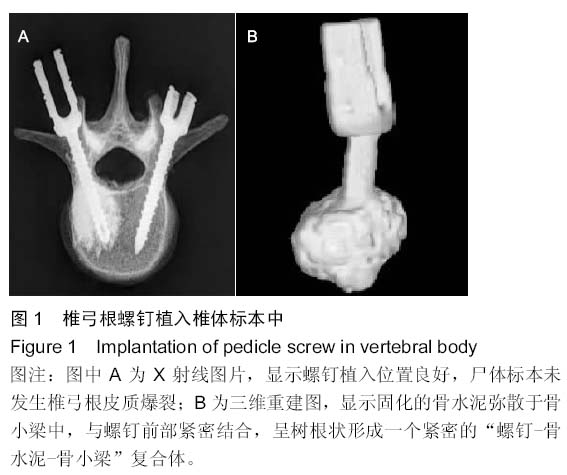
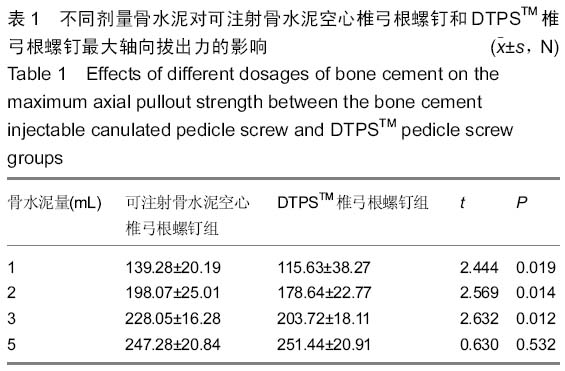
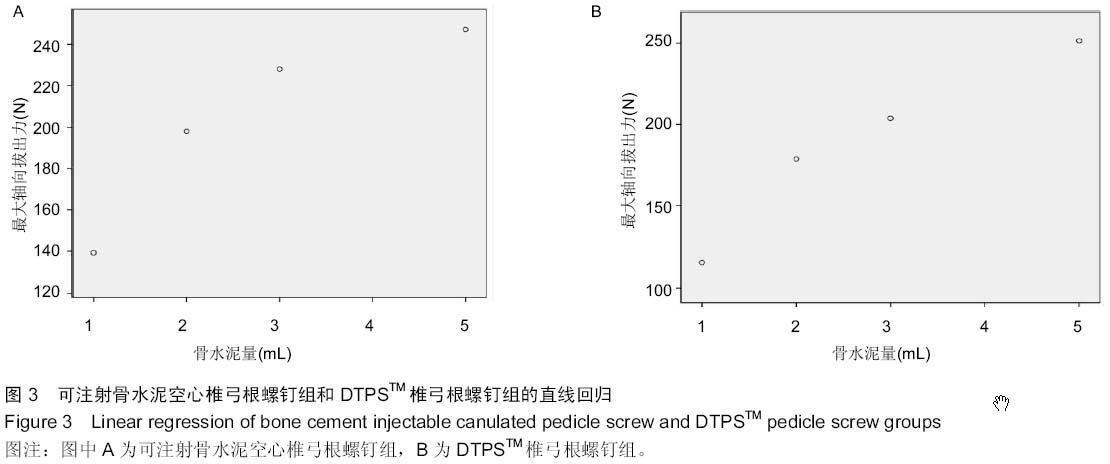
| [1] 李家谋,张昆亚,韩伟峰,等.短节段椎弓根螺钉置入内固定椎体成形治疗胸腰椎骨折的生物力学检测[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(39):7284-7287.
[2] 赵刘军,李杰,蒋伟宇,等.下颈椎前路椎弓根螺钉固定系统与普通前路椎体螺钉固定系统的静力学比较[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(2): 118-122.
[3] 印飞,孙振中,殷渠东,等.伤椎植骨植钉与跨节段椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014, (2):227-232.
[4] 岳文峰.不同方式骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定术的临床观察与预后分析[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013.
