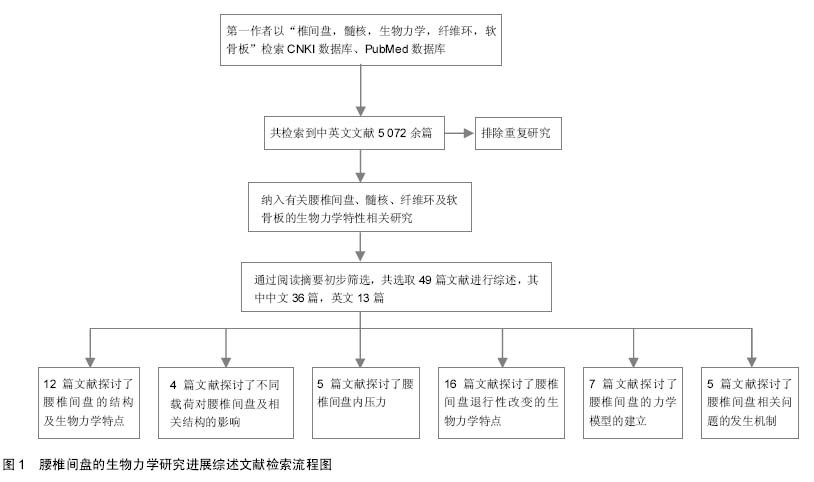
| [1] 周士枋,丁伯坦.运动学[M].北京:华夏出版社,2004:42.
[2] 任龙韬,卫陈刚,牛建鹏,等.正常与退变髓核细胞的变形能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(48):9030-9033.
[3] 范少勇,黄科棣,黄志荣,等.水凝胶替代摘除猪腰椎间盘髓核的生物力学分析[J]. 中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2012,4(3):198-202.
[4] 许海委,徐宝山,杨强,等. 不同脱细胞方法对猪尾纤维环生物力学特性及组织结构的影响[J]. 医用生物力学,2013,28(4): 448-453.
[5] 王宇,彭雄奇.人体椎间盘纤维环各向异性超弹性材料本构模型的数值验证[J]. 西北工业大学学报,2010,28(4):536-540.
[6] 董兴成. 组织工程椎间盘纤维环支架构建的实验研究[D]. 第二军医大学,2013.
[7] 胡声宇.运动解剖学[M].北京:人民体育出版社, 2000,84.
[8] Kozak JA,Heilman AE,O Brien JP. Anterior lumbar fusion options: Technique and graft materials. Clin Orthop. 1994; 3000 :45-51.
[9] Broberg KB. On the mechanical behaviour of the intervertebral disc. Spine. 1983;8:151-165.
[10] Natarajan RN, Ke JH, Andersson GB. A model to study the disc degeneration process. Spine. 1994; 19:259-265.
[11] 侯洋.腰椎终板生物力学特性及其与骨密度关系的实验研究[D].第四军医大学,2010.
[12] 肖学军. Tekscan系统测量腰椎软骨终板压力及后路固定对腰椎刚度的影响[D].南方医科大学,2011.
[13] 卢廷胜,王以进,尹海磊,等. 半椎板成形术对腰椎抗压强度的影响[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(23):2389-2391.
[14] 李建军,张远石,王溪源,等. C5-6、T12-L1、L4-5椎间盘与相邻椎体的压缩力学特性[J].生物医学工程研究,2010,29(3): 193-196.
[15] 孙培栋. L3/4不同运动范围对邻近运动节段的生物力学影响[D].南方医科大学,2009.
[16] 刘强. 循环载荷条件下模拟腰椎扳法对椎间盘内压的影响[D].中国中医科学院,2013.
[17] 鲍春雨,刘晋浩.人体脊柱腰椎节段三维有限元模型的研究与分析[J]. 机械设计,2009,26(9):61-63.
[18] 吕立江,包家立,范炳华,等. 杠杆定位手法作用下正常腰椎间盘的应力-应变特性初探[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报,2013,37(10): 1156-1159.
[19] 张兰凤,董黎敏,王永清,等.负重及非负重下腰椎间盘的位移测量及意义[J].天津理工大学学报,2013,29(6):50-54.
[20] 高巍巍,李殿宁,宋逸先,等.人体新鲜脊柱椎间盘样本拉伸蠕变的实验研究[J].中医药导报,2011,17(1):25-26+29.
[21] 姚女兆,王文军,金大地. 新型人工髓核置换对邻近上节段三维运动与椎间盘内压影响的实验研究[J]. 医用生物力学, 2011, 26(1):81-86.
[22] 夏冬冬,林胜磊,赵浩增,等. 建立剪切应力导致椎间盘退变模型[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(5):490-495.
