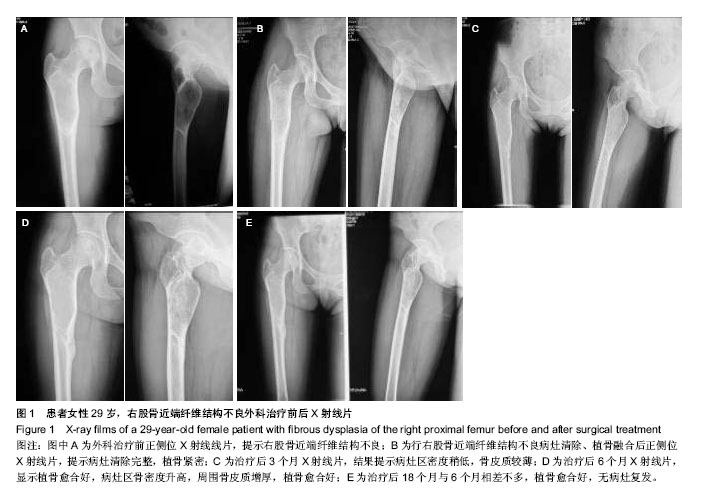
| [1] Bieniasz J, Maj A, Noczynska A. Fibrous dysplasia of bone in a 12 year old girl. Endokrynol Diabetol Chor Przemiany Materii Wieku Rozw.2006;12(1):69.
[2] Chow LT, Griffith J, Chow WH, et al.Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the spine: report of a case involving the lumbar transverse process and review of the literature.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2000; 120(7-8):460-464.648-658.
[3] Campanacci M. Bone and soft tissue tumors: clinical features,imaging, pathology and treatment, 2nd edn. New York.Springer.1999.
[4] Parekh SG, Donthineni-Rao R, Ricchetti E,et al.Fibrous dysplasia.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2004,12(5):305-313.
[5] Parisi MS, Oliveri B, Mautalen CA. Efect of intravenous pamidronate on bone markers and local bone mineral density in fibrous dysplasia. Bone.2003;33:582-588.
[6] Isaia GC, Lala R, Defilippi C, et al. Bone turnoverin children and adolescents with McCune-Albright syndrome treated with pamidronate for bone fibrous dysplasia. Calcif Tissue Int. 2002;71:121-128.
[7] Chapurlat RD.Medical therapy in adults with fibrousdysplasia of bone. J Bone Miner Res.2006;21,21:114-119.
[8] Riminucci M, Fisher LW, Shenker A,et al. Fibrous dysplasia of bone in the McCune-Albright syndrome: abnormalities in bone formation.Am J Pathol.1997;151(6):1587-1600.
[9] Bianco P, Kuznetsov SA, Riminucci M, et al. Reproduction of human fibrous dysplasia of bone in immunocompromised mice by transplanted mosaics of normal and Gsalpha- mutated skeletal progenitor cells. Clin Invest. 1998;101: 1737-1744.
[10] Candeliere GA, Glorieux FH, Prud’ homme J, et al. Increased expression of the c-fos protooncogene in bone from patients with fibrous dysplasia. N Engl J Med.1995;332:1546-1551.
[11] 李恩超.BMP-2、IL-6在骨的纤维结构不良中的表达及临床意义[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2005,4(3):162-166
[12] Jung ST, Chung JY, Seo HY,et al.Multiple osteotomies and intramedullary nailing with neck cross-pinning for Shepherd’s crook deformity in polyostotic fibrous dysplasia:7 femurs with a minimum of 2 years follow-up.Acta Orthop. 2006;77(3): 469-473.
[13] Dunstan E, Tilley S, Briggs TW, et al. A customised replacement for polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of the upper femur. A 51-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg (Br).2005;87(1): 114-115.
[14] Chen WJ, Chen WM, Chiang CC, et al. Shepherd’s crook deformity of polyostotic fibrous dysplasia treated with corrective osteotomy and dynamic hip screw. J Chin Med Assoc.2005;68(7):343-346.
[15] Watanabe K, Tsuchiya H, Sakurakichi K, et al. Double-level correction with the Taylor Spatial Frame for shepherd’s crook deformity in fibrous dysplasia. J Orthop Sci.2007;12(4): 390-394
[16] 牛艳辉,王臻.98例四肢骨纤维结构不良临床分析[J.中国矫形外科杂志,1998,5(4):329.
[17] 郭卫. 纤维异样增殖症//徐万鹏,冯传汉.骨科肿瘤学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2001:331-332.
[18] Arpornchayanon O, Leerapun T. Effectiveness of intravenous bisphosphonates in treatment of giant cell tumour: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Assoc Thai.2008; 91:1609-1612.
[19] Plotkin H,Ranch F,Zeitlin L, et al. Effect of pamidronate treatment in children with polyostotie fibrous dysplasia of bone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2003;88(10):4569-4575.
[20] Collins MT, Chebli C, Jones J, et al. Renal phosphate wasting in fibrous dysplasia of bone is part of a generalized renal tubular dysfunction similar to that seen in tumor induced osteomalacia. J Bone Miner Res.2001;16(5):806-813.
[21] Khadikar VV, Khadikar AV, Maskati GB. Oral bispho-sphonmes in polyostotic fibrous dysplasia.Indian Pediatr.2004;41(9):1069-1070.
[22] 胥少汀,朱兵.骨的纤维结构不良的临床特点和处理(附38例分析)[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病杂志,2004,3(6):325-329. |