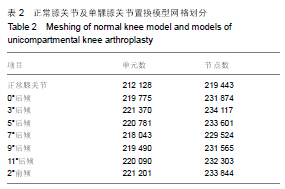
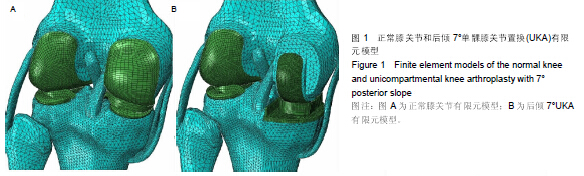
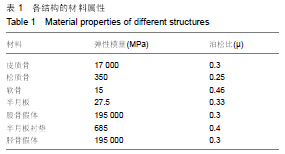
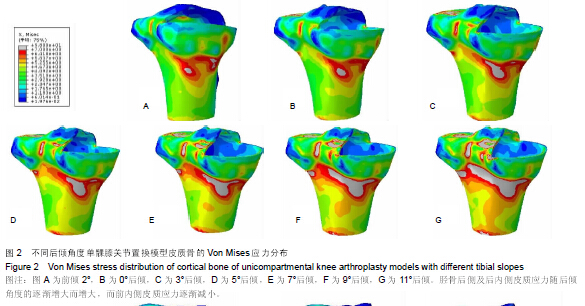
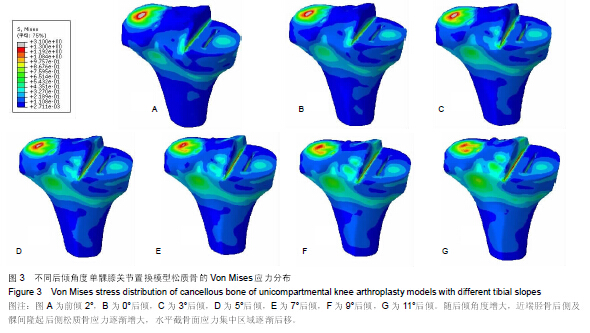
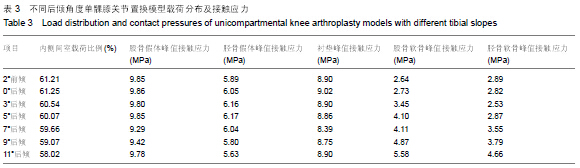
| [1] O'Rourke MR, Gardner JJ, Callaghan JJ, et al. The John Insall Award: unicompartmental knee replacement: a minimum twenty-one-year followup, end-result study. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2005;440:27-37.
[2] Murray DW, Goodfellow JW, O’connor JJ. The Oxford Medial unicompartmental arthroplasty A Ten-Year Survival Study. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1998; 80(6):983-989.
[3] Hamilton WG, Ammeen D, Engh CA Jr, et al. Learning curve with minimally invasive unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2010;25(5):735-740.
[4] Müller PE, Pellengahr C, Witt M, et al. Influence of minimally invasive surgery on implant positioning and the functional outcome for medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2004;19(3):296-301.
[5] Zeng C, Cheng L, Wei J, et al. The influence of the tibial plateau slopes on injury of the anterior cruciate ligament: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2014; 22(1):53-65.
[6] Chatellard R, Sauleau V, Colmar M, et al. Medial unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: does tibial component position influence clinical outcomes and arthroplasty survival? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2013;99(4):S219-S225.
[7] Barbadoro P, Ensini A, Leardini A, et al. Tibial component alignment and risk of loosening in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: a radiographic and radiostereometric study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2014;22(12): 3157-3162.
[8] Giffin JR, Vogrin TM, Zantop T, et al. Effects of increasing tibial slope on the biomechanics of the knee. Am J Sports Med. 2004;32(2):376-382.
[9] Donzelli PS, Spilker RL, Ateshian GA, et al. Contact analysis of biphasic transversely isotropic cartilage layers and correlations with tissue failure. J Biomech.1999;32(10): 1037-1047.
[10] LeRoux MA, Setton LA. Experimental and biphasic FEM determinations of the material properties and hydraulic permeability of the meniscus in tension. J Biomech Eng.2002; 124(3): 315-321.
[11] Cowin SC. The mechanical and stress adaptive properties of bone.Ann Biomed Eng.1983;11(3-4): 263-295.
[12] Goldstein SA, Wilson DL, Sonstegard DA, et al. The mechanical properties of human tibial trabecular bone as a function of metaphyseal location. J Biomech.1983;16(12): 965-969.
[13] Peña E, Calvo B, Martinez MA, et al. Finite element analysis of the effect of meniscal tears and meniscectomies on human knee biomechanics. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).2005;20(5): 498-507.
[14] Weiss JA, Gardiner JC. Computational modeling of ligament mechanics. Crit Rev Biomed Eng.2001;29(3):303-371.
[15] Bao HR, Zhu D, Gong H, et al. The effect of complete radial lateral meniscus posterior root tear on the knee contact mechanics: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Sci.2013;18(2): 256-263.
[16] Taylor M, Tanner KE, Freeman MA. Finite element analysis of the implanted proximal tibia: a relationship between the initial cancellous bone stresses and implant migration. J Biomech. 1998;31(4): 303-310.
[17] Yao J, Snibbe J, Maloney M, et al. Stresses and strains in the medial meniscus of an ACL deficient knee under anterior loading: a finite element analysis with image-based experimental validation. J Biomech Eng.2006;128(1): 135-141.
[18] Shepherd DE, Seedhom BB. The'instantaneous' compressive modulus of human articular cartilage in joints of the lower limb. Rheumatology (Oxford).1999;38(2): 124-132.
[19] Bendjaballah MZ, Shirazi-Adl A, Zukor DJ. Biomechanical response of the passive human knee joint under anterior-posterior forces. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).1998; 13(8): 625-633.
[20] Peña E, Calvo B, Martinez MA, et al. A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the combined behavior of ligaments and menisci in the healthy human knee joint. J Biomech. 2006; 39(9): 1686-1701.
[21] Hopkins AR, New AM, Rodriguez-y-Baena F, et al. Finite element analysis of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Med Eng Phys.2010;32(1): 14-21.
[22] Mootanah R, Imhauser CW, Reisse F, et al. Development and validation of a computational model of the knee joint for the evaluation of surgical treatments for osteoarthritis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin.2014;17(13): 1502-1517.
[23] Moglo KE, Shirazi-Adl A. On the coupling between anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments, and knee joint response under anterior femoral drawer in flexion: a finite element study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).2003;18(8): 751-759.
[24] Peña E, Martinez MA, Calvo B, et al. A finite element simulation of the effect of graft stiffness and graft tensioning in ACL reconstruction. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).2005;20(6): 636-644.
[25] Song Y, Debski RE, Musahl V, et al. A three-dimensional finite element model of the human anterior cruciate ligament: a computational analysis with experimental validation. J Biomech. 2004;37(3): 383-390.
[26] Pandit H, Jenkins C, Barker K, et al. The Oxford medial unicompartmental knee replacement using a minimally-invasive approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2006;88(1): 54-60.
[27] Kwon OR, Kang KT, Son J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of fixed-and mobile-bearing for unicomparmental knee arthroplasty using finite element analysis. J Orthop Res.2014; 32(2): 338-345.
[28] Crockett R, Roba M, Naka M, et al. Friction, lubrication, and polymer transfer between UHMWPE and CoCrMo hip‐implant materials: A fluorescence microscopy study. J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;89(4): 1011-1018.
[29] Innocenti B, Bilgen ÖF, Labey L, et al. Load Sharing and Ligament Strains in Balanced, Overstuffed and Understuffed UKA. A Validated Finite Element Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(7):1491-1498.
[30] Kurosawa H, Fukubayashi T, Nakajima H. Load-bearing mode of the knee joint: physical behavior of the knee joint with or without menisci. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1980;149: 283-290.
[31] Fukubayashi T, Kurosawa H. The contact area and pressure distribution pattern of the knee: a study of normal and osteoarthrotic knee joints. Acta Orthop Scand.1980;51(1-6): 871-879.
[32] Kim SJ, Bae JH, Lim HC. Factors affecting the postoperative limb alignment and clinical outcome after Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.2012; 27(6):1210-1215.
[33] Konyves A, Willis-Owen CA, Spriggins AJ. The long-term benefit of computer-assisted surgical navigation in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res. 2010;5(94): 54-59.
[34] Lewis JL, Lew WD, Schmidt J. Description and error evaluation of an in vitro knee joint testing system. J Biomech Eng.1988;110(3): 238-248.
[35] Simpson DJ, Price AJ, Gulati A, et al. Elevated proximal tibial strains following unicompartmental knee replacement-a possible cause of pain. Med Eng Phys.2009;31(7): 752-757.
[36] Small SR, Berend ME, Rogge RD, et al. Tibial loading after UKA: evaluation of tibial slope, resection depth, medial shift and component rotation. J Arthroplasty.2013;28(9): 179-183.
[37] Sawatari T, Tsumura H, Iesaka K, et al. Three‐dimensional finite element analysis of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty-the influence of tibial component inclination. J Orthop Res.2005;23(3): 549-554.
[38] Hernigou P, Deschamps G. Posterior slope of the tibial implant and the outcome of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2004;86(3): 506-511.
[39] Aleto TJ, Berend ME, Ritter MA, et al. Early failure of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty leading to revision. J Arthroplasty.2008;23(2): 159-163.
[40] Hadley NA, Brown TD, Weinstein SL. The effects of contact pressure elevations and aseptic necrosis on the long-term outcome of congenital hip dislocation. J Orthop Res.1990;8(4): 504-513.
[41] Suero EM, Citak M, Cross MB, et al. Effects of tibial slope changes in the stability of fixed bearing medial unicompartmental arthroplasty in anterior cruciate ligament deficient knees. Knee.2012;19(4): 365-369.
[42] Weber P, Schröder C, Schmidutz F, et al. Increase of tibial slope reduces backside wear in medial mobile bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).2013;28(8): 904-909.
|