[5] 周子红,程立,殷渠东.增加椎弓根螺钉稳定性的方法与技术研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(26): 4872-4875.
[6] 朱如森,冯世庆,刘岩.脊柱内固定椎弓根螺钉置入后生物力学的稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(17):3156-3163.
[7] Moon BJ, Cho BY, Choi EY, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate- augmented screw fixation for stabilization of the osteoporotic spine: a three-year follow-up of 37 patients. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009;46(4):305-311.
[8] Wu ZX, Gao MX, Sang HX, et al. Surgical treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar compressive fractures with open vertebral cement augmentation of expandable pedicle screw fixation: a biomechanical study and a 2-year follow-up of 20 patients. J Surg Res. 2012;173(1):91-98.
[9] 刘达,潘显明,廖冬发,等.不同剂量聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥强化骨质疏松人工骨模块中椎弓根螺钉稳定性的研究[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013(14):6477-6480.
[10] 王志荣.新型可灌注骨水泥椎弓根螺钉的研制和生物力学研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2008.
[11] 王广积,林明侠,沈宁江,等.影响椎弓根螺钉拔出力的相关因素[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(35):6919-6922.
[12] 邵景范,MR.Sarkar,L.Kinzl,等.可吸收骨水泥对椎弓根螺钉稳定性的生物力学影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(9):64-67.
[13] 刘瑶瑶,代飞,孙东,等.不同量骨水泥强化新型空心椎弓根螺钉的体外生物力学研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2012,34(16): 1626-1629.
[14] 刘达,伍红桦,郑伟,等.骨质疏松尸体腰椎中膨胀式椎弓根螺钉与骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定稳定性的比较研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014(7):638-643.
[15] 殷建新,高坤.不同椎弓根螺钉螺纹设计及各种强化材料的拔出力比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(17): 3320-3323.
[16] 刘达,雷伟,吴子祥,等.生物材料强化椎弓根螺钉稳定性研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2009,30(3):148-151.
[17] 刘达,谢庆云,张波,等.重度骨质疏松腰椎中椎弓根螺钉稳定性与骨水泥注射剂量的相关性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(4): 355-360.
[18] 杨曦,孔清泉,宋跃明,等.计算机导航辅助椎弓根螺钉后路固定在骨质疏松患者中的临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012(2): 196-200.
[19] 刘达,雷伟,吴子祥,等.膨胀式椎弓根螺钉与骨水泥强化方法增强螺钉稳定性的比较研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(20): 1689-1692.
[20] 俞杭平,唐天驷,杨同其,等.生物活性玻璃涂层改善椎弓根螺钉稳定性的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2002,18(12):17-21.
[21] 刘达,张译,潘显明.PMMA强化骨质疏松条件下椎弓根螺钉稳定性的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(5):525-528.
[22] 王瑞,靳安民,童斌辉,等.胸腰椎短节段椎弓根螺钉内固定翻修的原因和预防[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2004,19(11):721-723.
[23] 晏雄伟,张洪燕.椎体后凸成形治疗骨质疏松性脊柱骨折:注入骨水泥的要点[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(9):1471-1476.
[24] 刘达,雷伟,吴子祥,等.硫酸钙骨水泥强化去势绵羊体内椎弓根螺钉稳定性的动态生物力学研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010, 16(3):166-169.
[25] 樊仕才,刘世学,邓月兴,等.强化骨质疏松椎弓根螺钉对脊柱稳定性影响的生物力学研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2004,18(3): 168-170.
[26] 董献成.胸椎椎弓根螺钉固定失败经椎弓根外入路补救的生物力学研究[D].扬州:扬州大学,2008.
[27] 樊仕才,江振华,朱青安,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯强化椎弓根螺钉内固定对骨质疏松不稳定性胸腰椎损伤稳定性的影响[J].中华创伤杂志,2003,19(6):37-40.
[28] 陈文瑶,李新志.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(3):226-229.
[29] 申勇,任虎,张英泽,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折骨水泥渗漏的相关因素分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010(1):27-31.
