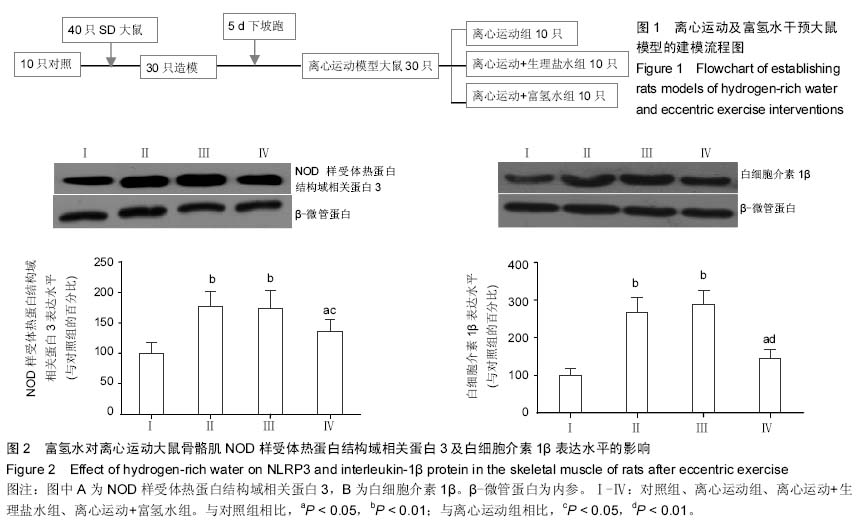
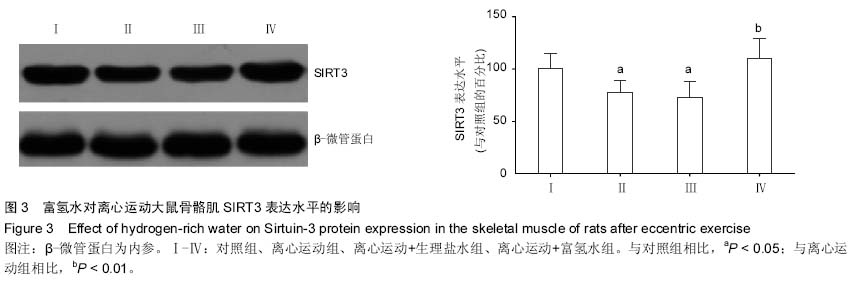
| [1] 刘向东,李阳.一次力竭性离心运动损伤模型大鼠骨骼肌波形蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(18):2880-2885.
[2] Rattray B, Thompson M, Ruell P, et al. Specific training improves skeletal muscle mitochondrial calcium homeostasis after eccentric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(2):427-436.
[3] Kullman EL, Campbell WW, Krishnan RK, et al. Age attenuates leucine oxidation after eccentric exercise. Int J Sports Med. 2013;34(8):695-699.
[4] McCarty MF. Potential ghrelin-mediated benefits and risks of hydrogen water. Med Hypotheses. 2015;84(4):350-355.
[5] Ostojic SM, Stojanovic MD. Hydrogen-rich water affected blood alkalinity in physically active men. Res Sports Med. 2014;22(1):49-60.
[6] Wang T, Zhao L, Liu M, et al. Oral intake of hydrogen-rich water ameliorated chlorpyrifos-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014;280(1):169-176.
[7] Su N, Wu Q, Liu Y, et al. Hydrogen-rich water reestablishes ROS homeostasis but exerts differential effects on anthocyanin synthesis in two varieties of radish sprouts under UV-A irradiation. J Agric Food Chem. 2014;62(27):6454-6462.
[8] Zhang JY, Song SD1, Pang Q, et al. Hydrogen-rich water protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(14):4195-4209.
[9] 孙延卿,陈雄生,曹东,等.氢盐水可抑制脊髓缺血再灌注损伤兔模型运动神经元的凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(18): 2861-2866.
[10] Chen M, Cui W, Zhu K, et al. Hydrogen-rich water alleviates aluminum-induced inhibition of root elongation in alfalfa via decreasing nitric oxide production. J Hazard Mater. 2014; 267:40-47.
[11] Tomofuji T, Kawabata Y, Kasuyama K, et al. Effects of hydrogen-rich water on aging periodontal tissues in rats. Sci Rep. 2014;4:5534.
[12] Jing L, Wang Y, Zhao XM, et al. Cardioprotective Effect of Hydrogen-rich Saline on Isoproterenol-induced Myocardial Infarction in Rats. Heart Lung Circ. 2015;24(6):602-610.
[13] Zhang JY, Wu QF, Wan Y, et al. Protective role of hydrogen-rich water on aspirin-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(6):1614-1622.
[14] Aoki K, Nakao A, Adachi T, et al. Pilot study: Effects of drinking hydrogen-rich water on muscle fatigue caused by acute exercise in elite athletes. Med Gas Res. 2012;2:12.
[15] Gac M, Bigda J, Vahlenkamp TW. Increased mitochondrial superoxide dismutase expression and lowered production of reactive oxygen species during rotavirus infection. Virology. 2010;404(2):293-303.
[16] Borodkina A, Shatrova A, Abushik P, et al. Interaction between ROS dependent DNA damage, mitochondria and p38 MAPK underlies senescence of human adult stem cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2014;6(6):481-495.
[17] 侯伊玲,薄海,刘子泉,等.缺血预处理抑制大鼠胰腺移植缺血再灌注胰腺细胞凋亡:活性氧与线粒体DNA修复酶的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(18):3279-3285.
[18] Nikolaidis MG, Kyparos A, Spanou C, et al. Aging is not a barrier to muscle and redox adaptations: applying the repeated eccentric exercise model. Exp Gerontol. 2013; 48(8):734-743.
[19] Nagi SS, Mahns DA. C-tactile fibers contribute to cutaneous allodynia after eccentric exercise. J Pain. 2013;14(5):538-548.
[20] Isner-Horobeti ME, Dufour SP, Vautravers P, et al. Eccentric exercise training: modalities, applications and perspectives. Sports Med. 2013;43(6):483-512.
[21] Chen TC, Chen HL, Lin MJ, et al. Effect of two maximal isometric contractions on eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage of the elbow flexors. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013; 113(6):1545-1554.
[22] Magalhães J, Fraga M, Lumini-Oliveira J, et al. Eccentric exercise transiently affects mice skeletal muscle mitochondrial function. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2013;38(4):401-409.
[23] Rattray B, Caillaud C, Ruell PA, et al. Heat exposure does not alter eccentric exercise-induced increases in mitochondrial calcium and respiratory dysfunction. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111(11):2813-2821.
[24] Liu Q, Simpson DC, Gronert S. Carbonylation of mitochondrial aconitase with 4-hydroxy-2-(E)-nonenal: localization and relative reactivity of addition sites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1834(6):1144-1154.
[25] Tsui KH, Chung LC, Wang SW, et al. Hypoxia upregulates the gene expression of mitochondrial aconitase in prostate carcinoma cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 2013;51(1):131-141.
[26] Gaziev AI, Abdullaev S, Podlutsky A. Mitochondrial function and mitochondrial DNA maintenance with advancing age. Biogerontology. 2014;15(5):417-438.
[27] Uebermuth C. Mitochondrial DNA plays an important role. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2014;111(20):366.
[28] Muftuoglu M, Mori MP, de Souza-Pinto NC. Formation and repair of oxidative damage in the mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondrion. 2014:164-181.
[29] Karbownik-Lewińska M, St?pniak J, Lewiński A. High level of oxidized nucleosides in thyroid mitochondrial DNA; damaging effects of Fenton reaction substrates. Thyroid Res. 2012;5(1):24.
[30] Dwivedi S, Saquib Q, Al-Khedhairy AA, et al. Butachlor induced dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential, oxidative DNA damage and necrosis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Toxicology. 2012;302(1):77-87.
[31] Alfonso-Loeches S, Ureña-Peralta JR, Morillo-Bargues MJ, et al. Role of mitochondria ROS generation in ethanol-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death in astroglial cells. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:216.
[32] Oka T, Hikoso S, Yamaguchi O, et al. Mitochondrial DNA that escapes from autophagy causes inflammation and heart failure. Nature. 2012;485(7397):251-255.
[33] Lawlor KE, Vince JE. Ambiguities in NLRP3 inflammasome regulation: is there a role for mitochondria? Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(4):1433-1440.
[34] Wu J, Yan Z, Schwartz DE, et al. Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in alveolar macrophages contributes to mechanical stretch-induced lung inflammation and injury. J Immunol. 2013;190(7):3590-3599.
[35] Mao K, Chen S, Chen M, et al. Nitric oxide suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation and protects against LPS-induced septic shock. Cell Res. 2013;23(2):201-212.
[36] Connelly SJ, Wiedner ES, Appel AM. Predicting the reactivity of hydride donors in water: thermodynamic constants for hydrogen. Dalton Trans. 2015;44(13):5933-5938.
[37] Noda K, Tanaka Y, Shigemura N, et al. Hydrogen-supplemented drinking water protects cardiac allografts from inflammation-associated deterioration. Transpl Int. 2012;25(12):1213-1222.
[38] Cui Y, Zhang H, Ji M, et al. Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates neuronal ischemia--reperfusion injury by protecting mitochondrial function in rats. J Surg Res. 2014;192(2):564-572.
[39] Zhou L, Wang X, Xue W, et al. Beneficial effects of hydrogen-rich saline against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rabbits. Brain Res. 2013;1517:150-160.
[40] Hou Z, Luo W, Sun X, et al. Hydrogen-rich saline protects against oxidative damage and cognitive deficits after mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Res Bull. 2012;88(6):560-565.
[41] 肖频,庞奕辉,彭朋,等.α-硫辛酸抑制慢性低氧大鼠骨骼肌线粒体的氧化应激[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(28):5216-5222.
[42] Lin L, Chen K, Abdel Khalek W, et al. Regulation of skeletal muscle oxidative capacity and muscle mass by SIRT3. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e85636.
[43] Ahn BH, Kim HS, Song S, et al. A role for the mitochondrial deacetylase Sirt3 in regulating energy homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(38):14447-14452.
[44] Sack MN. The role of SIRT3 in mitochondrial homeostasis and cardiac adaptation to hypertrophy and aging. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;52(3):520-525.
[45] 张国华.运动诱导骨骼肌线粒体生成中沉默信息调节因子1的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(33):6041-6048.
[46] Kong X, Wang R, Xue Y, et al. Sirtuin 3, a new target of PGC-1alpha, plays an important role in the suppression of ROS and mitochondrial biogenesis. PLoS One. 2010;5(7):e11707.
[47] Qiu X, Brown K, Hirschey MD, et al. Calorie restriction reduces oxidative stress by SIRT3-mediated SOD2 activation. Cell Metab. 2010;12(6):662-667.
[48] Cheng Y, Ren X, Gowda AS, et al. Interaction of Sirt3 with OGG1 contributes to repair of mitochondrial DNA and protects from apoptotic cell death under oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e731.
[49] Kim SJ, Cheresh P, Williams D, et al. Mitochondria-targeted Ogg1 and aconitase-2 prevent oxidant-induced mitochondrial DNA damage in alveolar epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289(9):6165-6176.
[50] Ren JD, Ma J, Hou J, et al. Hydrogen-rich saline inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and attenuates experimental acute pancreatitis in mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014: 930894. |