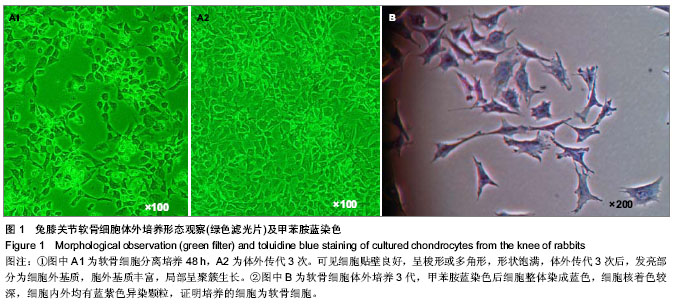
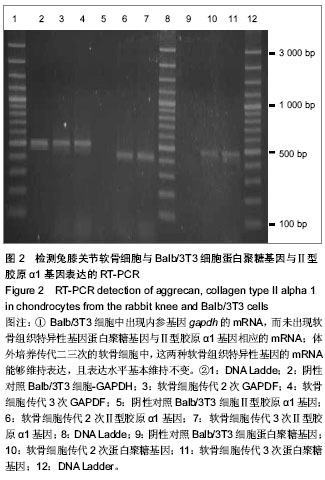
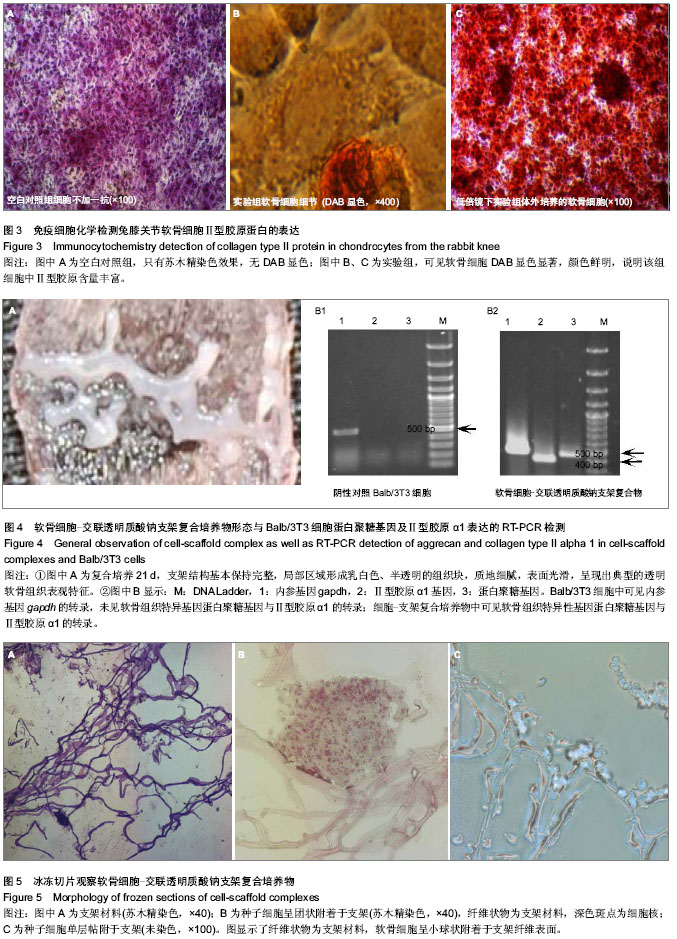
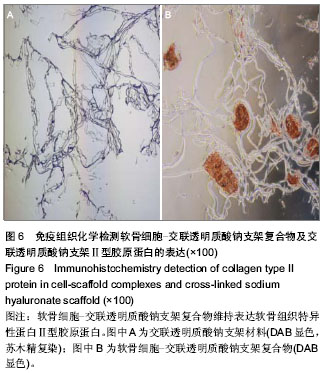
| [1] Buckwalter JA. Mechanical injuries of articular cartilage.Iowa Orthop J.1992;12:50-57.[2] 王建华,李靖年.骨性关节炎关节软骨损伤与修复的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2006,14(12):941-944.[3] Brittberg M,Lindahl A,Nilsson A,et al.Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the knee with autologous chondrocyte transplantation.New Engl J Med.1994;331(14):889-895.[4] Peterson L,Menche D,Grande D,et al. Chondrocyte transplantation-an experimental model in the rabbit. In: Transactions of the 30th Annual Orthopedic Research Society, Atlanta,1984.[5] Browne JE,Anderson AF,Arciero R,et al.Clinical outcome of autologous chondrocyte implantation at 5 years in US subjects.Clin Orthop.2005;436:237-245.[6] Lee CH,Marion NW,Hollister S,et al.Tissue formation and vascularization of anatomically shaped human tibial condyle in vivo.Tissue Eng Part A.2009;12:3923-3930.[7] Papadopoulos A,Bichara DA,Zhao X,et al.Injectable and photopolymerizable tissue-engineered auricular cartilage using poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate copolymer hydrogels.Tissue Engineering Part A. 2011;17(1-2): 161-169. [8] 王师平.组织工程软骨种子细胞研究进展[J].中国美容医学,2012, 21(11):1655-1658.[9] 裴国献,魏宽海,金丹.组织工程学实验技术[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2006:69-70.[10] Yan H,Yu C.Repair of full-thickness cartilage defects with cells of different origin in a rabbit model.Arthroscopy. 2007;23(2): 178-187.[11] 柳菁,宇丽,许超.间充质干细胞向软骨细胞表型分化的研究进展[J].中国生物工程杂志,2011,31(6):129-134.[12] 鄂征,刘流.医学组织工程技术与临床应用[M].北京:北京出版社, 2003:378-379.[13] 凌沛学,梁虹,贺艳丽,等.透明质酸钠在关节疾病中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2002,16(1):1-4.[14] 杜国辉,屈爱存,陈建英,等.透明质酸对关节软骨蛋白聚糖 aggrecan的影响[J].中国生化药物杂志,2011,32(2):125-127.[15] 陈祥娥,凌沛学.透明质酸与化妆品[J].