[30] 陈柏龄,谢登辉,黎艺强,等.单侧PKP骨水泥注射过中线分布对压缩性骨折椎体两侧刚度的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011, 21(2):118-121.
[31] 黄晓慧.骨骼有限元精确建模方法及骨水泥断裂和疲劳损伤研究[D].济南:山东大学,2012.
[32] 厉孟,刘旭东,刘兴炎,等.多孔明胶微球/磷酸钙骨水泥的制备及其性能研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(7):526-529.
[33] 杨述华,傅德皓,刘昌胜,等.磷酸钙骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉对骨质疏松性椎体骨折的临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003, 11(23): 31-33.
[34] 吉浩宇,霍洪军.骨水泥并椎弓根螺钉脊柱内固定的力学效应[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(1):36-40.
[35] 王宇,邑晓东,李淳德,等.可注射硫酸钙强化椎弓根螺钉内固定的实验研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009,19(1):64-68,82.
[36] Wichmann JL, Booz C, Wesarg S, et al. Quantitative dual-energy CT for phantomless evaluation of cancellous bone mineral density of the vertebral pedicle: correlation with pedicle screw pull-out strength. Eur Radiol. 2015;25(6): 1714-1720.
[37] Gerard CS, Fessler RG. Accurate pedicle screw placement--a perspective statement. World Neurosurg. 2015;83(5): 747-749.
[38] 李辉,任明亮,刘鹄,等.可注射骨水泥型椎弓根螺钉治疗脊柱退变性疾病的临床研究[J].当代医学,2014(6):37-38.
[39] 刘洋,申连成,任乾,等.可注射骨水泥椎弓根螺钉在老年性骨质疏松型胸腰椎压缩性骨折中的临床应用[J].亚太传统医药,2014, 10(9):71-73.
[40] 代飞,刘瑶瑶,孙东,等.新型可注射骨水泥椎弓根螺钉与骨水泥钉道强化在治疗腰椎滑脱伴骨质疏松中的比较研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2014(5):257-261.
[41] 高明暄,李旭升,任民,等.可注射磷酸钙骨水泥对不同骨质椎弓根螺钉的强化作用[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(12):1094-1097, 1109.
[42] 牛通.新型可灌注骨水泥椎弓根螺钉联合普通椎弓根螺钉撑开复位治疗胸腰椎椎体爆裂骨折[J].济宁医学院学报,2013(6): 415-416,419.
[43] 黎逢峰,张庆宏,黄野,等.磷酸钙骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定的生物力学特性[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(25):187-190.
[44] 杨述华,胡勇,陈中海,等.空心侧孔椎弓根螺钉添加聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥的生物力学研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2002,18(1): 16-21.
[45] 张海兵,金大地,瞿东滨.骨水泥在骨质疏松椎体中强化和翻修椎弓根螺钉的生物力学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2007,25(5): 587-589.
[46] 苏楠,费琦,王炳强,等.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉手术相关并发症及分析[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2015(12):1012-1016.
[47] 陈德玉,JMSpivak,FJKumme.骨水泥加固椎弓根螺钉固定的实验研究[J].第二军医大学学报,1997(6):72-74.
[48] Padányi Csaba, Misik F, Papp Z, et al. Treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with PMMA-augmented pedicle screw fixation. Ideggyogy Sz. 2015;68(1-2):52-58.
[49] Pfeiffer FM, Choma TJ, Kueny R. Finite element analysis of Stryker Xia pedicle screw in artificial bone samples with and without supplemental cement augmentation. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2015;18(13):1459-1467.
[50] Frankel BM, Jones T, Wang C. Segmental polymethylmethacrylate-augmented pedicle screw fixation in patients with bone softening caused by osteoporosis and metastatic tumor involvement: a clinical evaluation. Neurosurgery. 2007;61(3):531-537; discussion 537-538.
[51] 岳文峰,夏虹,王建华.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定对骨质疏松患者有利无弊?[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(17):3081-3088. |