中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (42): 6730-6734.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.42.002
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
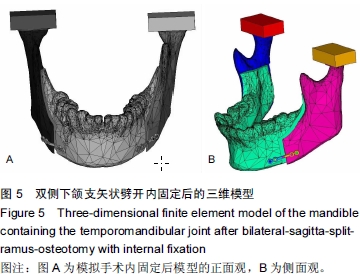
建立包含颞下颌关节下颌骨双侧下颌支矢状劈开内固定后的有限元模型
马 文1,侯 敏2,宋大立2,杨静文1,戴 智1,程家龙1,柴国良3,周卫源4,张瑞泽5
- 1天津医科大学,天津市 300070;2天津市口腔医院,天津市 300041;3天津市蓟县人民医院,天津市 301900;4天津大学,天津市 300072;5四川省林业中心医院,四川省成都市 610010
Establishing a finite element model of the mandible containing the temporomandibular joint after bilateral-sagitta-split-ramus-osteotomy with internal fixation
Ma Wen1, Hou Min2, Song Da-li2, Yang Jing-wen1, Dai Zhi1, Cheng Jia-long1, Chai Guo-liang3, Zhou Wei-yuan4, Zhang Rui-ze5
- 1Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China; 2Tianjin Stomatological Hospital, Tianjin 300041, China; 3Jixian County People’s Hospital, Tianjin 301900, China; 4Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China; 5Sichuan Province Forestry Center Hospital, Chengdu 610010, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
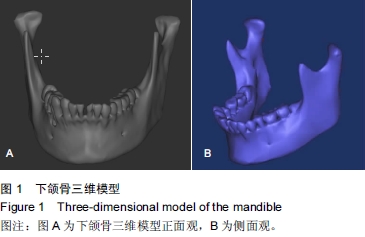
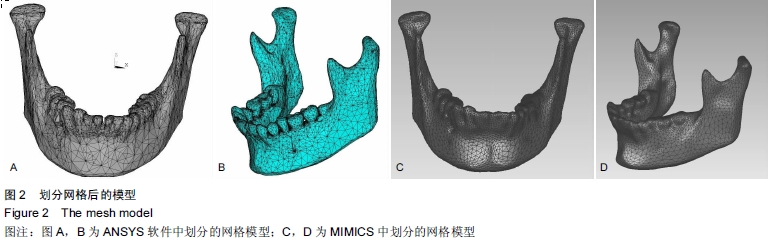
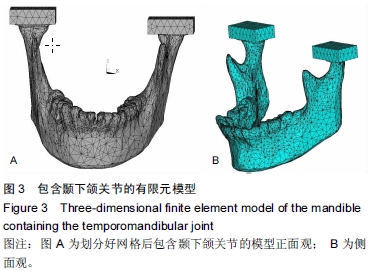
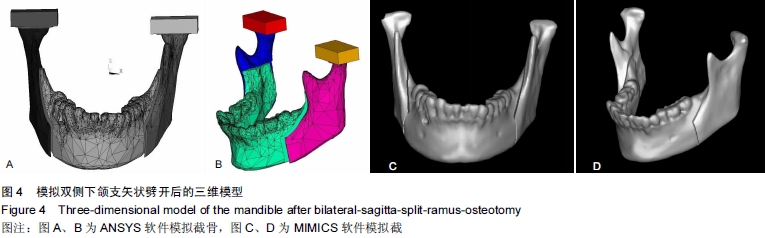
背景:双侧升支矢状劈开截骨已经成为矫正面部畸形的常规方法,运用有限元方法研究双侧下颌支矢状劈开内固定后颞下颌关节及下颌骨的生物力学是一种重要途径。 目的:建立精确、高仿真的双侧下颌支矢状劈开内固定后包含颞下颌关节的下颌骨模型,为研究双侧下颌支矢状劈开内固定后下颌骨及颞下颌关节生物力学提供基础。 方法:螺旋CT扫描后得到DICOM格式数据导入MIMICS软件建立下颌骨三维模型。将三维模型包裹成单一的封闭壳,在ANSYS中进行网格划分及转换,再将模型写入ANSYS软件进行颞下颌关节相应部分的重建并模拟双侧下颌支矢状劈开及术后固定。 结果与结论:运用MIMICS及ANSYS软件建立双侧下颌支矢状劈开内固定后的带有颞下颌关节及下颌骨的三维有限元模型。此模型和人体组织相比,具有生物相似性及几何相似性。双侧下颌支矢状劈开内固定后的模型,可以通过前移、后移、旋转移动远心端,再行各种方式的内固定。所建立的三维有限元模型可以根据实验目的不同,对各个部位施加载荷,用来研究双侧下颌支矢状劈开内固定后不同组织应力及位移的改变,也可以研究不同固定材料对固定后稳定性的影响。