| [1]Mulhall HJ, Hughes MP, Kazmi B, et al. Epithelial cancer cells exhibit different electrical properties when cultured in 2D and 3D environments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830(11): 5136-5141.
[2]da Rocha EL, Porto LM, Rambo CR. Nanotechnology meets 3D in vitro models: tissue engineered tumors and cancer therapies. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;34: 270-279.
[3]Ramaiahgari SC, den Braver MW, Herpers B, et al. A 3D in vitro model of differentiated HepG2 cell spheroids with improved liver-like properties for repeated dose high-throughput toxicity studies. Arch Toxicol. 2014;88(5): 1083-1095.
[4]Kimlin L, Kassis J, Virador V. 3D in vitro tissue models and their potential for drug screening. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013;8(12):1455-1466.
[5]Jiguet Jiglaire C, Baeza-Kallee N, Denicolaï E, et al. Ex vivo cultures of glioblastoma in three-dimensional hydrogel maintain the original tumor growth behavior and are suitable for preclinical drug and radiation sensitivity screening. Exp Cell Res. 2014;321(2):99-108.
[6]Xu F, Wu J, Wang S, et al. Microengineering methods for cell-based microarrays and high-throughput drug-screening applications. Biofabrication. 2011;3(3):034101.
[7]Elliott NT, Yuan F. A review of three-dimensional in vitro tissue models for drug discovery and transport studies. J Pharm Sci. 2011;100(1):59-74.
[8]Damania A, Jain E, Kumar A. Advancements in in vitro hepatic models: application for drug screening and therapeutics. Hepatol Int. 2014;8(1):23-28.
[9]Moscona A, Moscona H. The dissociation and aggregation of cells from organ rudiments of the early chick embryo. J Anat. 1952;86(3):287-301.
[10]Moscona AA. Studies on cell aggregation: demonstration of materials with selective cell-binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963;49(5):742-747.
[11]Lilien JE, Moscona AA. Cell aggregation: its enhancement by a supernatant from cultures of homologous cells. Science. 1967;157(3784):70-72.
[12]Margolaish E, Schenck JR, Hargie MP, et al. Characterization of specific cell aggregating materials from sponge cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965;20(4):383-388.
[13]Moscona MH, Moscona AA. Inhibition of adhesiveness and aggregation of dissociated cells by inhibitors of protein and rna synthesis. Science. 1963;142(3595):1070-1071.
[14]Moscona A. Rotation-mediated histogenetic aggregation of dissociated cells. A quantifiable approach to cell interactions in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1961;22:455-475.
[15]Moscona A. The development in vitro of chimeric aggregates of dissociated embryonic chick and mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957;43(1):184-194.
[16]Gonzalez-Cordero A, West EL, Pearson RA, et al. Photoreceptor precursors derived from three-dimensional embryonic stem cell cultures integrate and mature within adult degenerate retina. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31(8): 741-747.
[17]Lou YR, Kanninen L, Kuisma T, et al. The use of nanofibrillar cellulose hydrogel as a flexible three-dimensional model to culture human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2014; 23(4):380-392.
[18]Naito H, Yoshimura M, Mizuno T, et al. The advantages of three-dimensional culture in a collagen hydrogel for stem cell differentiation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(10): 2838-2845.
[19]Han J, Chen L, Luo G, et al. Three-dimensional culture may promote cell reprogramming. Organogenesis. 2013;9(2): 118-120.
[20]Eiraku M, Sasai Y. Self-formation of layered neural structures in three-dimensional culture of ES cells. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2012;22(5):768-777.
[21]Vollmers A, Wallace L, Fullard N, et al. Two- and three-dimensional culture of keratinocyte stem and precursor cells derived from primary murine epidermal cultures. Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8(2):402-413.
[22]Pampaloni F, Reynaud EG, Stelzer EH. The third dimension bridges the gap between cell culture and live tissue. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(10):839-845.
[23]Fang C, Man YG, Cuttitta F, et al. Novel phenotypic fluorescent three-dimensional co-culture platforms for recapitulating tumor in vivo progression and for personalized therapy. J Cancer. 2013;4(9):755-763.
