| [1] 刘永锋.心脏死亡供者器官评估及体外修复[J].中华器官移植杂志,2010,31(7):393-396.[2] 邓永林,沈中阳.我国心脏死亡器官捐献的现状及影响因素[J].中华外科杂志,2012,50(8):673-674.[3] 董权,李超,王胤佳,等.中国实行心脏死亡器官捐献供体的可行性分析[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2012,19(5):498-501.[4] 尹志科,严谨.心脏死亡器官捐献的困境及对策[J].医学与哲学, 2012,33(1):28-29,32.[5] 刘永锋.心脏死亡供者器官评估及体外修复[J].中华器官移植杂志, 2010,31(7):393-396.[6] 杨春华,陈雪霞,谢文锋,等.器官捐献与供体维护[J].新医学,2013, 44(6):363-365.[7] 门贺伟,蔡金贞.心脏死亡供肝热缺血-损伤的研究进展[J].国际移植与血液净化杂志,2011,9(4):8-12.[8] 刘学民,王博,于良,等.心脏死亡供体经典原位肝移植的单中心临床研究[J].器官移植,2013,4(1):23-27.[9] 王毅,赵闻雨,朱有华.心脏死亡供肾评估和保存的现状及进展[J].中华器官移植杂志,2011,32(8):510-512.[10] Hill DJ, Evans DW, Gresham GA. Availability of cadaver organs for transplantation. BMJ. 1991;303(6797):312.[11] 骆助林,权毅,潘显明,等.外科缺血再灌注过程中的线粒体损伤[J].西南军医,2008,10(4):113-114.[12] 姜斌,朱有华.线粒体靶向小分子多肽减轻供者器官缺血再灌注损伤的研究进展[J].中华器官移植杂志,2011,32(5): 314-316.[13] 林杰,何飞,吴林熹,等.线粒体途径在缺血后处理减轻大鼠肝脏缺血再灌注损伤作用中的机制研究[J].中华器官移植杂志,2012, 33(10):624-628.[14] Flameng W, Borgers M, Daenen W,et al. Ultrastructural and cytochemical correlates of myocardial protection by cardiac hypothermia in man.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980;79(3): 413-424.[15] 王苏华,张薇,邢光伟,等.细胞色素C氧化酶活力测定方法概况[J].毒理学杂志,2010,24(5):412-414.[16] 薛亮,郑树森.活体肝移植术后胆道并发症一例[J].中华移植杂志(电子版),2013,7(1):36-38.[17] Pompili M, Francica G, Ponziani FR,et al. Bridging and downstaging treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients on the waiting list for liver transplantation.World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(43):7515-7530.[18] Martínez-Alarcón L, Ríos A, Ramis G,et al. Factor Analysis of Sources of Information on Organ Donation and Transplantation in Journalism Students.Transplant Proc. 2013; 45(10):3579-3581. [19] Lee Cheah Y, K H Chow P. Liver Transplantation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Appraisal of Current Controversies.Liver Cancer. 2012;1(3-4):183-189.[20] Yoo PS, Umman V, Rodriguez-Davalos MI,et al. Retransplantation of the liver: review of current literature for decision making and technical considerations.Transplant Proc. 2013;45(3):854-859. [21] Reddy MS, Varghese J, Venkataraman J,et al. Matching donor to recipient in liver transplantation: Relevance in clinical practice.World J Hepatol. 2013;5(11):603-611.[22] Singal AK, Chaha KS, Rasheed K, et al.Liver transplantation in alcoholic liver disease current status and controversies. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(36):5953-5963.[23] Jones PD, Hayashi PH, Barritt S 4th. Liver transplantation in 2013: challenges and controversies.Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2013;59(2):117-131.[24] 俞栋栋,周琳,郑树森.肝移植临床可操作性耐受的研究现状及展望[J].中华移植杂志(电子版),2013,7(2):103-107.[25] 周健,胡安斌,何晓顺.在体劈离式肝移植的外科技术进展[J].中华医学杂志,2013,93(40):3241-3243.[26] Neyrinck A, Van Raemdonck D, Monbaliu D. Donation after circulatory death: current status.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2013;26(3):382-390. [27] Siminoff LA, Agyemang AA, Traino HM.Consent to organ donation: a review.Prog Transplant. 2013;23(1):99-104. [28] 丁义涛.心脏死亡供者肝移植的现状与展望[J].中华器官移植杂志,2013,34(1):1-4.