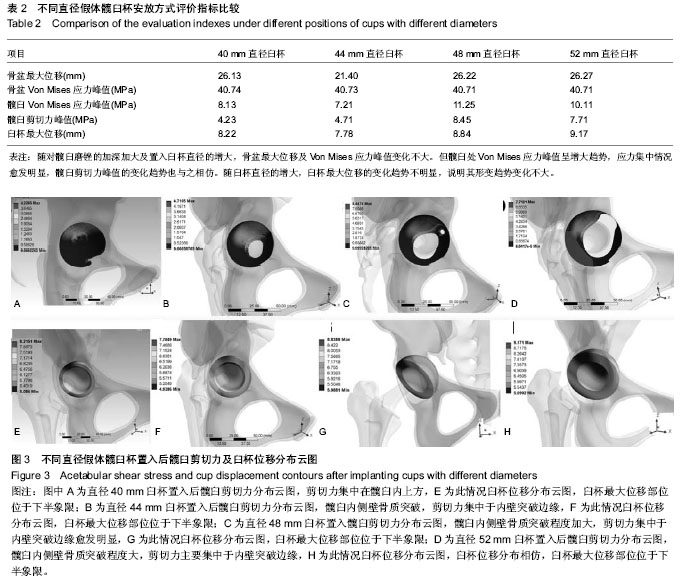
| [1] Aksoy C, Yilgor C, Demirkiran G, et al. Evaluation of acetabular development after Dega acetabuloplasty in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2013; 22(2):91-95.[2] Bracken J, Tran T, Ditchfield M. Developmental dysplasia of the hip: controversies and current concepts. J Paediatr Child Health. 2012;48(11):963-973.[3] Nemeth BA, Narotam V. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatr Rev. 2012. 33(12): 553-561.[4] Rogers BA, Garbedian S, Kuchinad RA, et al. Total hip arthroplasty for adult hip dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(19): 1809-1821.[5] Westacott D, Pattison G, Cooke S. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Community Pract. 2012;85(11): 42-44.[6] Hvid I. Neonatal hip instability, developmental dysplasia of the acetabulum, and the risk of early osteoarthrosis. Acta Orthop. 2008;79(3): 311-312.[7] Inan M, Chan G, Bowen JR. The correction of leg-length discrepancy after treatment in developmental dysplasia of the hip by using a percutaneous epiphysiodesis. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2008;17(1): 43-46.[8] Bozek M, Bielecki T, Nowak R, et al. Arthroplasty in patients with congenital hip dysplasia--early evaluation of a treatment method. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2013; 15(1):49-59.[9] Li H, Wang L, Dai K, et al. Autogenous impaction grafting in total hip arthroplasty with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(4): 637-643.[10] Schofer MD, Pressel T, Schmitt J, et al. Reconstruction of the acetabulum in THA using femoral head autografts in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011; 6: 32.[11] Yang S, Cui Q. Total hip arthroplasty in developmental dysplasia of the hip: Review of anatomy, techniques and outcomes. World J Orthop. 2012; 3(5): 42-48.[12] 艾进伟, 韩叶萍. Zweymüller系统在Crowe-Ⅲ、Ⅳ型髋臼发育不良全髋置换中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 12(44): 8615-8618.[13] Hintermann B, Morscher EW. Total hip replacement with solid autologous femoral head graft for hip dysplasia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1995;114(3): 137-144.[14] Mulroy RD Jr, Harris WH. Failure of acetabular autogenous grafts in total hip arthroplasty. Increasing incidence: a follow-up note. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990; 72(10):1536-1540.[15] Mitsuo N. Recent research and development in titanium alloys for biomedical applications and healthcare goods. Sci Technol Advan Mater. 2003;4:445-454.[16] Callaghan JJ, Rosenberg AC, Rubash HE, et al. The adult hip. lippincott. 1st ed. Williams & Wilkins, 1988: 15.[17] 赵诗奎. 氧化锆基纳微米复合陶瓷模具材料及其摩擦磨损特性研究[D]. 山东轻工业学院. 2009.[18] Herman S, Jaklic A, Herman S, et al. Hip stress reduction after Chiari osteotomy. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2002;40(4): 369-375.[19] Hipp JA, Sugano N, Millis MB, et al. Planning acetabular redirection osteotomies based on joint contact pressures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(364): 134-143.[20] 李永奖,张力成,杨国敬,等.全髋关节置换术后假体脱位的有限元研究[J].中医正骨,2007,19(12): 66-68.[21] 樊继波,覃勇,李莎,等.骨质疏松症全髋关节有限元模型的建立与分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011, 17(11): 989-992.[22] 胡敏,王兵,赵宏斌,等.先天性髋关节脱臼的干预策略进展[J].中国临床康复, 2005,9(2):198-199.[23] Scholz R, Hoffmann F, von Sachsen S, et al. Validation of density-elasticity relationships for finite element modeling of human pelvic bone by modal analysis. J Biomech. 