• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
椎弓根螺钉置入修复胸腰椎骨折:影响椎体高度恢复的相关因素分析
桂忠山1,徐晓峰2
- 1解放军第359医院骨科,江苏大学临床医学院,江苏省镇江市 212001;2江苏大学附属江滨医院骨科,江苏省镇江市 212001
Pedicle screw fixation for treating thoracolumbar fracture: related factors influencing vertebral height restoration
Gui Zhong-shan1, Xu Xiao-feng2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the 359 Hospital of Chinese PLA, Clinical Medical College of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212001, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Jiangbin Hospital Affiliated to Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212001, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
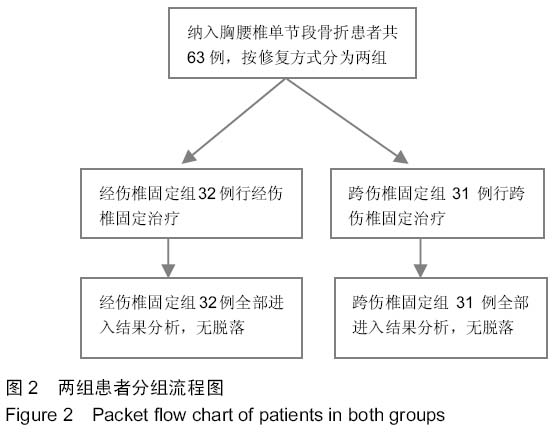
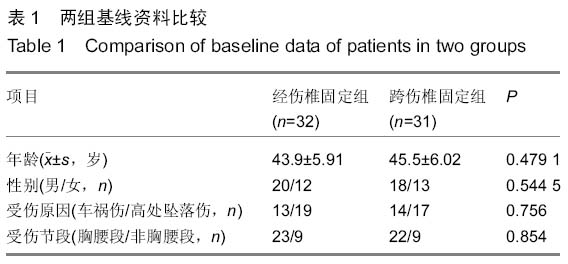
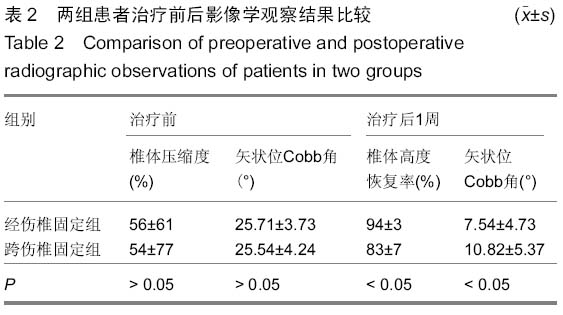
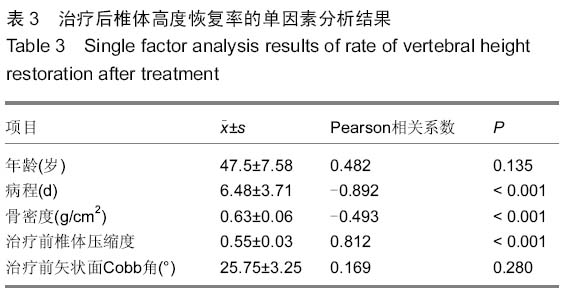
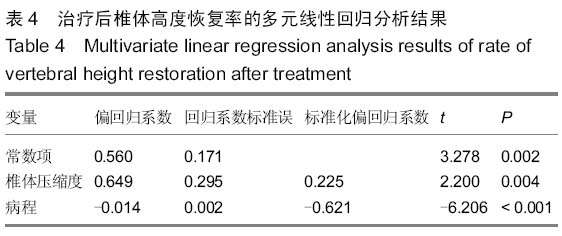
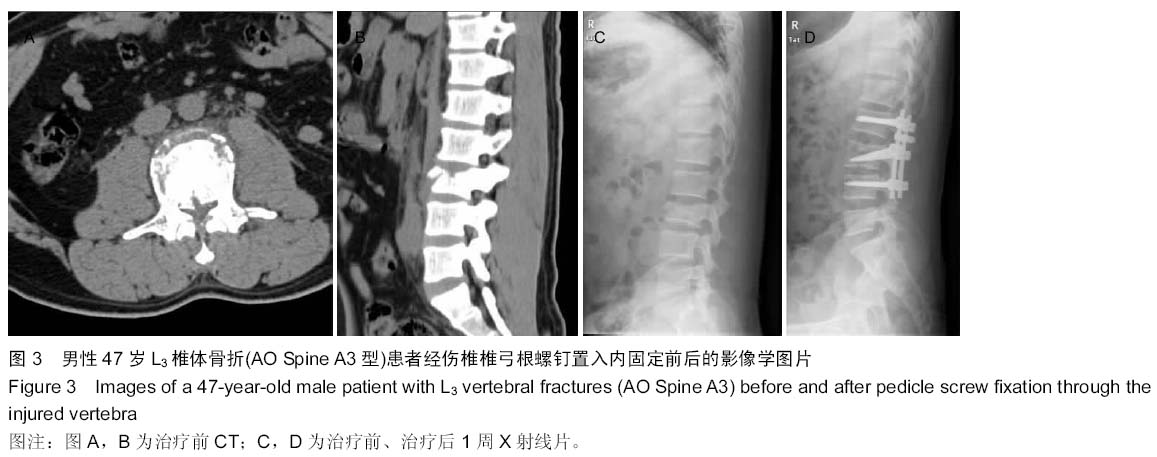
背景:应用椎弓根钉内固定系统修复胸腰椎骨折能有效地恢复椎体的高度及生理弧度,被广泛运用于临床。临床工作中发现不同修复方式对椎体高度恢复存在差异,同时患者在修复前的各种相关因素存在差异, 导致修复后椎体高度恢复的程度亦不一致。 目的:探讨应用椎弓根螺钉内固定系统修复胸腰椎骨折影响椎体高度恢复的相关因素。 方法:总结2012年9月至2015年3月应用后路复位椎弓根螺钉内固定系统修复胸腰椎骨折63例患者的临床资料,骨折类型均为AO Spine胸腰椎损伤分类系统中的A3、A4型,根据修复方式将患者分为两组,经伤椎固定组32例,跨伤椎固定组31例。分别记录两组患者的年龄、病程(3周以内)、骨密度、治疗前椎体压缩程度、治疗前矢状面Cobb角等指标,观察患者治疗后压缩椎体高度恢复情况,应用独立样本t检验行组间分析,组内应用双变量回归分析行单因素分析,应用多元线性回归分析行多因素分析,探讨影响椎体高度恢复的相关因素。 结果与结论:两组患者治疗前椎体压缩率及Cobb角比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),治疗后经伤椎固定组椎体高度恢复率明显大于跨伤椎固定组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。组内单因素分析结果显示患者的病程、治疗前椎体压缩程度、骨密度与治疗后椎体高度恢复情况有一定的相关性(P < 0.05),而患者的年龄、治疗前矢状面Cobb角与治疗后椎体高度恢复情况无相关性(P > 0.05)。多因素分析结果显示,患者治疗前椎体压缩程度、病程是影响治疗后椎体高度恢复情况的主要因素,其标准化偏回归系数分别为0.225,-0.621。提示经伤椎置钉椎弓根内固定较传统的跨伤椎固定能更有效的恢复压缩椎体的高度。患者治疗前椎体压缩程度、病程是影响椎体高度恢复的主要因素,观察这些指标有助于预测修复后椎体高度恢复情况。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
t1.jpg)