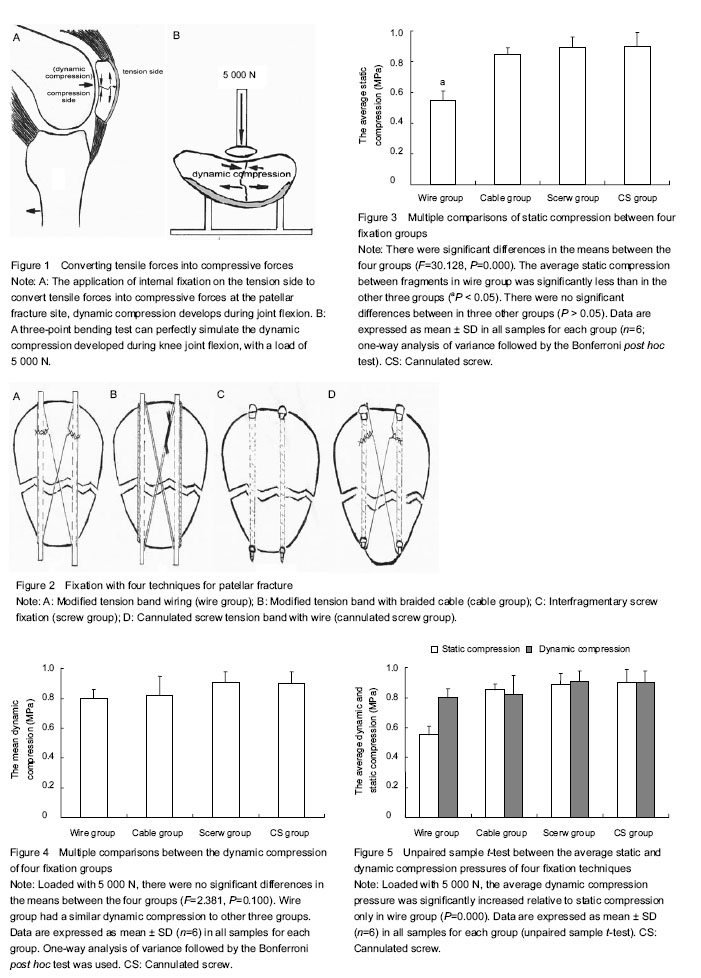
A three-point bending test simulated the progress of dynamic compression. In John
et al ’s study
[15], samples were subjected to a cyclic loading test using a three-point bending test. Dynamic compression develops with joint flexion, as with a patellar fracture, and the tensile forces (
e.g., between the quadriceps muscle and the tibial tuberosity) cannot convert to compressive forces without the support or resistance of the femoral trochlea. That is, the tensile forces must be converted to a compressive articular contact load, effectively putting the entire structure (patella and/or Kirschner wires) in a bending position, which then converts to an interfragmentary compression, a three-point bending test can simulate the progress of converting tensile force into compression force (
i.e., dynamic compression) at the opposite cortex during knee joint flexion. The increased static compression weakened the effective dynamic compression and the process of mechanotransduction. The use of cable in conjunction with Kirschner wires or interfragmentary screws or of cannulated screws with wires provided significantly greater static compression. However, it had less effect on dynamic compression than the classic modified tension band wiring technique consisting of two Kirschner wires and monofilament wire. Dynamic compression can provide additional interfragmentary compression during joint flexion, which can induce osteoblasts to grow, thereby promoting bone healing. Dynamic mechanical loading can promote osteogenesis through the process of mechanotransduction
[18], using appropriate mechanical tension-stress, does not break the callus but rather it stimulates and maintains osteogenesis
[19]. The interfragmentary pressure should be higher under dynamic compression than under static compression. The classic modified tension band wiring can generate good dynamic co
mpression but poor static compression (unstable fixation). This is because if the wire is tightened too much for interfragmentary compression, the wire may break, causing fixation failure. A flexible fixation of the fractured site can induce fracture callus formation, whereas an unstable fixation can lead to a nonunion[20]. If monofilament wire is replaced by braided cable, the static compression and the fixation stability would increase significantly, but the effect of dynamic compression and the process of mechanotransduction would also weaken. As opposed to secondary healing in cortical bone, healing in cancellous bone (patella) occurs without the formation of significant external callus. Under stable conditions, cancellous bone healed by direct formation of woven bone, instability resulted in an internal cartilaginous callus[21]. Less fixation rigidity and increased fracture gap induce a later response of bone formation and greater endochondral bone formation, leading to prolonged time for full ossification[22]. Thus, for patella (cancellous bone) healing, enhancing stability by increasing static compression should be prior to dynamic compression.