[24]Nolte DD, An R, Turek J, et al. Tissue dynamics spectroscopy for phenotypic profiling of drug effects in three-dimensional culture. Biomed Opt Express. 2012;3(11):2825-2841.
[25]Shimko VF, Claycomb WC. Effect of mechanical loading on three-dimensional cultures of embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Tissue Eng Part A. 2008;14(1):49-58..
[26]Ajalloueian F, Lim ML, Lemon G, et al. Biomechanical and biocompatibility characteristics of electrospun polymeric tracheal scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2014;35(20):5307-5315.
[27]Chen H, Liu Y, Jiang Z, et al. Cell-scaffold interaction within engineered tissue. Exp Cell Res. 2014;323(2):346-351.
[28]Kaczmarek M, Jurczyk MU, Rubis B, et al. In vitro biocompatibility of Ti-45S5 bioglass nanocomposites and their scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(5):1316-1324.
[29]Rahmanian-Schwarz A, Held M, Knoeller T, et al. In vivo biocompatibility and biodegradation of a novel thin and mechanically stable collagen scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(4):1173-1179.
[30]Mercuri JJ, Patnaik S, Dion G, et al. Regenerative potential of decellularized porcine nucleus pulposus hydrogel scaffolds: stem cell differentiation, matrix remodeling, and biocompatibility studies. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(7-8): 952-966.
[31]García Cruz DM, Salmerón-Sánchez M, Gómez-Ribelles JL. Stirred flow bioreactor modulates chondrocyte growth and extracellular matrix biosynthesis in chitosan scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(9):2330-2341.
[32]Oliveira JM, Rodrigues MT, Silva SS, et al. Novel hydroxyapatite/chitosan bilayered scaffold for osteochondral tissue-engineering applications: Scaffold design and its performance when seeded with goat bone marrow stromal cells. Biomaterials. 2006;27(36):6123-6137.
[33]Almeida CR, Serra T, Oliveira MI, et al. Impact of 3-D printed PLA- and chitosan-based scaffolds on human monocyte/macrophage responses: unraveling the effect of 3-D structures on inflammation. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(2): 613-622.
[34]Ikeda T, Ikeda K, Yamamoto K, et al. Fabrication and characteristics of chitosan sponge as a tissue engineering scaffold. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:786892.
[35]Inzana JA, Olvera D, Fuller SM, et al. 3D printing of composite calcium phosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2014;35(13):4026-4034.
[36]Deponti D, Di Giancamillo A, Gervaso F, et al. Collagen scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering: the benefit of fibrin glue and the proper culture time in an infant cartilage model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(5-6):1113-1126.
[37]Fagerholm P, Lagali NS, Ong JA, et al. Stable corneal regeneration four years after implantation of a cell-free recombinant human collagen scaffold. Biomaterials. 2014; 35(8):2420-2427.
[38]Lozoya OA, Wauthier E, Turner RA, et al. Regulation of hepatic stem/progenitor phenotype by microenvironment stiffness in hydrogel models of the human liver stem cell niche. Biomaterials. 2011;32(30):7389-7402.
[39]Pedron S, Becka E, Harley BA. Regulation of glioma cell phenotype in 3D matrices by hyaluronic acid. Biomaterials. 2013;34(30):7408-7417.
[40]Drury JL, Mooney DJ. Hydrogels for tissue engineering: scaffold design variables and applications. Biomaterials. 2003;24(24):4337-4351.
[41]Poellmann MJ, Harrell PA, King WP, et al. Geometric microenvironment directs cell morphology on topographically patterned hydrogel substrates. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(9): 3514-3523.
[42]Ingber DE, Dike L, Hansen L, et al. Cellular tensegrity: exploring how mechanical changes in the cytoskeleton regulate cell growth, migration, and tissue pattern during morphogenesis. Int Rev Cytol. 1994;150:173-224.
[43]Yamada M, Utoh R, Ohashi K, et al. Controlled formation of heterotypic hepatic micro-organoids in anisotropic hydrogel microfibers for long-term preservation of liver-specific functions. Biomaterials. 2012;33(33):8304-8315.
[44]You J, Shin DS, Patel D, et al. Multilayered heparin hydrogel microwells for cultivation of primary hepatocytes. Adv Healthc Mater. 2014;3(1):126-132.
