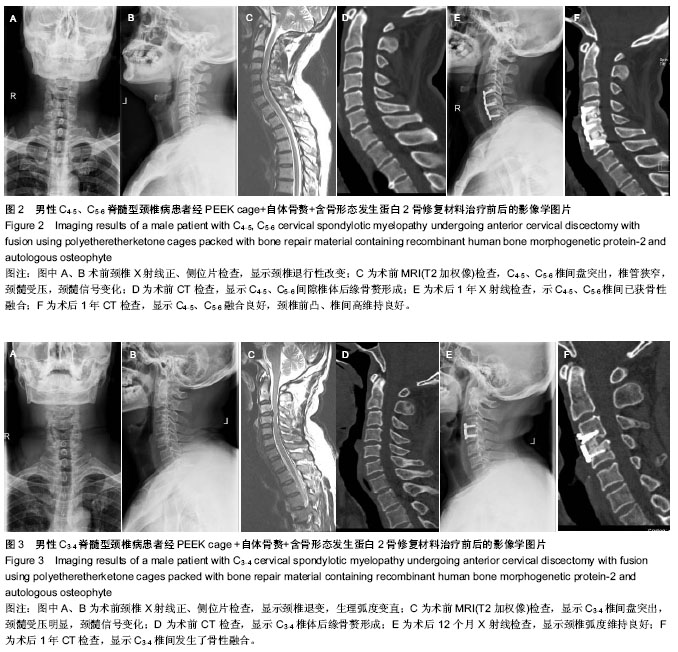
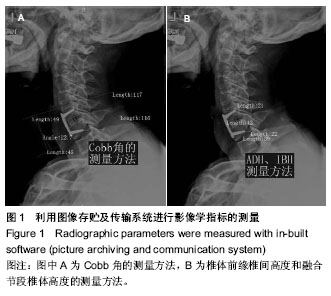
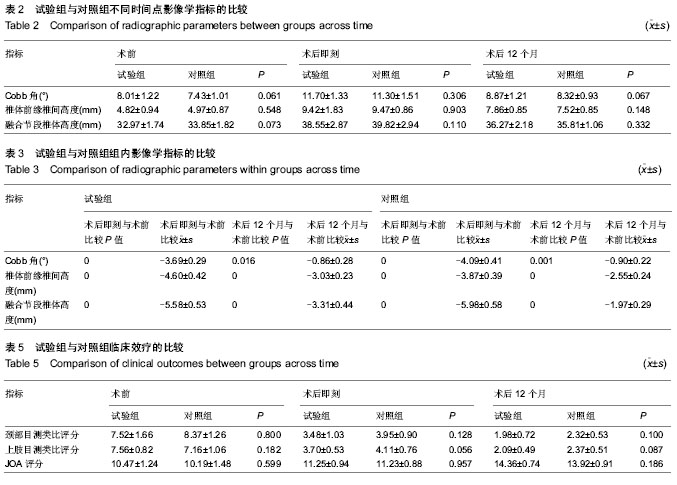
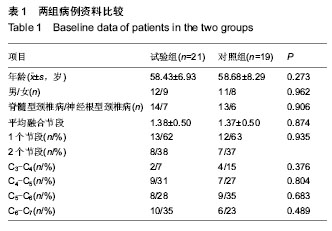
| [1] Smith GW,Robinson RA.The treatment of certain cervical- spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1958;40-A(3):607-624.
[2] Cahill KS,Chi JH,Day A,et al.Prevalence, complications, and hospital charges associated with use of bone-morphogenetic proteins in spinal fusion procedures. JAMA. 2009;302(1): 58-66.
[3] Smucker JD,Rhee JM,Singh K,et al.Increased swelling complications associated with off-label usage of rhBMP-2 in the anterior cervical spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2006;31(24): 2813-2819.
[4] Buttermann GR.Prospective nonrandomized comparison of an allograft with bone morphogenic protein versus an iliac-crest autograft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Spine J.2008;8(3):426-435.
[5] Vaidya R,Carp J,Sethi A,et al.Complications of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion using recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2.Eur Spine J.2007;16(8): 1257-1265.
[6] Poynton AR,Lane JM.Safety profile for the clinical use of bone morphogenetic proteins in the spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(16 Suppl 1):S40-48.