The more rigid fixation, the less dynamic compression was. This study performed the three-point bending test at 5 000 N, which is far more than a physiological loading force. The peak patellofemoral joint reaction force of humans during forward step-down is (51.1±2.7) N/kg[23] –about 3 500 N for
70 kg of weight. Hence, with fixation using the tension band technique in vivo, dynamic compression should be weaker than our test at 5 000 N in vitro. Nevertheless, in our experiments, there were still no significant increases in dynamic compression pressures when compared with static compression. Why? The use of Kirschner wires must resist the bending stress exerted on the concave side with joint flexion, and dynamic compression should be reduced. The larger the diameter of the Kirschner wires, the stronger the resistance to bending stress on the concave side is and with less dynamic compression. If Kirschner wires were replaced by more rigid fixation (e.g., a lag or cannulated screw), which can generate better static compression, dynamic compression would be almost unmeasurable.
How should we think about the contradiction between static and dynamic compression? The principles of the tension band technique should include two components: (1) fixation on the side of tension stress (e.g., the convex side or extra-articular anterior surface of the patella); (2) application of a tension band to neutralize or, ideally, convert tensile force (e.g., between the quadriceps muscle and the tibial tuberosity) into compression force at the opposite cortex when the joint is flexed. The current patellar fracture fixation techniques seem to follow only the principle of fixation on the side of tension stress. This usage loses sight of the effect of dynamic compression, although it is highly praised for the more stable fixation with more static compression[3-4, 7-10, 14], but is that a bad thing?
The more rigid fixation, the better biomechanical performance is. Although the effect of fixation with braided cable or screws on dynamic compression is not better than with the traditional tension band fixation with Kirschner wires and monofilament wire, many studies have shown that the biomechanical performance of the screw fixation system is superior to that of the tension band wiring technique[3-9, 24-28]. Addition of screws to tension band techniques reduces fracture separation by providing compression throughout the range of motion and by resisting tensile loading during terminal extension[8]. Some studies with simulated knee extensions proved that fractures stabilized with a modified tension band are displaced more often than those fixed with screws alone or screws plus a tension band[3-4]. Fractures fixed with cannulated screws plus the tension band failed at higher loads than those stabilized with screws alone or those with a modified tension band[8-9]. Tested by applying a cyclic load, the screws plus tension band technique was performed significantly better than the screws alone or the modified tension band, with a smaller fracture gap[3-4, 8]. Regarding the modified tension band, the braided cable tension loop was superior to the monofilament wire tension loop during cyclic loading[4-5, 11-12].
The greater static compression, the more stable fixation is. Although dynamic compression must exist regardless of whether it can be measured, the fact is that greater static compression is associated with more stable patellar fixation and less dynamic compression. Therefore, the prime aim of current patellar fracture fixation techniques is more stable fixation with high static compression-giving little thought to dynamic compression, which does reduce the displacement of a fragment under a load[3-14] and ensures good healing of patellar fractures[3-14, 27-29]. Simple wiring techniques alone may provide better dynamic compression, but not provide sufficient fixation to allow immediate range of motion[26, 30]. In that sense, compared with dynamic compression, more stable fixation with greater static compression is more necessary, more advantageous, and more efficient, so this is not a bad thing.
For now, the stronger static compression, the better fixation technique is. The strength of static compression depends on the strength of the wire or braided cable or on the compression of screws. Although addition of the tension band wire to the screws did not significantly increase static compression in our test, it can effectively resist tensile stress on the convex side of the patella during cyclic loading[3-4, 8, 14]. Combining interfragmentary screw fixation with the tension band principle appears to provide better stability than the modified tension band or screws alone for transverse patellar fractures[3, 8, 14]. Thus, under physiological cyclic loading conditions, addition of the tension band wire or cable is still effective. In patella fractures, cannulated screws with tension band wiring technique provide stable fixation, allows early motion exercise[25-26] and maintains an anatomic reduction in oteoporotic bone[28]. Nevertheless, in Baran study, cyclic loading tests indicate that all tension band wiring applications lose their initial stability, excessive initial compression by the tension band resulted in bending of the Kirschner wire and thus reduction failure[29-30]. At present, if stability and dynamic compression cannot be balanced, although expensive, combining interfragmentary cannulated screw fixation with the tension band (cable) principle seems to be the best choice for achieving osteosynthesis of transverse patellar fractures, because it provides the most stable fixation and the best static compression. A new fixation technique for both stable fixation and dynamic static may be developed in the future.
The numerical values in this study are thus not the same as would be found in humans, although the conclusions should be the same. The cow model of a patella used in this test has much higher bone density and is also much more likely to allow higher wire or cable tension or interfragmentary screw compression than in human bone. Therefore, the load is increased for the three-point bending test accordingly, although is far higher than the physiological loading force on the human patella. However, it was much easier to find similar cow models than cadaveric patellas. With this in mind, we were able to focus our study on the interesting biomechanical characteristics of fixation techniques, without the wide variations that may caused by differences in properties of cadaveric patellas[9, 14-15], such as shape and bone density.
Comparing current patellar fracture fixation techniques, the use of braided cable or screws provided significantly greater static compression, but had less effect on dynamic compression than the classic modified tension band wiring technique consisting of two Kirschner wires and monofilament wire. The increased static compression may weaken the effect of dynamic compression. At present, more stable patellar fracture fixation with high static compression can be achieved by combining interfragmentary cannulated screw fixation with the tension band (cable) principle.