[45]Du C, Narayanan K, Leong MF, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatocytes and endothelial cells in multi-component hydrogel fibers for liver tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2014;35(23):6006-6014.
[46]Edelman GM. Cell adhesion molecules in the regulation of animal form and tissue pattern. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2: 81-116.
[47]Takeichi M. Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science. 1991;251(5000): 1451-1455.
[48]Gallin WJ, Sanders EJ. Development of bile canaliculi between chicken embryo liver cells in vivo and in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1992;200(1):58-69.
[49]Kelly HT, Hill E, Reid F, et al. Comparison of RAP-PCR analysis of gene expression in fresh and immortalised rat hepatocyte cell lines. Cytotechnology. 2000;34(1-2): 159-163.
[50]Klausner RD. The fabric of cancer cell biology-Weaving together the strands. Cancer Cell. 2002;1(1):3-10.
[51]Albini A, Sporn MB. The tumour microenvironment as a target for chemoprevention. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(2):139-147.
[52]Liotta LA, Kohn EC. The microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature. 2001;411(6835):375-379.
[53]Kunz-Schughart LA, Kreutz M, Knuechel R. Multicellular spheroids: a three-dimensional in vitro culture system to study tumour biology. Int J Exp Pathol. 1998 Feb;79(1):1-23.
[54]Yamada KM, Cukierman E. Modeling tissue morphogenesis and cancer in 3D. Cell. 2007;130(4):601-610.
[55]Jiguet Jiglaire C, Baeza-Kallee N, Denicolaï E, et al. Ex vivo cultures of glioblastoma in three-dimensional hydrogel maintain the original tumor growth behavior and are suitable for preclinical drug and radiation sensitivity screening. Exp Cell Res. 2014;321(2):99-108.
[56]Fischbach C1, Chen R, Matsumoto T, et al. Engineering tumors with 3D scaffolds. Nat Methods. 2007;4(10): 855-860.
[57]Teicher BA, Herman TS, Holden SA, et al. Tumor resistance to alkylating agents conferred by mechanisms operative only in vivo. Science. 1990;247(4949 Pt 1):1457-1461.
[58]Ng CP, Bonavida B. A new challenge for successful immunotherapy by tumors that are resistant to apoptosis: two complementary signals to overcome cross-resistance. Adv Cancer Res. 2002;85:145-174.
[59]Lewis JT, Ketterling RP, Halling KC, et al. Analysis of intratumoral heterogeneity and amplification status in breast carcinomas with equivocal (2+) HER-2 immunostaining. Am J Clin Pathol. 2005;124(2):273-281.
[60]Minchinton AI, Tannock IF. Drug penetration in solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(8):583-592.
[61]Comerford KM, Wallace TJ, Karhausen J, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent regulation of the multidrug resistance (MDR1) gene. Cancer Res. 2002;62(12): 3387-3394. |
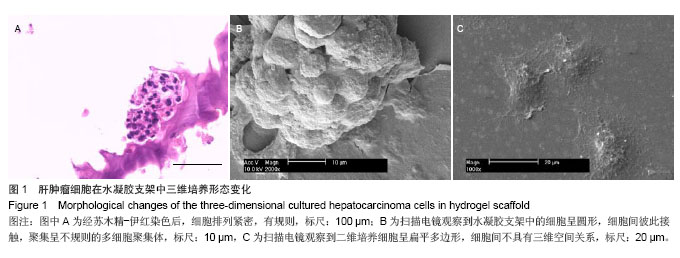
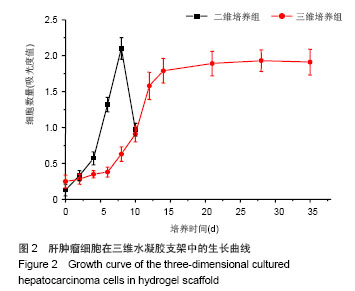
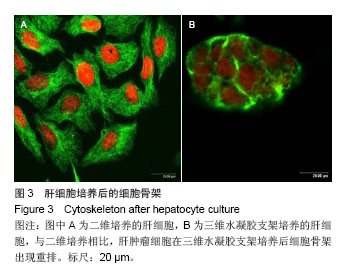

.jpg)