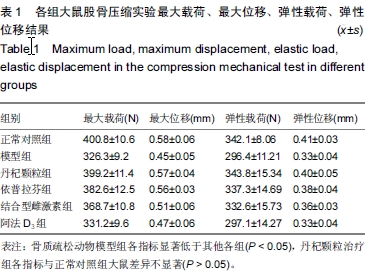
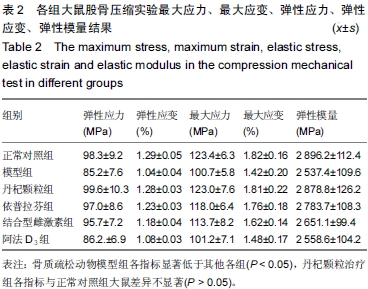
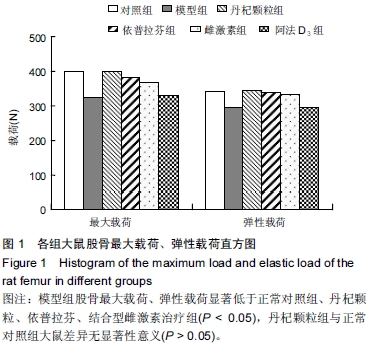
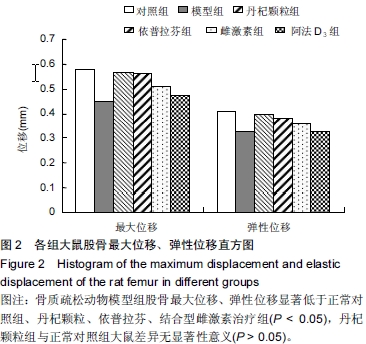
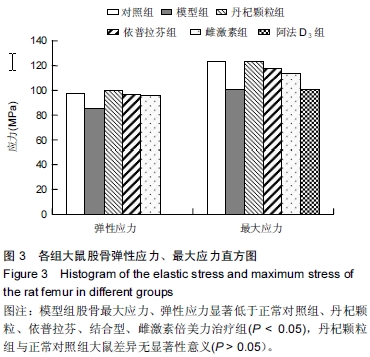
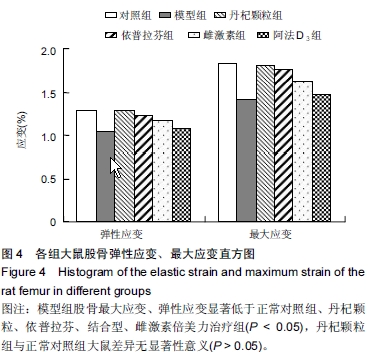
| [1] Marcus R. Post-menopausal osteoporosis. Best Pract ResClin Obste Gynaecol. 2002;16(3):309-327.
[2] Raisz LG. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concep ts, conflicts andp rospects. Clin Invest.2005;115(12):3318-3325.
[3] Umland EM, Rinaldi C, Parks SM, et al. The impact of estro2gen rep lacement therapy and raloxifene on osteoporosis, cardio2vascular disease and gynecologic cancers. Ann Pharmacoth2er.1999;33(12):1315-132.
[4] 刘忠厚.骨质疏松学[M].北京:科学出版社,1998:502.
[5] Kim JH, Liu X, Wang JH, et al. Wnt signaling in bone formation and its therapeutic potential for bone diseases. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis.2013;5:13-31.
[6] Chen GQ, Deng CX, Li YP. TGF-and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8: 272-288.
[7] 邢燕,毕宏焱,张倩楠,等.骨质疏松常用中成药介绍[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(1):83-96.
[8] Cao Y, Zhang LQ. A Smurf1 tale: Function and regulation of an ubiquitin ligase in multiple cellular networks. Cell Mol Life Sci.2013;70:2305-2317.
[9] Cao Y, Zhang LQ. Pharmaceutical perspectives of HECT-TYPE ubiquitin ligase smurf1. Curr Pharm Design. 2013;19: 3226-3233.
[10] Lu KF, Yin XS, Weng TJ, et al. Targeting WW domains linker of HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 for activation by CKIP-1. Nat CellBiol.2008;10: 994-1002.
[11] Nie J, Liu L, He F C, et al. CKIP-1: A scaffold protein and potential therapeutic target integrating multiple signaling pathways and physiologicalfunctions. Ageing Res Rev.2013; 12:276-281.
[12] Das S, Crockett JC. Osteoporosis-A current view of pharmacological prevention and treatment. Drug Des Devel Ther.2013;7:435-448.
[13] Ng KW. Potential role of odanacatib in the treatment of osteoporosis. Clin Interv Aging.2012;7:235-247.
[14] Zhang G, Guo BS, Wu H, et al. A delivery system targeting bone formation surfaces to facilitate RNAi-based anabolic therapy. Nat Med.2012;18: 307-314.
[15] 孙树东,高明,李新颖,等.脊髓损伤继发骨质疏松大鼠椎骨的力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15 (20):3661- 3664.
[16] 徐宏,吴铁,许碧莲,等. 蛇床子总黄酮对去卵巢骨质疏松股骨骨密度及生物力学的影响[J].中国现代医药杂志,2009, 11(6): 28-30.
[17] 付萍,杨铭,王清,等.骨质宁胶囊对维甲酸所致骨质疏松大鼠骨骼力学的影响[J].中国中医药科技,2009,9 (5):397-398.
[18] 杜联,殷丽平,陈敏,等.补肾壮骨胶囊对糖尿病骨质疏松症骨代谢及股骨生物力学相关指标的影响[J].甘肃中医学院学报, 2010, 27(3):17-21.
[19] 王亚芬,罗民,佟文霞,等.几种药物干预骨质疏松动物模型骨剪切力学特性的对比分析[J].生物医学工程研究,2013,32(3): 171-173.
[20] 钟显春,罗民,李新颖,等.几种药物治疗骨质疏松模型大鼠股骨蠕变特性的对比分析[J].生物医学工程研究,2012,31(3):180-183.
[21] 徐宏,吴铁,许碧莲.复方脑复康对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠股骨骨密度及生物力学的影响[J].现代诊断与治疗,2009,20(3):136-139.
[22] 江大雷,赵卓.中药骨疏灵和运动联合应用对去势大鼠骨量丢失的抑制作用研究[J].首都体育学院学报,2008,20(6):75-77.
[23] 刘忠厚.中国人骨质疏松症建议诊断标准(第二稿)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2000,6(1):1-3.
[24] 韩跃武,吴春娥.中医药治疗骨质疏松的临床观察[J].山西中医学院学报,2007,7(6):126-128. |