| [1]Day CS, Yeh AC, Franko O, et al. Musculoskeletal medicine: an assessment of the attitudes and knowledge of medical students at Harvard Medical School. Acad Med. 2007;82(5):452-457.
[2]Sarmiento A, Waddell JP, Latta LL. Diaphyseal humeral fractures: treatment options. Instr Course Lect. 2002;51: 257-269.
[3]Kreb DL, Blokhuis TJ, van Wessem KJ, et al. Intramedullary nailing without interlocking screws for femoral and tibial shaft fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(8):1109-1113.
[4]Heineman DJ, Poolman RW, Nork SE, et al. Plate fixation or intramedullary fixation of humeral shaft fractures. Acta Orthop. 2010;81(2):216-223.
[5]Tsourvakas S, Alexandropoulos C, Papachristos I, et al. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures with antegrade intramedullary locking nail. Musculoskelet Surg. 2011;95(3): 193-198.
[6]Steffner RJ, Lee MA. Emerging concepts in upper extremity trauma: humeral shaft fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. 2013; 44(1):21-33.
[7]Strohm PC, Reising K, Hammer T, et al. Humerus shaft fractures - where are we today? Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2011;78(3):185-189.
[8]Benegas E, Amódio DT, Correia LFM, et al. Prospective randomized comparative study between surgical treatment of humeral shaft fractures with bridging plate and interlocking nail (preliminary). Acta Ortop Bras. 2007;15(2):87-92.
[9]Bolano LE, Vasicek V. Operative treatment of humerus shaft fractures: A prospective randomized study comparing intramedullary nailing with dynamic compression plating. Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 1995.
[10]Changulani M, Jain UK, Keswani T. Comparison of the use of the humerus intramedullary nail and dynamic compression plate for the management of diaphyseal fractures of the humerus. A randomised controlled study. Int Orthop. 2007; 31(3):391-395.
[11]Chapman JR, Henley MB, Agel J, et al. Randomized prospective study of humeral shaft fracture fixation: intramedullary nails versus plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2000; 14(3):162-166.
[12]Chiu FY, Chen CM, Lin CF, et al. Closed humeral shaft fractures: a prospective evaluation of surgical treatment. J Trauma. 1997;43(6):947-951.
[13]Da?lar B, Delialio?lu OM, Ta?ba? BA, et al. Comparison of plate-screw fixation and intramedullary fixation with inflatable nails in the treatment of acute humeral shaft fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2007;41(1):7-14.
[14]Kesemenli CC, Suba?i M, Arslan H, et al. Comparison between the results of intramedullary nailing and compression plate fixation in the treatment of humerus fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2003;37(2):120-125.
[15]Li Y, Wang C, Wang M, et al. Postoperative malrotation of humeral shaft fracture after plating compared with intramedullary nailing. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011;20(6): 947-954.
[16]McCormack RG, Brien D, Buckley RE, et al. Fixation of fractures of the shaft of the humerus by dynamic compression plate or intramedullary nail. A prospective, randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(3):336-339.
[17]Putti AB, Uppin RB, Putti BB. Locked intramedullary nailing versus dynamic compression plating for humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2009;17(2):139-141.
[18]Raghavendra S, Bhalodiya HP. Internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the humerus by dynamic compression plate or intramedullary nail: A prospective study. Indian J Orthop. 2007; 41(3):214-218.
[19]Rodríguez-Merchán EC. Compression plating versus hackethal nailing in closed humeral shaft fractures failing nonoperative reduction. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(3):194-197.
[20]Singisetti K, Ambedkar M. Nailing versus plating in humerus shaft fractures: a prospective comparative study. Int Orthop. 2010;34(4):571-576.
[21]黄鹏,唐佩福,姚琦,等.带锁髓内钉与锁定加压钢板内固定治疗肱骨干骨折的随机对比研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008, 23(9):3.
[22]李丹,王刚,谷贵山,等.髓内钉与钢板治疗肱骨干骨折患者的疗效及安全性比较[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2011,37(2):342-344.
[23]An ZQ, He XJ, Jiang CL, et al. Treatment of middle third humeral shaft fractures: minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis versus expandable nailing. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2012;22(3):193-199.