食品与药品,2010,12(7): 278-280.[16] 田峰,崔学生,张帅,等.改良分步消化法培养原代软骨细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(20):3633-3635.[17] 王朝强,田丰德,谢辉,等.犬关节软骨细胞的体外分离与培养[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(46):8593-8598.[18] Dragoo JL,Samimi B,Zhu M,et al.Tissue-engineered cartilage and bone using stem cells from human infrapatellar fat pads.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2003;85(5):740-747.[19] Cheng NC,Estes BT,Young TH,et al.Engineered cartilage using primary chondrocytes cultured in a porous cartilage-derived matrix.Regen Med.2011;6(1):81-93.[20] Chua KH,Aminuddin BS,Fuzina NH,et al. Insulin-transferrin- selenium prevent human chondrocyte dedifferentiation and promote the formation of high quality tissue engineered human hyaline cartilage.Eur Cell Mater. 2005;9(9):58-67.[21] Responte D,Natoli R,Athanasiou K.Identification of potential biophysical and molecular signalling mechanisms underlying hyaluronic acid enhancement of cartilage formation.J R Soc Interface.2012;9(77):3564-3573.[22] Cianflocco AJ. Viscosupplementation in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee.Postgrad Med.2013;125(1): 97-105.[23] Becker LC,Bergfeld WF,Belsito DV,et al.Final report of the safety assessment of hyaluronic acid, potassium hyaluronate, and sodium hyaluronate.Int J Toxicol. 2009; 28(4 suppl):5-67.[24] 凌沛学,梁虹,贺艳丽,等.透明质酸钠在关节疾病中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2002,16(1):1-4.[25] Dover JS,Rubin MG,Bhatia AC.Review of the efficacy, durability, and safety data of two nonanimal stabilized hyaluronic acid fillers from a prospective, randomized, comparative,multicenter study.Dermatol Surg.2009;35 Suppl 1:322-330.[26] Agerup B,Berg P,Akermark C.Non-animal stabilized hyaluronic acid: a new formulation for the treatment of osteoarthritis.BioDrugs.2005;19(1):23-30.[27] 石艳丽,王凤山,郭学平,等.发酵法生产玻璃酸研究概况[J].药物生物技术, 2004,11(6):410-410. |