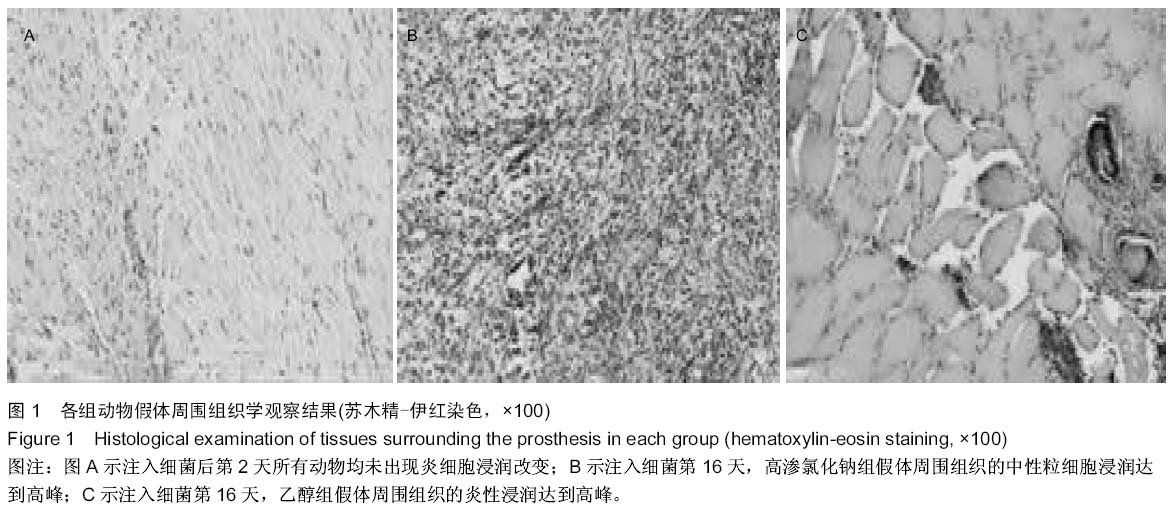
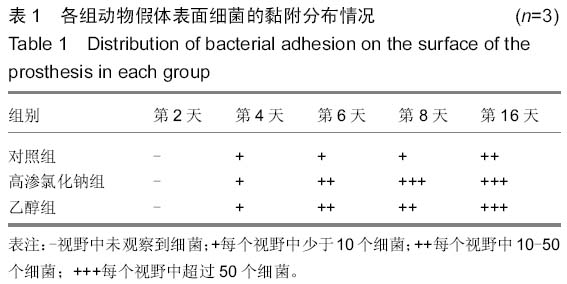
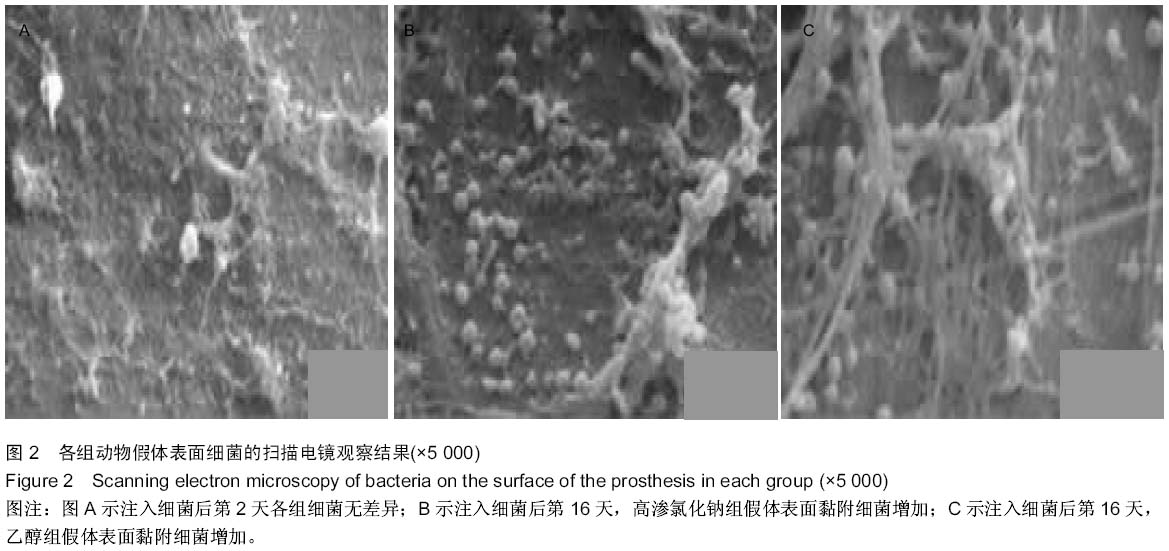
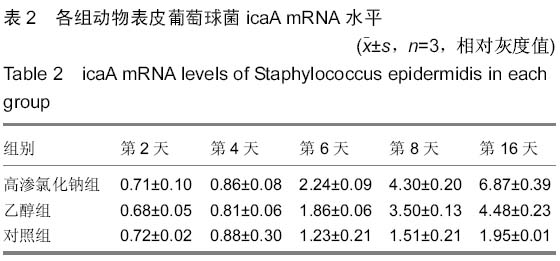
| [1] Trampuz A,Widmer AF.Infection associated with orthopedic implants,Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2006;19(4):349-354.