[24]Chao TC, Chou WY, Chung JC, et al. Humeral shaft fractures treated by dynamic compression plates, Ender nails and interlocking nails. Int Orthop. 2005;29(2):88-91.
[25]Chen F, Wang Z, Bhattacharyya T. Outcomes of nails versus plates for humeral shaft fractures: a Medicare cohort study. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(2):68-72.
[26]Denies E, Nijs S, Sermon A, et al. Operative treatment of humeral shaft fractures. Comparison of plating and intramedullary nailing. Acta Orthop Belg. 2010;76(6):735-742.
[27]Flinkkilä T, Hyvönen P, Siira P, et al. Recovery of shoulder joint function after humeral shaft fracture: a comparative study between antegrade intramedullary nailing and plate fixation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124(8):537-541.
[28]Khan AS, Afzal W, Anwar A. Comparison of shoulder function, radial nerve palsy and infection after nailing versus plating in humeral shaft fractures. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2010; 20(4):253-257.
[29]Lin J. Treatment of humeral shaft fractures with humeral locked nail and comparison with plate fixation. J Trauma. 1998;44(5):859-864.
[30]Bhandari M, Devereaux PJ, McKee MD, et al. Compression plating versus intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures--a meta-analysis. Acta Orthop. 2006;77(2):279-284.
[31]李连华,孙天胜,刘智,等.钢板内固定和髓内针固定比较治疗成人肱骨干骨折疗效的系统评价[J].中国循证医学杂志,2008, 8(8): 662-667.
[32]Kurup H, Hossain M, Andrew JG. Dynamic compression plating versus locked intramedullary nailing for humeral shaft fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(6): CD005959.
[33]Ouyang H, Xiong J, Xiang P, et al. Plate versus intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures: an updated meta-analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(3): 387-395.
[34]Wang X, Chen Z, Shao Y, et al. A meta-analysis of plate fixation versus intramedullary nailing for humeral shaft fractures. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(3):388-397.
[35]Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12. |
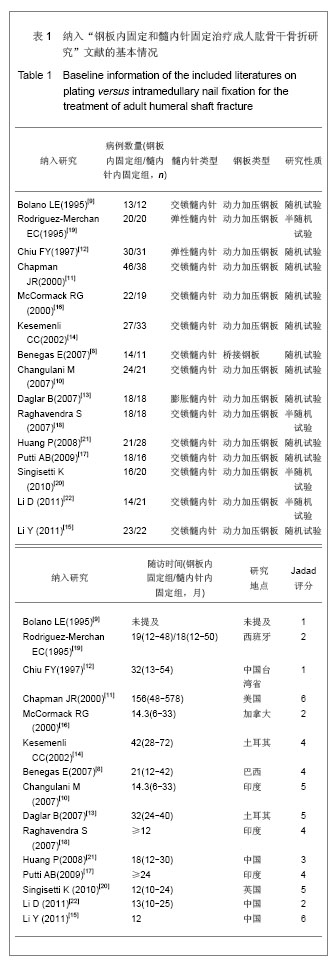
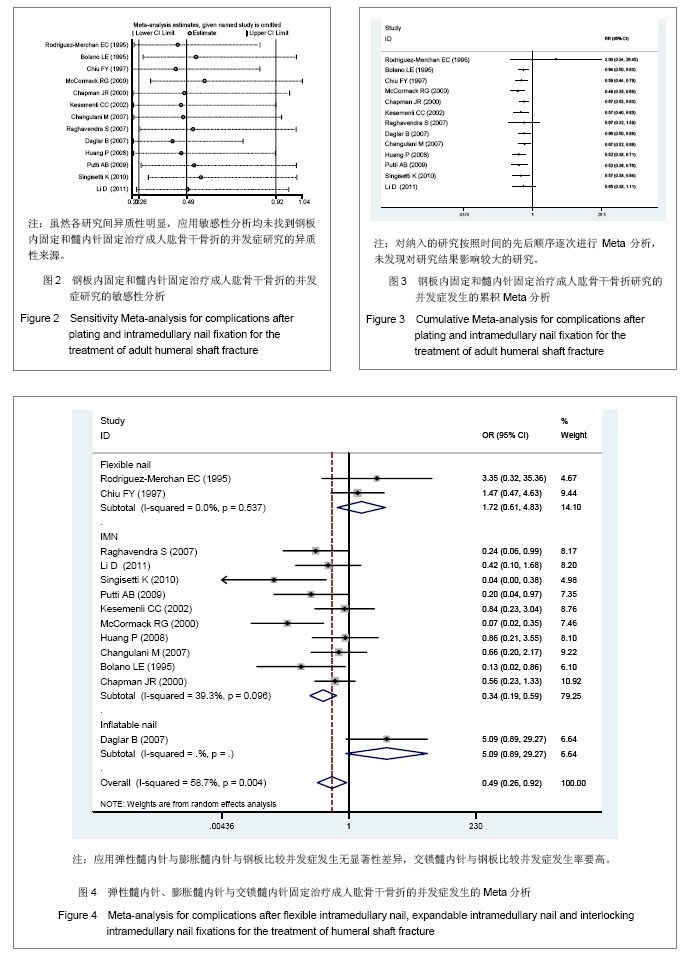
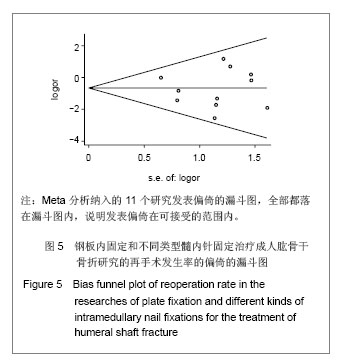
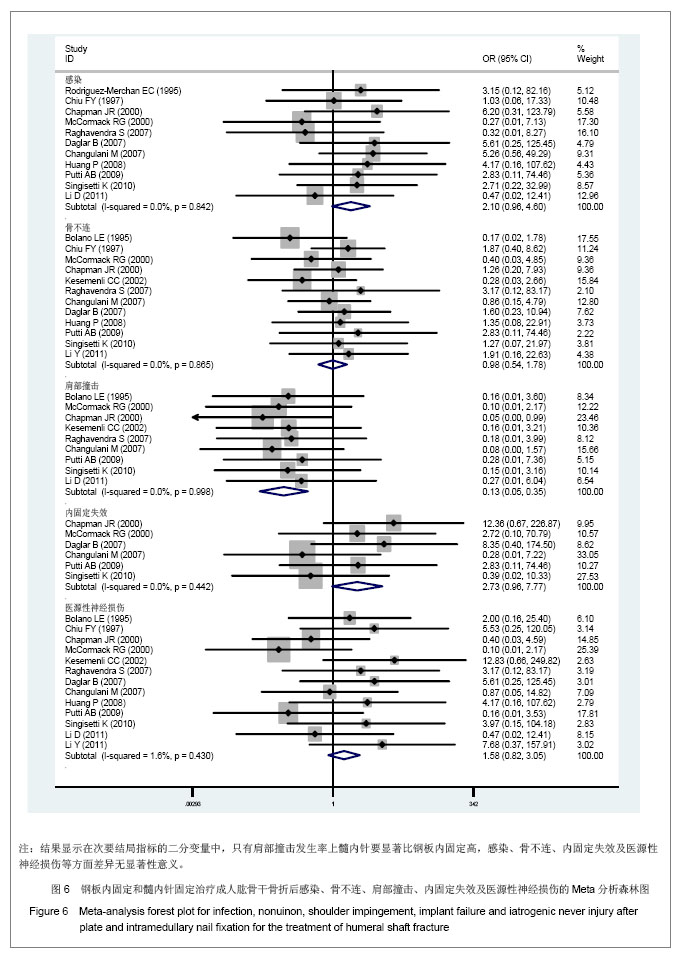
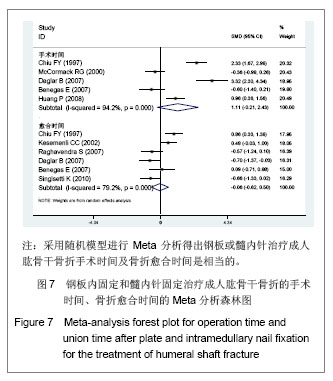
.jpg)