| [1] Arthur A, Zannettino A, Panagopoulos R,et al.EphB/ephrin-B interactions mediate human MSC attachment, migration and osteochondral differentiation.Bone. 2011;48(3):533-542.
[2] Bian L, Zhai DY, Tous E,et al.Enhanced MSC chondrogenesis following delivery of TGF-β3 from alginate microspheres within hyaluronic acid hydrogels in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 2011;32(27):6425-6434.
[3] Du Z, Wang L, Zhao Y,et al.Sympathetic denervation-induced MSC mobilization in distraction osteogenesis associates with inhibition of MSC migration and osteogenesis by norepinephrine/adrb3.PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105976.
[4] Jamnig A, Lepperdinger G.From tendon to nerve: an MSC for all seasons.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;90(3):295-306.
[5] Lv F, Lu M, Cheung KM,et al.Intrinsic properties of mesemchymal stem cells from human bone marrow, umbilical cord and umbilical cord blood comparing the different sources of MSC.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2012;7(6):389-399.
[6] Bessout R, Sémont A, Demarquay C,et al.Mesenchymal stem cell therapy induces glucocorticoid synthesis in colonic mucosa and suppresses radiation-activated T cells: new insights into MSC immunomodulation.Mucosal Immunol. 2014; 7(3):656-669.
[7] Prata Kde L, Orellana MD, De Santis GC,et al.Effects of high-dose chemotherapy on bone marrow multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells isolated from lymphoma patients. Exp Hematol. 2010;38(4):292-300.
[8] Stute N, Fehse B, Schröder J,et al.Human mesenchymal stem cells are not of donor origin in patients with severe aplastic anemia who underwent sex-mismatched allogeneic bone marrow transplant.J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2002; 11(6):977-984.
[9] Cilloni D, Carlo-Stella C, Falzetti F,et al.Limited engraftment capacity of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells following T-cell-depleted hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Blood. 2000;96(10):3637-3643.
[10] Wu KH, Wu HP, Chan CK,et al.The role of mesenchymal stem cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: from bench to bedsides.Cell Transplant. 2013;22(4):723-729.
[11] Epstein RB, Sarpel SC.Autologous bone marrow infusion following high dose chemotherapy of the canine transmissible venereal tumor (TVT).Exp Hematol. 1980;8(6):683-689.
[12] Majumdar MK, Thiede MA, Haynesworth SE,et al.Human marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) express hematopoietic cytokines and support long-term hematopoiesis when differentiated toward stromal and osteogenic lineages.J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2000; 9(6):841-848.
[13] Carrancio S, Romo C, Ramos T,et al.Effects of MSC coadministration and route of delivery on cord blood hematopoietic stem cell engraftment.Cell Transplant. 2013; 22(7):1171-1183.
[14] Zhang C, Zhang X, Chen XH.Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor-mobilized mesenchymal stem cells: A new resource for rapid engraftment in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Med Hypotheses. 2011;76(2):241-243.
[15] Yeh SP, Lo WJ, Lin CL,et al.Anti-leukemic therapies induce cytogenetic changes of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Ann Hematol. 2012;91(2):163-172.
[16] Li J, Law HK, Liu YL,et al.Effect of cisplatin, topotecan, daunorubicin and hydroxyurea on human mesenchymal stem cells.Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2010;18(4): 991-996.
[17] Domenech J, Cartron G, Clement N,et al.Persistent decrease in proliferative potential of marrow CD34(+)cells exposed to early-acting growth factors after autologous bone marrow transplantation.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;29(7):557-562.
[18] Koç ON, Day J, Nieder M,et al.Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell infusion for treatment of metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) and Hurler syndrome (MPS-IH).Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;30(4):215-222.
[19] Li J, Law HK, Lau YL,et al.Differential damage and recovery of human mesenchymal stem cells after exposure to chemotherapeutic agents.Br J Haematol. 2004;127(3): 326-334.
[20] Ben-Ishay Z, Barak V.Bone marrow stromal dysfunction in mice administered cytosine arabinoside.Eur J Haematol. 2001;66(4):230-237.
[21] Kushwaha P, Khedgikar V, Gautam J,et al.A novel therapeutic approach with Caviunin-based isoflavonoid that en routes bone marrow cells to bone formation via BMP2/Wnt-β-catenin signaling.Cell Death Differ. 2014;5:e1422.
[22] Cartron G, Herault O, Benboubker L,et al.Quantitative and qualitative analysis of the human primitive progenitor cell compartment after autologous stem cell transplantation.J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2002;11(2):359-368.
[23] Banfi A, Bianchi G, Galotto M,et al.Bone marrow stromal damage after chemo/radiotherapy: occurrence, consequences and possibilities of treatment.Leuk Lymphoma. 2001;42(5):863-870. |
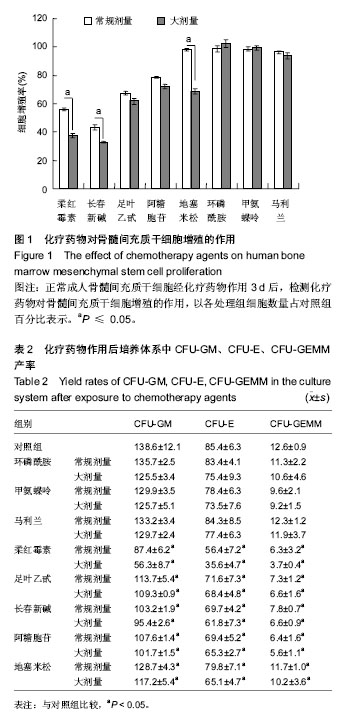

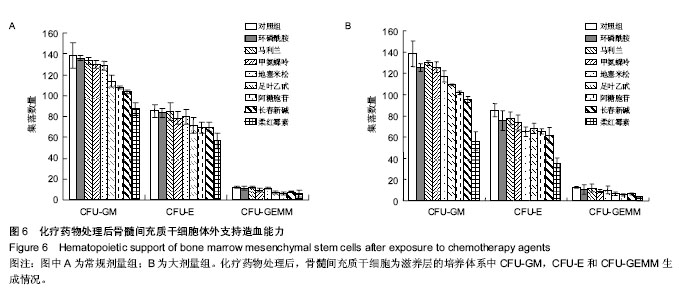
.jpg)