[23] 邓超,蔡显义,孙永青,等. 压力影响干细胞向兔椎间盘内迁移的初步研究[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2013,21(12):4-7.
[24] 孙旗. 静水压下川芎嗪对兔椎体终板软骨细胞相关基因表达的影响[D].北京中医药大学,2014.
[25] 陈江. 静水压下芹菜素对人椎间盘髓核细胞凋亡及基质代谢的影响[D].北京中医药大学,2011.
[26] Handa T,Ishihara H,Ohshima H,et al. Effects of hydrostatic pressure on matrix synthesis and matrix metalloproteinase production in the human lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine. 1997; 22: 1085-1091.
[27] Ishihara H,McNally DS,Urban JP, et al. Effect of hydrostatic pressure on matrix synthesis in different regions of the intervertebral disk. Appl Physiol. 1996; 80: 839-846.
[28] Sauerland K,Raiss RX,Steinmeyer J. Proteoglycan metabolism and viability of articular cartilage explants as modulated by the frequency of intermittent loading osteoarthritis cartilage. Osteoarthritis Catilage. 2003;11: 343-350.
[29] Lotz JC,Collons OK,Chin JR,et al.Compression-induced degeneration of the intervertebral disc: An invivo mouse model and finite-element study. Spine. 1998; 23: 2493 -2506.
[30] Lotz JC,Chin JR. Interverebral disc cell death is dependent on the magnitude and duration of spinal loading.Spine. 2000; 12: 1477-1483.
[31] Hutton WC, Toribatake Y, Elmer WA, et al. The effect of compressive force applied to the intervertebral disc invivo. A study of proteoglycans and collagen. Spine. 1998; 23: 2524-2537.
[32] Rannou F, Lee TS, Zhou RH,et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration: the role of the mitochondrial pathway in annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis induced by overload. Am J Pathol. 2004; 164: 915-924.
[33] Ruberté LM, Natarajan RN, Andersson GB. Influence of single- level lumbar degenerative disc disease on the behavior of the adjacent segments-a finite element model study. J Biomech. 2009; 42(3):341-348.
[34] 邢泽军.腰椎减压对不同程度退变椎间盘应力分布影响的有限元分析[D].中国协和医科大学,2010.
[35] 黄菊英,李海云,吴浩. 腰椎间盘突出症力学特征的仿真计算方法[J]. 医用生物力学,2012,27(1):96-101.
[36] 黄菊英,李海云,菅凤增,等.腰椎间盘突出症有限元模型的建立与分析[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志,2012,12(4):394-398.
[37] 闫家智,吴志宏,汪学松,等.腰椎间盘退变后应力变化的有限元分析[J]. 中国医学科学院学报,2009,31(4):464-467.
[38] 杨学锋,李具宝,李延红,等.模拟按压手法腰椎运动节段三维有限元模型分析[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2009,17(10):18-19.
[39] 李成山,张晓刚.模拟拔伸按压手法对腰部结构生物力学变化的影响[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2013,21(3):15-17.
[40] 秦明芳,柴晟,黄立新,等.不同工况对腰椎运动节段作用的三维有限元模型分析[J].广西医科大学学报.2010,27(3):417-419.
[41] 卫陈刚. 正常和退变髓核细胞粘弹性的测量[D].山西医科大学, 2011.
[42] 葛磊,李康华,胡建中,等.腰椎间盘摘除和假体置换对相邻近端节段椎间载荷的影响[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2009,34(3): 230-235.
[43] Chagnon A, Aubin CE, Villemure I. Biomechanical influence of disk properties on the load transfer of healthy and degenerated disks using a poroelastic finite element model. J Biomech Eng. 2010;132(11):111006.
[44] Noailly J, Planell JA, Lacroix D. On the collagen criss-cross angles in the annuli fibrosi of lumbar spine finite element models. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2011;10(2):203-219.
[45] 段红光.腰椎间盘突出症的发病机制和诊断[J].中国全科医学, 2012,15(36):4227-4230.
[46] 段吉芳.腰椎间盘突出症病人的康复保健与健康教育[J].内蒙古中医药,2012,31(2):124-125.
[47] 彭宝淦,吴闻文,侯树勋,等.椎间盘源性下腰痛的发病机制[J].中华外科杂志,2004,42(12):19-23.
[48] 石善龙.腰椎间盘突出合并侧隐窝狭窄症的发病机制及诊治探讨[D].成都中医药大学,2006.
[49] 金晓娜,张党锋.腰椎间盘突出症的发病机制及健康教育[J].医学理论与实践,2011,24(10):1152-1154. |