[2] Shahi A, Parvizi J. Prevention of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Arch Bone Jt Surg.2015;3(2):72-81.
[3] Bergin C,Speroni KG, Travis T,et al.Effect of preoperative incentive spirometry patient education on penitent outcomes in the knee and hip joint replacement population. J Perianesth Nurs. 2014;29(1):20-27.
[4] Deirmengian C, Kardos K, Kilmartin P, et al. Combined measurement of synovial fluidα-Defensin and C-reactive protein levels: highly accurate for diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96(17):1439- 1445.
[5] Vuong C,Otto M. Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. Microbes Infeet. 2002;4:481-489.
[6] Hartford O,O’Brien L,Sehofield K,et al. The Fbe(SdrG) protein oI Staphylococcus epidermidis HB promotes bacterial adherenee to fibrinogen. Microbiology. 2001;147: 2545-2552.
[7] 吴秋季,李强,张绍,等.手术室环境预防人工关节置换后感染的有效性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(39):2095-4344.
[8] Zhuang YF, Wei MY. Risk factors of incision in fections after artificial total knee arthroplasty and counter measures. Chin J Nosocomiol. 2013;23(14):3390-3391.
[9] Knobloch JK, Bartscht K, Sabottke A, et al. Biofilm formation by Staphylococcus epidermidis depends on functional RsbU, an activator of the sigB operon: differential activation mechanisms due to ethanol and salt stress. J Bacteriol. 2001; 183(8):2624-2633.
[10] Milisavljevic V, Tran LP, Batmalle C, et al. Benzyl alcohol and ethanol can enhance the pathogenic potential of clinical Staphylococcus epidermidis strains. Am J Infect Control. 2008;36(8):552-558.
[11] 王志酬,曹力,龚时国,等.兔膝关节置换术后感染模型的建立[J].中华实验外科杂志,2010,27(2):258-260
[12] Gallo J, Kolár M, Florschütz AV, et al. In vitro testing of gentamicin-vancomycin loaded bone cement to prevent prosthetic joint infection. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2005;149(1):153-158.
[13] Thalhamer T, McGrath M, Harnett M. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology. 2008; 47(4):409-414.
[14] Watanabe K, Minowa T, Takeda S, et al. Outcomes of knee arthrodesis following infected total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective analysis of 8 cases. Mod Rheumatol. 2014;24: 243-249.
[15] 毕衡.尺桡骨开放性骨折伤口感染的临床特征[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(1);89-90.
[16] Knobloch JK, Jager S, Homtkotte MA, et al. RsbU-dependentegulation of Staphylococcus epidermldis biofilm formation is mediated via the alternative sigma factor sigmaB by repression of the negative regulator gene icaR. Infect Immun. 2004;72(7):3838-3848.
[17] Christensen GD, Simpson WA, Bisno AL, et al. Adherence of slim-produceing Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth sufaces. Infect Immun. 1982;37(1):318-326.
[18] Del Pozo JL, Patel R. Clinical practice. Infection associated with prosthetic joints. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:787-794.
[19] Bémer P, Plouzeau C, Tande D, et al. Evaluation of 16S Rrna gene PCR sensitivity and specificity for diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection: a prospective multicenter cross-sectional study. J Clin Microbiol. 2014; 10:3583-3589.
[20] Christiane G, Angelika K. Characterization of the N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase activity involved in the biosynthesis of the Staphylococcus epidermidis polysaccharide intercellular adhesin. J Biol Chem. 1998; 279(29):18586-18593.
[21] 王子明,王爱民,唐桂阳.骨水泥型人工股骨头置换和术后感染模型的建立[J].中华实验外科杂志,2007,24(4):509.
[22] Conlon KM, Humphreys H, O'Gara JP. icaR encodes a transcriptional repressor involved in environmental regulation of ica operon expression and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Bacteriol. 2002;184(16): 4400-4408.
[23] Stewart PS, Costerton JW. Antibiotic resistance of bacteria in biofilms. Lancet. 2001;358:135-138
[24] Zmistowski B, Della Valle C, Bauer TW, et al. Diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(2 Suppl): 77-83.
[25] Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010; 233(1):233-255.
[26] Broekhuizen CA, de Boer L, Schipper K, et al. Peri-implant tissue is an important niche for Staphylococcus epidermidis in experimental biomaterial-associated infection in mice. Infect Immue. 2007;75(3):1129-1136.
[27] Mack D, Davies AP, Harris LG, et al. Microbial interactions in Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;387(2):399-408.
[28] Peel TN, Dowsey MM, Buising KL, et al. Cost analysis of debridement and retention for management of prosthetic joint infection. Clin Microbiol Infect.2013;19: 181-186.
[29] Milisavljevic V, Tran LP, Batmalle C, et al. Benzyl alcohol and ethanol can enhance the pathogenic potential of clinical Staphylococcus epidermidis strains American journal of infection control. Am J Infect Control. 2008;36(8):552-558.
[30] Yang ZG, Chen WP, Wu LD. Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in total knee arthroplasty :a meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(13):1153-1159.
[31] Greenwood-Quaintance KE, Uhl JR, Hanssen AD, et al. Diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection by use of PCR-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52:642-649.
[32] Ghanem E, Parvizi J, Burnett RS, et al. Cell count and differential of aspirated fluid in the diagnosis of infection at the site of total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90:1637-1643. |