[29] Ohe H, Hoshino J, Ozawa M.Factors affecting outcomes of liver transplantation: an analysis of OPTN/UNOS database. Clin Transpl. 2011:39-53.[30] 沈中阳.供肝短缺背景下我国肝癌患者肝移植的策略[J].中华器官移植杂志,2013,34(9):513-515.[31] 黄洁夫.创建符合中国国情的器官捐献与移植体系[J].中华外科杂志,2013,51(1):1-3.[32] Wertheim JA, Petrowsky H, Saab S,et al. Major challenges limiting liver transplantation in the United States.Am J Transplant. 2011;11(9):1773-1784. [33] Farmer DG, Amersi F, Kupiec-Weglinski J, et al. Current status of ischemia and reperfusion injury in the liver.Transplantation Reviews. 2000;14(2):106-126.[34] Reich DJ, Munoz SJ, Rothstein KD,et al. Controlled non-heart-beating donor liver transplantation: a successful single center experience, with topic update.Transplantation. 2000;70(8):1159-1166.[35] Abt P, Crawford M, Desai N,et al.Liver transplantation from controlled non-heart-beating donors: an increased incidence of biliary complications.Transplantation. 2003;75(10): 1659-1663.[36] Baldwin WM 3rd, Larsen CP, Fairchild RL.Innate immune responses to transplants: a significant variable with cadaver donors.Immunity. 2001;14(4):369-376.[37] Halloran PF, Autenried P, Ramassar V,et al. Local T cell responses induce widespread MHC expression. Evidence that IFN-gamma induces its own expression in remote sites.J Immunol. 1992;148(12):3837-3846.[38] Weiser MR, Williams JP, Moore FD Jr,et al.Reperfusion injury of ischemic skeletal muscle is mediated by natural antibody and complement.J Exp Med. 1996;183(5):2343-2348.[39] Weisman HF, Bartow T, Leppo MK,et al.Soluble human complement receptor type 1: in vivo inhibitor of complement suppressing post-ischemic myocardial inflammation and necrosis.Science. 1990;249(4965):146-151.[40] Sun X, Kimura T, Kobayashi T,et al.Viability of liver grafts from fasted donor rats: relationship to sinusoidal endothelial cell apoptosis.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2001;8(3):268-273.[41] Noormohamed MS, Kanwar A, Ray C,et al.Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for resuscitation of deceased cardiac donor livers for hepatocyte isolation.J Surg Res. 2013;183 (2):e39-48. [42] Taylor MJ, Baicu SC.Current state of hypothermic machine perfusion preservation of organs: The clinical perspective. Cryobiology. 2010;60(3 Suppl):S20-35.[43] Domínguez-Gil B, Haase-Kromwijk B, Van Leiden H,et al.Current situation of donation after circulatory death in European countries.Transpl Int. 2011;24(7):676-686.[44] 杨春华,陈雪霞,谢文锋,等.器官捐献与供体维护[J].新医学, 2013,44(6):363-365.[45] 候萍,李剑平. 器官移植前保存的理论研究与临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(5):895-898.[46] Shen XD, Ke B, Uchida Y,et al. Native macrophages genetically modified to express heme oxygenase 1 protect rat liver transplants from ischemia/reperfusion injury.Liver Transpl. 2011;17(2):201-210. [47] 张静,李胜兰,吴媛,等. 定位在线粒体的肝刺激因子对线粒体膜电势的影响[J]. 中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2013,22(2): 89-94.[48] 何晓顺,马毅,陈规划,等.大鼠肝脏热缺血损伤后组织学与超微结构变化的动态观察[J].中华实验外科杂志,2002,19(3):249-251.[49] Khalimonchuk O, Bird A, Winge DR.Evidence for a pro-oxidant intermediate in the assembly of cytochrome oxidase.J Biol Chem. 2007;282(24):17442-17449.[50] Srinivasan S, Avadhani NG.Cytochrome c oxidase dysfunction in oxidative stress.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012; 53(6):1252-1263. [51] 李保良,赵晓山,罗仁,等. 亚健康疲劳状态时血清对骨骼肌细胞线粒体膜细胞色素C氧化酶活性和线粒体能量负荷的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(37):7258-7262.[52] Yoshikawa S, Muramoto K, Shinzawa-Itoh K.Reaction mechanism of mammalian mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;748:215-236. [53] Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J,et al. Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell. 1996;86(1):147-157.[54] Ferraro E, Corvaro M, Cecconi F. Physiological and pathological roles of Apaf1 and the apoptosome.J Cell Mol Med. 2003;7(1):21-34.[55] 杨栎,余时沧.线粒体DNA损伤与细胞凋亡[J].标记免疫分析与临床,2013,20(5):325-328.[56] 兰春慧,房殿春,樊丽琳,等.线粒体损伤在幽门螺杆菌诱导胃癌细胞凋亡中的作用[J].中华内科杂志,2005,44(10):748-750.[57] 李云,刘菲.线粒体与细胞凋亡的研究进展[J].中国实用眼科杂志, 2013,31(8):957-960.[58] 闫鹏,吕刚,胡萌,等.细胞色素C释放与Caspase-3表达在脊髓损伤后神经元细胞凋亡过程中的作用[J].山东医药,2009,49(52): 46-48.[59] 史洪涛,李陶,陈东风,等.线粒体-细胞色素C途径在非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠肝细胞凋亡中的作用[J].重庆医学,2007,36(8):701-703.[60] 黄卡特,吴秀玲,黄海霞,等.细胞色素C在急性肝衰竭大鼠中的蛋白表达变化及其意义[J].实用医学杂志,2009,25(17):2826- 2828.[61] Fujimura M, Morita-Fujimura Y, Murakami K,et al. Cytosolic redistribution of cytochrome c after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1998;18(11): 1239-1247.[62] Monian P, Jiang X.Clearing the final hurdles to mitochondrial apoptosis: regulation post cytochrome C release.Exp Oncol. 2012;34(3):185-191.[63] Choi DW.Ischemia-induced neuronal apoptosis.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1996;6(5):667-672.[64] 王楠,马庆久,鲁建国,等.缺血后处理对大鼠移植肝缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].中华外科杂志,2005,43(23):1533-1536.[65] 彭勇,刘作金,龚建平,等.Kupffer细胞CD14及Toll样受体4介导大鼠肝移植缺血再灌注损伤的机制[J].中华外科杂志,2005, 43(5):274-276.[66] 吴勤荣,时军,王永刚.细胞凋亡与肝移植缺血再灌注损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(18):3371-3375.[67] 刘现忠,姚爱华,仲跻巍,等.缺血预处理对大鼠减体积肝移植缺血再灌注损伤的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2007,17(19): 2313-2317.[68] 张雷达,王曙光,李晓武,等.冷保存对肝移植术后肝内胆管微循环的影响[J].中华外科杂志,2007,45(5):339-343.[69] 崔东旭,尹剑桥,柴芳,等.不同胆道灌洗液对肝移植供体胆道冷保存损伤的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(38): 7556-7560.[70] 马毅,何晓顺. 肝脏移植热缺血损伤的研究进展[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志,2001,7(8) :508-510.[71] 徐根云,吕国才,陈瑜,等.血清对氧磷酯酶1活性监测在肝移植术中的意义[J].中华检验医学杂志,2004,27(8):493-495.[72] 池萍,卢实春,王孟龙,等.肝移植手术中心血管活性物质对血流动力学和肾功能的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2009,25(9):741-744.[73] 宋丽洁,姚桂玲,刘煜,等.亲体肝移植患者围手术期止血与凝血指标的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(31): 5737-5740.[74] 孙强,余元龙,胡泽民,等.心脏死亡供体热缺血再灌注损伤对肝内胆道微循环影响的实验研究[J].中华普通外科杂志,2009,24(4): 333-334.[75] 邰强,何晓顺,王东平,等.心脏死亡器官捐献供者应用血管活性药物对供肝质量及肝移植受者的影响[J].中华器官移植杂志,2013, 34(7):411-414.[76] Campbell P.Clinical relevance of human leukocyte antigen antibodies in liver, heart, lung and intestine transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2013;18(4): 463-469. |
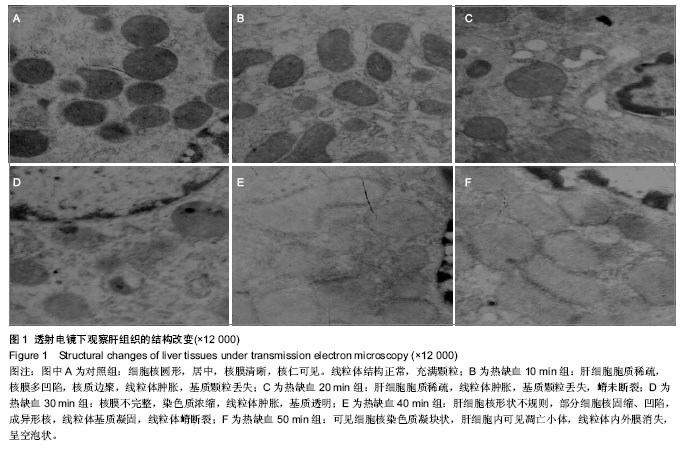

.jpg)
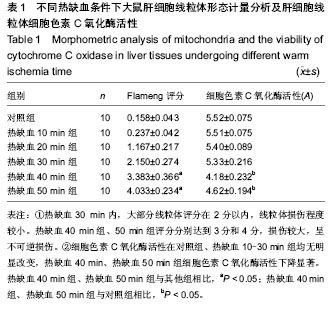
.jpg)