| [1] 赛力克•对山拜,周凯,党木仁,等.血管生长因子和结构基质蛋白在新疆哈萨克族破裂和未破裂颅内动脉瘤中的表达[J].中华神经外科杂志,2011,27(11):1157-1160.
[2] Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF. Aneurysm packing with HydroCoil Embolic System vers-us platinum coils: initial clinical experience. J AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25(6):60-62.
[3] Al-Shahi Salman R, Hall JM, Horne MA, et al. Untreated clinical course of cerebral ca-vernous malformations: a prospective, population-based cohort study. J Lancet Neurol. 2012;11(3):150-156.
[4] Wouters V, Limaye N. Hereditary cutaneomucosal venous malformati-ons are caused by TIE2 mutations with widely variable hyper-phosphorylating effects. J Eur J Hum Genet. 2010;18(4):414-420.
[5] Nishida T, Faughnan ME, Krings T, et al. Brain arteriovenous malformations associated with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: gene-phenotype correlations. J Am J Med Genet A. 2012;(11):2829-2834.
[6] Warlow C. Management of brain arteriovenous malformations. J Lancet. 2014;383(9929):1632-1633.
[7] Classen CF, Haffner D, Hauenstein C, et al. Long-time octreotide in an adolescent wi-th severe haemorrhagic gastrointestinalvascular malformation. J BMJ Case Rep 2011;2(1):87-92.
[8] Choi JH1, Pile-Spellman J, Brisman J. Trends in the management of intracranial vascular malformations in the USA from 2000 to 2007. J Troke Res Treat. 2012;35(5): 348-369.
[9] TamakiM, Mc Donald W, Del Maestro RF. Release of collagen type IV degradin-g activity from C6 astrocytom a cells and celldensity. J Neurosurg. 1996;84(6):1013-1019.
[10] Plasencia AR, Santillan A. Embolization and radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations. J Surg Neurol Int. 2012;3(2): 90-104.
[11] Wong JH, Awad IA, Kim JH. Ultrastructural pathological features of cerebrovascular malformations: a preliminary report. J Neurosurg. 2000;46(6):1454-1459.
[12] 赵明光,王晨,高永中,等.脑动静脉畸形血管生成素表达与血管超微结构的观察[J].中华实验外科杂志,2003,20(8):689-690.
[13] 宋建蓉,杨志健,张馥敏,等.人血管内皮细胞生长因子-165和人血管生成素-1促进大鼠缺血下肢血管新生[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2003,13(1):103-107.
[14] 赵明光,陈游力,宋振全,等.血管生成因子在脑动静脉血管畸形发生发展过程中的生物学效应[J].中国临床康复,2003,9(1):73-75.
[15] Adams JC, Watt FM. Regulation of development and differentiation by the extracellular matrix. J Devebpment, 1993;117:1183-1198.
[16] Risau W, Lemmon V. Changes in the vascular extracellular matrix during embryonic vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. J Dev Biol. 1988;125(2):441-150.
[17] Streeter I, de Leeuw NH. Atomistic Modeling of Collagen Proteins in Their Fibrillar Environment. J Phys Chem B. 2010; 114(41):13263-13270.
[18] 陈光忠,李铁林,姜晓丹,等.TGF-β1及MMP-2,9在脑动静脉畸形中的表达及意义[J].中国神经精神疾病杂志,2006,32(1):48-52.
[19] 袁葛,赵继宗.结构基质蛋白在脑血管畸形的表达[J].首都医科大学学报,2000,21(1):53-55.
[20] 李宝山,王喆.层粘连蛋白和血管内皮生长因子受体-2在脑动静脉畸形出血中的表达及意义[J].潍坊医学院学报, 2010,33(3): 189-192. |
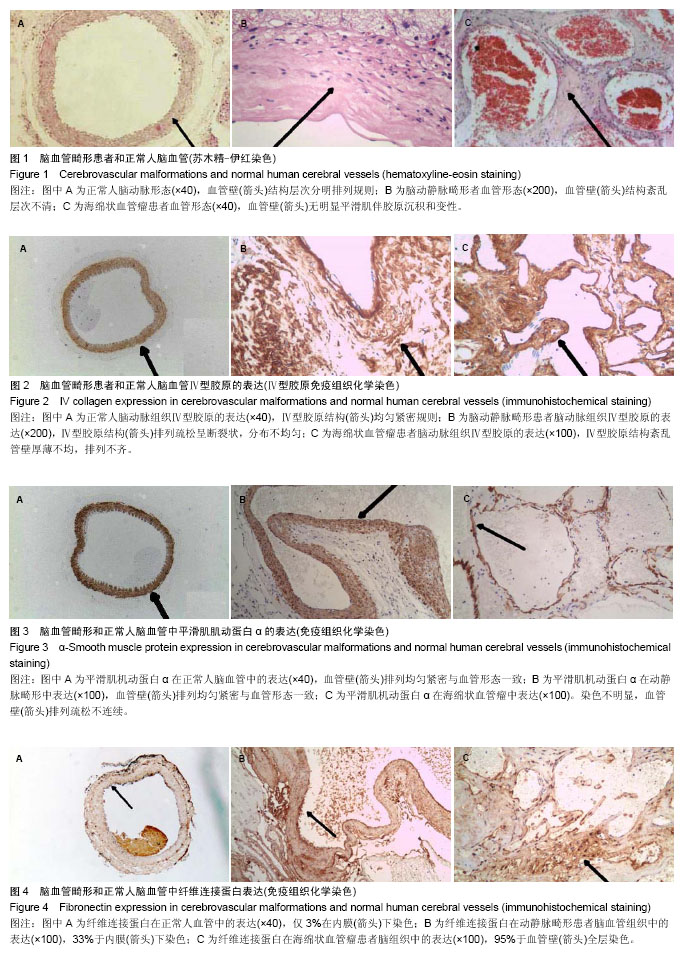
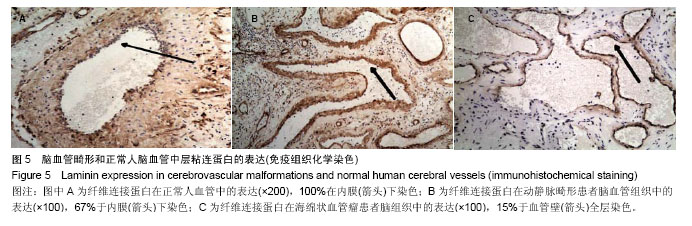
.jpg)