[7] McKay B,Sandhu HS.Use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in spinal fusion applications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2002;27(16 Suppl 1):S66-85.
[8] Anderson DW,Burton DC,Jackson RS.Postoperative cervical myelopathy and cord compression associated with the use of recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-2 in posterior cervical decompression, instrumentation, and arthrodesis: a report of two cases.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2011;36(10): E682-686.
[9] Haid RW Jr,Branch CL Jr,Alexander JT,et al.Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein type 2 with cylindrical interbody cages.Spine J.2004;4(5):527-538.
[10] Vaccaro AR,Carrino JA,Venger BH,et al.Use of a bioabsorbable anterior cervical plate in the treatment of cervical degenerative and traumatic disc disruption. J Neurosurg.2002;97(4 Suppl):473-480.
[11] Semantic D,Shen FH,Matthews DK,et al.Comparision of allograft to autograft in multilevel anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with rigid plate fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 3(2):451.
[12] Baskin DS,Ryan P,Sonntag V,et al.A prospective, randomized, controlled cervical fusion study using recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 with the CORNERSTONE-SR allograft ring and the ATLANTIS anterior cervical plate. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003;28(12):1219-1224.
[13] Shields LB,Raque GH,Glassman SD,et al.Adverse effects associated with high-dose recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 use in anterior cervical spine fusion.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2006;31(5):542-547.
[14] Boakye M,Mummaneni PV,Garrett M,et al.Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion involving a polyetheretherketone spacer and bone morphogenetic protein.J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2(5):521-525.
[15] Lanman TH,Hopkins TJ.Early findings in a pilot study of anterior cervical interbody fusion in which recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 was used with poly (L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) bioabsorbable implants.Neurosurg Focus. 2004;16(3):E6.
[16] Tumialán LM,Pan J,Rodts GE,et al.The The safety and efficacy of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with polyetheretherketone spacer and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: a review of 200 patients.J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;8(6):529-535.
[17] Vaidya R,Carp J,Sethi A,et al.Complications of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion using recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(8): 1257-1265.
[18] Vaidya R,Weir R,Sethi A,et al.Interbody fusion with allograft and rhBMP-2 leads to consistent fusion but early subsidence.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2007;89(3):342-345.
[19] Tumialán LM,Pan J,Rodts GE,et al.The safety and efficacy of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with polyetheretherketone spacer and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: a review of 200 patients. J Neurosurg Spine.2008;8(6):529-535.
[20] Frenkel MB,Cahill KS,Javahary RJ,et al.Fusion rates in multilevel, instrumented anterior cervical fusion for degenerative disease with and without the use of bone morphogenetic protein. J Neurosurg Spine.2013;18(3): 269-273.
[21] Kandziora F,Bail H,Schmidmaier G,et a1.Bone morphogenetic protein-2 application by a poly(D,L-lactide)-coated interbody cage: in vivo results of a new carrier for growth factors.J Neurosurg.2002;97(1 Suppl):40-48.
[22] Dickerman RD,Reynolds AS,Morgan BC,et al.rh-BMP-2 can be used safely in the cervical spine: dose and containment are the keys! Spine J. 2007;7(4):508-509.
[23] Agrillo U,Mastronardi L,Puzzilli F.Anterior cervical fusion with carbon fiber cage containing coralline hydroxyapatite: preliminary observations in 45 consecutive cases of soft-disc herniation.J Neurosurg.2002;96(3 Suppl):273-276.
[24] Chang WC,Tsou HK,Chen WS,et al.Preliminary comparison of radiolucent cages containing either autogenous cancellous bone or hydroxyapatite graft in multilevel cervical fusion.J Clin Neurosci.2009;16(6):793-796.
[25] Niu CC,Liao JC,Chen WJ,et al.Outcomes of interbody fusion cages used in 1 and 2-levels anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: titanium cages versus polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cages.J Spinal Disord Tech.2010;23(5):310-316.
[26] Cho DY,Liau WR,Lee WY,et al.Preliminary experience using a polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cage in the treatment of cervical disc disease.Neurosurgery.2002;51(6):1343-1349.
[27] Topuz K,Colak A,Kaya S,et al.Two-level contiguous cervical disc disease treated with peek cages packed with demineralized bone matrix: results of 3-year follow-up.Eur Spine J.2009;18(2):238-243. |