2013; 46(15): 2667-2673.[24] Zhao X, Chosa E, Yamako G, et al. Effect of acetabular reinforcement ring with hook for acetabular dysplasia clarified by three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(10): 1765-1769.[25] Er MS, Verim O, Altinel L, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis used to compare six different methods of syndesmosis fixation with 3.5- or 4.5-mm titanium screws: a biomechanical study. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2013;103(3):174-180.[26] Goffin JM, Pankaj P, Simpson AH. The importance of lag screw position for the stabilization of trochanteric fractures with a sliding hip screw: a subject-specific finite element study. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(4): 596-600.[27] 曹振华,闫金玉,银和平,等.数字及逆向工程技术在复杂骨科应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(39): 7370-7374.[28] 陈宣煌,林海滨.数字化设计在脊柱疾病中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(22): 4159-4168.[29] Lerch M, Weigel N, Windhagen H, et al. Finite element model of a novel short stemmed total hip arthroplasty implant developed from cross sectional CT scans. Technol Health Care. 2013;21(5): 493-500.[30] Lam L, Drew T, Boscainos P. Effect of Acetabular Orientation on Stress Distribution of Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Liners. Orthopedics. 2013;36(11): e1346-e1352.[31] 徐灵军,朱海波,张银网,等.人工髋关节活体有限元建模及力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(26): 4770-4775.[32] 赵海波,龙腾河,杨伟江,等.CT和有限元数字化骨盆模型构建的研究和临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(39): 7327-7332.[33] 覃小东,符俏.人工髋关节假体的分类及设计[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(35): 6607-6614.[34] Chen DW, Lin CL, Hu CC, et al. Biomechanical consideration of total hip arthroplasty following failed fixation of femoral intertrochanteric fractures - a finite element analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2013;35(5): 569-575.[35] Elkins JM, Stroud NJ, Rudert MJ, et al. The capsule's contribution to total hip construct stability--a finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(11): 1642-1648.[36] Epasto G, Foti A, Guglielmino E, et al. Total hip arthroplasty by using a cementless ultrashort stem: a subject-specific finite element analysis for a young patient clinical case. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2013; 227(7): 757-766.[37] Munro JT, Anderson IA, Walker CG, et al. Finite element analysis of retroacetabular osteolytic defects following total hip replacement. J Biomech. 2013;46(14):2529-2533.[38] Britton JR, Walsh LA, Prendergast PJ. Mechanical simulation of muscle loading on the proximal femur: analysis of cemented femoral component migration with and without muscle loading. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003;18(7). 637-646.[39] Taylor ME, Tanner KE, Freeman MA, et al. Stress and strain distribution within the intact femur: compression or bending? Med Eng Phys. 1996;18(2): 122-131.[40] Phillips Andrew TM. Numerical modelling of the pelvis and acetabular construct following hip arthroplasty. PhD thesis, The University of Edinburgh, 2005.[41] 安明勋.人工髋关节假体的设计及界面应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(30): 5634-5638.[42] Gallo J, Goodman SB, Konttinen YT, et al. Osteolysis around total knee arthroplasty: a review of pathogenetic mechanisms. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(9): 8046-8058. |