中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (11): 1668-1672.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.11.006
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
低强度脉冲超声波联合骨形态发生蛋白2促进人牙周膜细胞的成骨分化
刘 俊1,胡 波1,蒋欣益2,孙吉成1,邓 锋1,宋锦璘1
- 1重庆医科大学附属口腔医院,口腔疾病与生物医学重庆市重点实验室,重庆市 401147;2绵阳市中心医院口腔科,四川省绵阳市 621000
Osteogenic effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound combined with bone morphogenetic protein 2 on human periodontal ligament cells
Liu Jun1, Hu Bo1, Jiang Xin-yi2, Sun Ji-cheng1, Deng Feng1, Song Jin-lin1
- 1The Affiliated Hospital of Stomatology, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing Research Center for Oral Diseases and Biomedical Science, Chongqing 401147, China; 2Department of Stomatology, the Center Hospital of Mianyang, Mianyang 62100, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
背景:低强度脉冲超声波和骨形态发生蛋白2均可促进人牙周膜细胞成骨分化,但两者联合应用尚未见报道。
目的:验证低强度脉冲超声波和骨形态发生蛋白2联合应用诱导牙周膜细胞成骨分化的生物学效应。
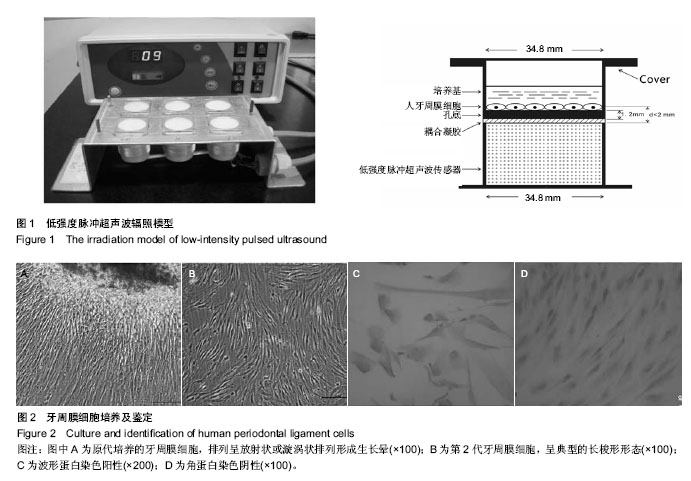
方法:体外分离、原代、传代培养与鉴定牙周膜细胞。取生长良好的第4代牙周膜细胞接种至六孔板中,实验分为4组:对照组、低强度脉冲超声波诱导组、骨形态发生蛋白2诱导组、低强度脉冲超声波联合骨形态发生蛋白2诱导组。采用碱性磷酸酶检测试剂盒检测细胞碱性磷酸酶活性,RT-PCR检测牙周膜细胞成骨相关基因Ⅰ型胶原、骨桥蛋白的表达。
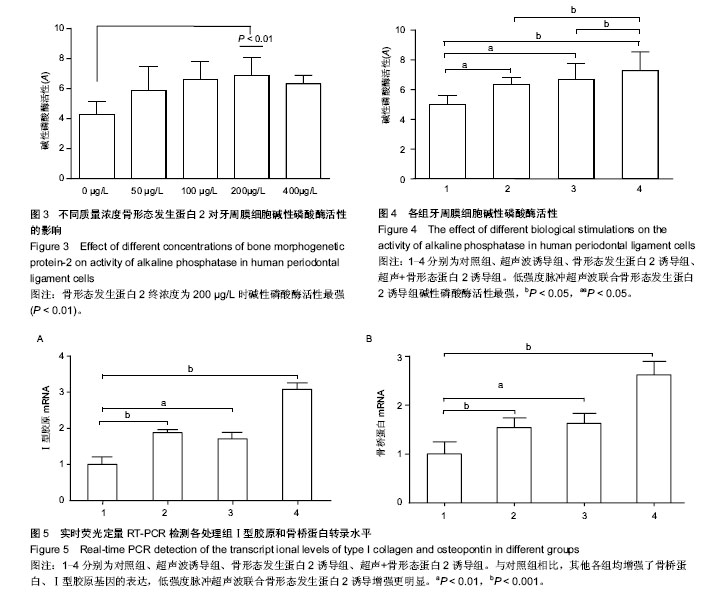
结果与结论:通过低强度脉冲超声波、骨形态发生蛋白2和低强度脉冲超声波+骨形态发生蛋白2诱导后,体外培养的牙周膜细胞碱性磷酸酶活性均显著高于对照组(P < 0.05),其中低强度脉冲超声波+骨形态发生蛋白2组碱性磷酸酶活性最强(P < 0.05)。RT-PCR结果分析显示,低强度脉冲超声波与骨形态发生蛋白2都可以上调Ⅰ型胶原、骨桥蛋白基因的表达(P < 0.01),两者联合处理作用更为明显(P < 0.001)。结果初步提示,低强度脉冲超声波和骨形态发生蛋白2均可以增强牙周膜细胞成骨能力,两者联合应用其成骨诱导能力更强。
中图分类号:
.jpg)