中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (13): 2113-2118.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.13.024
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
夹板与石膏管型外固定物治疗儿童前臂远端隆突样骨折的系统评价
李小磊1,李国华2
- 1新疆石河子大学医学院第一附属医院骨二科,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832000;2新疆医科大学第二附属医院骨科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830028
Splint versus plaster cast external fixator for the treatment of distal forearm buckle fracture in children: systematic review
Li Xiao-lei1, Li Guo-hua2
- 1Second Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University School of Medicine, Shihezhi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830028, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
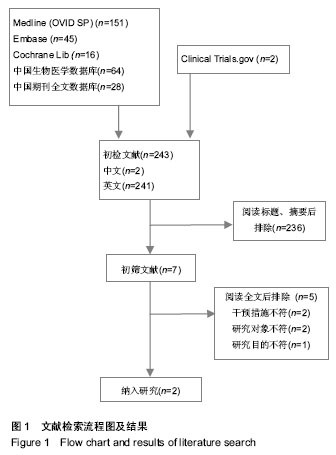
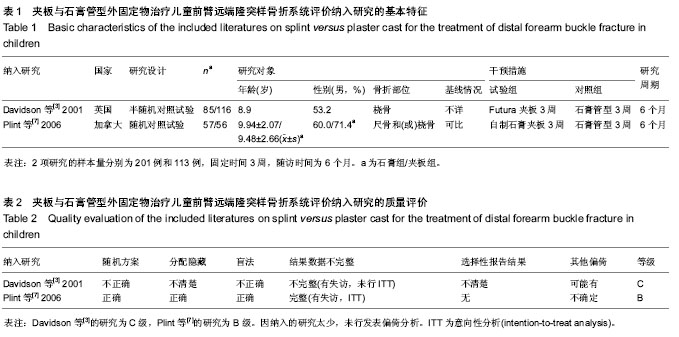
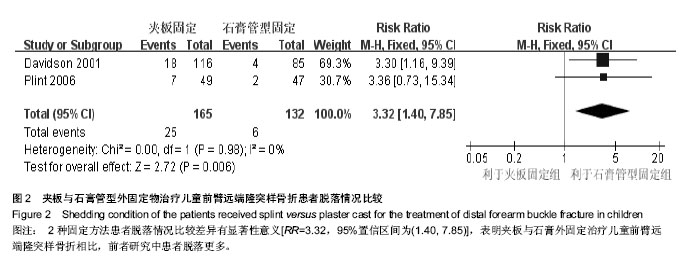
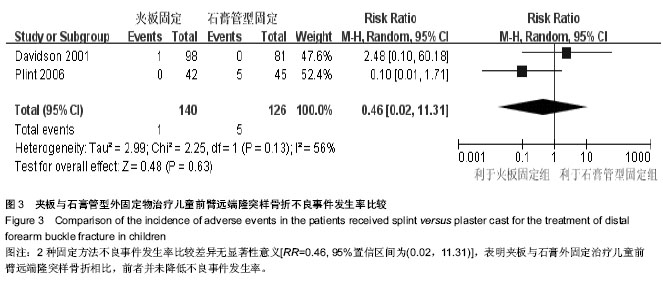
背景:儿童前臂远端隆突样骨折一般无继发移位风险,文献报道可通过石膏管型、掌侧托、夹板、支具以及绷带等外固定物治疗获得满意疗效。但是不同外固定物治疗对患儿功能恢复及生活能力的影响并不明确。 目的:评价夹板与石膏管型外固定物治疗儿童前臂远端隆突样骨折的疗效和安全性。 方法:计算机检索Medline、Embase、Cochrane 图书馆(2011年第3期)及中国生物医学数据库、中国期刊全文数据库,检索时限为建库至2011年4月;手工检索相关会议论文;在线检索重要临床试验注册中心,文献检索无语种限制。收集随机对照及半随机对照试验,行质量评价并采用Revman 5.1行Meta分析。 结果与结论:纳入2项研究,包括314例患者,1项随机对照试验评价为B级,1项半随机对照试验评价为C级。结果表明,夹板与石膏管型外固定物治疗后均无骨折、骨折不愈合以及再骨折,患肢疼痛以及书写、绘画、自理饮食、洗漱4方面生活能力差异无显著性意义;而固定后患儿洗澡能力夹板组早期优于石膏管型组,后期差异无显著性意义。参加规律运动方面亦为夹板固定组优于石膏管型固定组。两种固定方法不良事件发生率比较差异无显著性意义。提示夹板与石膏管型外固定物治疗儿童前臂远端隆突样骨折后患肢疼痛无明显改善,但夹板固定有利于维持洗澡能力及参加规律运动,且安全性良好。但仍需设计良好、实施完善的大样本、多中心随机对照试验验证。
中图分类号: