中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (8): 1160-1164.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.08.003
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/半水硫酸钙为可注射骨组织工程支架材料的可行性
薛 震1,牛丽媛2,安 刚3,郭亚山3,吕松岑1
- 哈尔滨医科大学附属第二医院,1骨科四病房,3急诊创伤病房,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150086;2哈尔滨工业大学校医院,黑龙江省哈尔滨市 150086
Feasibility of nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan/calcium sulphate hemihydrate as an injectable bone tissue engineering scaffold
Xue Zhen1, Niu Li-yuan2, An Gang3, Guo Ya-shan3, Lv Song-cen1
- 1The Fourth Ward, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150086, Heilongjiang Province, China; 3Department of Emergency Trauma, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, Heilongjiang Province, China
摘要:
背景:前期实验采用仿生学原理制备了可注射性纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/半水硫酸钙复合材料,但其与骨髓间充质干细胞的生物相容性还不十分清楚。
目的:探讨纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/半水硫酸钙作为注射型骨组织工程支架材料的可行性。
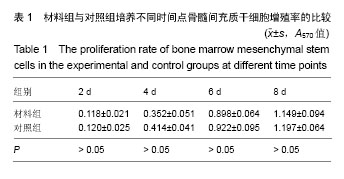
方法:将第3代兔骨髓间充质干细胞与可注射纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/半水硫酸钙支架复合培养,作为实验组;以单纯接种培养的骨髓间充质干细胞为对照组,倒置显微镜下观察细胞生长情况,MTT法检测细胞增殖,扫描电镜观察细胞在材料表面生长与增殖。将纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/半水硫酸钙支架埋植在家兔背部肌袋内,埋植后2,4,6,8周进行病理学观察。
结果与结论:实验组细胞生长、增殖良好,与对照组无明显差异。支架埋植后2周,材料周围有中等量中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞和巨细胞浸润,可见小血管与纤维母细胞增生,材料已被炎性细胞分割、围绕散碎;埋植后4周,可见少量淋巴细胞、纤维母细胞聚集,炎症反应进一步消退,肌纤维排列、形态正常;埋植后6周,材料周围炎症反应轻微,组织水肿不明显;埋植后8周,炎症反应基本消退,材料基本降解完成,肌纤维形态基本正常。表明纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/半水硫酸钙复合物具有良好的细胞相容性和生物降解性,可作为注射型支架材料。
中图分类号: