中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (25): 3998-4003.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.25.011
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
纤维蛋白凝胶促进大鼠间充质干细胞的成骨分化
买 霞,李 威,王英慧,扎拉嘎胡,陈小义
- 武装警察部队后勤学院临床医学系细胞生物学与医学遗传学教研室,天津市 300039
-
收稿日期:2014-05-28出版日期:2014-06-18发布日期:2014-06-18 -
通讯作者:陈小义,硕士,教授,硕士生导师,武装警察部队后勤学院临床医学系细胞生物学与医学遗传学教研室,天津市 300039 -
作者简介:买霞,女,1972年生,山西省运城市人,回族,武警部队后勤学院在读硕士,实验师,主要从事干细胞定向分化研究。 -
基金资助:中国人民武警部队资助重点项目(WKH2009Z04),中国人民武警部队后勤学院资助项目(WHM201209)
Fibrin gel enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells
Mai Xia, Li Wei, Wang Ying-hui, Zha La Ga Hu, Chen Xiao-yi
- Research Room of Cell Biology and Medical Genetics, Department of Clinical Medicine, Logistics College of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Tianjin 300039, China
-
Received:2014-05-28Online:2014-06-18Published:2014-06-18 -
Contact:Chen Xiao-yi, Master, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Research Room of Cell Biology and Medical Genetics, Department of Clinical Medicine, Logistics College of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Tianjin 300039, China -
About author:Mai Xia, Studying for master’s degree, Experimentalist, Research Room of Cell Biology and Medical Genetics, Department of Clinical Medicine, Logistics College of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, Tianjin 300039, China -
Supported by:the Key Program of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, No. WKH2009Z04; the Program of Logistics College of Chinese People’s Armed Police Forces, No. WHM201209
摘要:
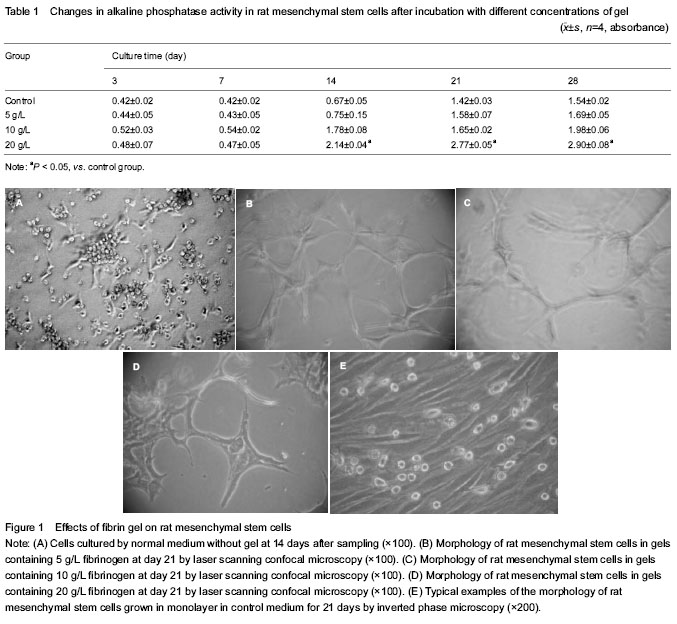
背景:纤维蛋白是一种天然的可生物降解、组织相容性好的高分子材料,是一种能促进细胞和外源性生长因子释放的载体,其中血纤维蛋白稳定因子ⅩⅢ已证明有利于未分化的间充质干细胞在高度交联的凝胶支架内迁移,并且促进这些细胞的增殖与分化能力。 目的:观察大鼠间充质干细胞在纤维蛋白凝胶内的行为。 方法:无菌条件下分离大鼠胎肢细胞获得间充质干细胞,取第3代细胞分别接种于0,5,10,20 g/L纤维蛋白凝胶内,用倒置相差显微镜和激光扫描共聚焦显微镜分析细胞在凝胶内的形态学变化; 酶标仪和Von Kossa染色分析碱性磷酸酶活性和钙盐沉积。 结果与结论:5 g/L低浓度纤维蛋白凝胶有利于细胞形态的发生,20 g/L高浓度凝胶有利于细胞的成骨分化。20 g/L纤维蛋白凝胶碱性磷酸酶活性高于对照组,10和20 g/L浓度纤维蛋白凝胶矿化结节出现在21至28 d,而对照组无矿化结节出现。提示大鼠间充质干细胞的形态与成骨分化依赖于纤维蛋白凝胶浓度,提示纤维蛋白凝胶有助于间充质干细胞的成骨分化。
中图分类号:
引用本文
买 霞,李 威,王英慧,扎拉嘎胡,陈小义. 纤维蛋白凝胶促进大鼠间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(25): 3998-4003.
Mai Xia, Li Wei, Wang Ying-hui, Zha La Ga Hu, Chen Xiao-yi. Fibrin gel enhances osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(25): 3998-4003.
Fibrin gel effects on morphology of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
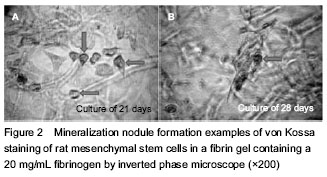
(20 g/L) fibrinogen concentration showed the presence of mineralization nodules after 21 and 28 days of incubation. The nodules appeared in areas with cells, and mostly in the areas with holes in the fibrin gels. No nodules were observed on top of the gel, which was covered by a monolayer of cells (Figure 2).
| [1] Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 1991; 9(5):641-650. [2] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147. [3] Bianco P, Robey PG, Simmons PJ. Mesenchymal stem cells: revisiting history, concepts, and assays. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(4):313-319. [4] Jaiswal RK, Jaiswal N, Bruder SP, et al. Adult human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to the osteogenic or adipogenic lineage is regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(13):9645-9652. [5] Wang X, Wang Y, Gou W, et al. Role of mesenchymal stem cells in bone regeneration and fracture repair: a review. Int Orthop. 2013;37(12):2491-2498. [6] Cao L, Liu G, Gan Y, et al. The use of autologous enriched bone marrow MSCs to enhance osteoporotic bone defect repair in long-term estrogen deficient goats. Biomaterials. 2012;33(20):5076-5084. [7] Guan M, Yao W, Liu R, et al. Directing mesenchymal stem cells to bone to augment bone formation and increase bone mass. Nat Med. 2012;18(3):456-462. [8] Pino AM, Rosen CJ, Rodríguez JP. In osteoporosis, differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) improves bone marrow adipogenesis. Biol Res. 2012; 45(3):279-287. [9] Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Doglioli P, de Peppo GM, et al. Choukroun's platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) stimulates in vitro proliferation and differentiation of human oral bone mesenchymal stem cell in a dose-dependent way. Arch Oral Biol. 2010;55(3):185-194. [10] Wong C, Inman E, Spaethe R, et al. Fibrin-based biomaterials to deliver human growth factors. Thromb Haemost. 2003;89(3):573-582. [11] Gorodetsky R, Clark RA, An J, et al. Fibrin microbeads (FMB) as biodegradable carriers for culturing cells and for accelerating wound healing. J Invest Dermatol. 1999; 112(6): 866-872. [12] Horch RE, Bannasch H, Kopp J, et al. Single-cell suspensions of cultured human keratinocytes in fibrin-glue reconstitute the epidermis. Cell Transplant. 1998;7(3): 309-317. [13] Catelas I, Dwyer JF, Helgerson S. Controlled release of bioactive transforming growth factor beta-1 from fibrin gels in vitro. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2008;14(2):119-128. [14] Mosesson MW, Siebenlist KR, Meh DA. The structure and biological features of fibrinogen and fibrin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:11-30. [15] Marktl W, Rudas B. The effect of factor XIII on wound granulation in the rat. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1974;32 (2-3):578-581. [16] Lin B, Cai ZG, Yu GY, et al. Osteoblastoma of the maxilla and mandible: a report of 2 cases and literature review. Chin J Dent Res. 2012;15(2):153-158. [17] Nöth U, Steinert AF, Tuan RS. Technology insight: adult mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis therapy. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008;4(7):371-380. [18] Yu Y, Shao B, Shuai Y, et al. Role of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in treating colitis through Fas/FasL-mediated immune regulation. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013;29(10):1028-1031. [19] Ishii M, Shibata R, Numaguchi Y, et al. Enhanced angiogenesis by transplantation of mesenchymal stem cell sheet created by a novel magnetic tissue engineering method. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31(10): 2210-2215. [20] Li X, van Blitterswijk CA, Feng Q, et al. The effect of calcium phosphate microstructure on bone-related cells in vitro. Biomaterials. 2008;29(23):3306-3316. [21] Sun N, Yang L, Li Y, et al. Effect of advanced oxidation protein products on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 2013;32(2):485-491. [22] Tang X, Sheng L, Xie F, et al. Differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes using chondrocyte extract. Mol Med Rep. 2012;6(4): 745-749. [23] Scotti C, Pozzi A, Mangiavini L, et al. Healing of meniscal tissue by cellular fibrin glue: an in vivo study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2009;17(6):645-651. [24] Chien CS, Ho HO, Liang YC, et al. Incorporation of exudates of human platelet-rich fibrin gel in biodegradable fibrin scaffolds for tissue engineering of cartilage. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100(4):948-955. [25] Sha'ban M, Yoon SJ, Ko YK, et al. Fibrin promotes proliferation and matrix production of intervertebral disc cells cultured in three-dimensional poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2008;19(9):1219- 1237. [26] Even-Ram S. Fibrin gel model for assessment of cellular contractility. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;522:251-259. [27] de Jonge N, Kanters FM, Baaijens FP, et al. Strain-induced collagen organization at the micro-level in fibrin-based engineered tissue constructs. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(4): 763-774. [28] Gerard C, Forest MA, Beauregard G, et al. Fibrin gel improves the survival of transplanted myoblasts. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(1):127-137. [29] Lee F, Kurisawa M. Formation and stability of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels consisting of fibrin and hyaluronic acid for tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(2):5143-5152. [30] Allan P, Uitte de Willige S, Abou-Saleh RH, et al. Evidence that fibrinogen γ' directly interferes with protofibril growth: implications for fibrin structure and clot stiffness. J Thromb Haemost. 2012;10(6):1072-1080. [31] Beck GR Jr. Inorganic phosphate as a signaling molecule in osteoblast differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2003;90(2):234- 243. [32] Simão AM, Beloti MM, Cezarino RM, et al. Membrane-bound alkaline phosphatase from ectopic mineralization and rat bone marrow cell culture. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2007;146(4): 679-687. [33] Kim A, Benning MM, OkLee S, et al. Divergence of chemical function in the alkaline phosphatase superfamily: structure and mechanism of the P-C bond cleaving enzyme phosphonoacetate hydrolase. Biochemistry. 2011;50(17): 3481-3494. [34] Tobe BT, Hou J, Crain AM, et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis: an emerging role in deciphering cellular signaling in human embryonic stem cells and their differentiated derivatives. Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8(1):16-31. [35] Brill LM, Xiong W, Lee KB, et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis of human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5(2):204-213. [36] Tian XF, Heng BC, Ge Z, et al. Comparison of osteogenesis of human embryonic stem cells within 2D and 3D culture systems. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2008;68(1):58-67. [37] Bensaïd W, Triffitt JT, Blanchat C, et al. A biodegradable fibrin scaffold for mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Biomaterials. 2003;24(14):2497-2502. [38] Ho W, Tawil B, Dunn JC, et al. The behavior of human mesenchymal stem cells in 3D fibrin clots: dependence on fibrinogen concentration and clot structure. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(6):1587-1595. [39] Catelas I, Sese N, Wu BM, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in fibrin gels in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(8):2385-2396. [40] Rose LC, Fitzsimmons R, Lee P, et al. Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor in mouse embryonic stem cell culture and osteogenic differentiation. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7(5):371-382. [41] Luan J, Cui Y, Zhang Y, et al. Effect of CXCR4 inhibitor AMD3100 on alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralization in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Biosci Trends. 2012;6(2):63-69. [42] Mauney JR, Blumberg J, Pirun M, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells on partially demineralized bone scaffolds in vitro. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(1-2):81-92. [43] Kitamura S, Ohgushi H, Hirose M, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells cultured on alumina ceramics. Artif Organs. 2004;28(1):72-82. [44] Lee SJ, Atala A. Scaffold technologies for controlling cell behavior in tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2013;8(1): 010201 |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 林清凡, 解一新, 陈婉清, 叶振忠, 陈幼芳. 人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [4] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [5] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [6] | 孔德胜, 何晶晶, 冯宝峰, 郭瑞云, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, 吕 飞, 张舒涵, 张晓琳, 马 隽, 崔慧先. 间充质干细胞修复大动物模型脊髓损伤疗效评价的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [8] | 史洋洋, 秦英飞, 吴福玲, 何 潇, 张雪静. 胎盘间充质干细胞预处理预防小鼠毛细支气管炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [9] | 梁学奇, 郭黎姣, 陈贺捷, 武 杰, 孙雅琪, 邢稚坤, 邹海亮, 陈雪玲, 吴向未. 泡状棘球绦虫原头蚴抑制骨髓间充质干细胞向成纤维细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [10] | 樊全宝, 罗惠娜, 王丙云, 陈胜锋, 崔连旭, 江文康, 赵明明, 王静静, 罗冬章, 陈志胜, 白银山, 刘璨颖, 张 晖. 低氧培养犬脂肪间充质干细胞的生物学特性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [11] | 耿 瑶, 尹志良, 李兴平, 肖东琴, 侯伟光. hsa-miRNA-223-3p调控人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [12] | 伦志刚, 金 晶, 王添艳, 李爱民. 过氧化物还原酶6干预骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及体外向神经谱系诱导分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [13] | 朱雪芬, 黄 成, 丁 健, 戴永平, 刘元兵, 乐礼祥, 王亮亮, 杨建东. 胶质细胞神经营养因子诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向功能性神经元分化的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [14] | 段丽芸, 曹晓沧. 人胎盘间充质干细胞来源细胞外囊泡调节肠炎小鼠肠黏膜胶原的沉积[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [15] | 裴丽丽, 孙贵才, 王 弟. 丹酚酸B抑制骨髓间充质干细胞氧化损伤及促进分化为心肌样细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
tissue sites[17-19]. Mesenchymal stem cells isolated from a variety of species can be induced to differentiate into osteoblasts and have also been shown to form bone tissue when seeded into ceramic or calcium phosphate carriers and implanted in vivo [20-22]. The purpose of this study was to analyze the morphology and osteogenic differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells within a fibrin gel in vitro and to analyze the effects of variations in the fibrinogen concentrations on cell behavior. Our goal is to examine the potential of this fibrin gel as an injectable and biodegradable scaffold for mesenchymal stem cells for possible bone regeneration applications.
Design
|
||||||||||||
The data were statistically processed using SPSS 11.0 software and were expressed as mean ± SD. One-way analysis of variance and least significant difference were used. A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
1文章要点:
干细胞的增殖与分化除需要适当细胞外环境的调节外,还需要生长因子的刺激和调节特异性基因表达转录因子的活化作用等,这些均是组织工程研究中面临的问题。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||