| [1]Shrader MW, Jacofsky DJ, Stans AA,et al. Femoral neck fractures in pediatric patients: 30 years experience at a level 1 trauma center. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;454: 169-173.
[2]Li Y, Heyworth BE, Glotzbecker M, et al. Comparison of titanium elastic nail and plate fixation of pediatric subtrochanteric femur fractures. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013; 33(3):232-238.
[3]王满宜,杨庆铭,曾烦芳,等.骨折治疗的AO原则[M].北京:华夏出版社.2003:682-683.
[4]吉士俊.小儿髋关节外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社. 2005:15-23.
[5]赵炬才,张铁良,髋关节外科学[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社出版.1992:32-42.
[6]马若凡,刘尚礼,许杰.国人股骨上段测量及其临床意义[J].临床骨科杂志,2002,5 (3):164-166.
[7]Heidari N, Eberl R, Wiklicky S, et al. Anatomical landmarks in the paediatric distal radius: a new method for measuring epiphyseal height. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011;33(8):683-687.
[8]陈振光,余国荣,喻爱喜,等.儿童股骨头骺板的解剖定位及其临床意义[J].中华实验外科,1997,14(2):92-93.
[9]Ogden JA. Changing patterns of proximal femoral vascularity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56(5):941-950.
[10]郭世绂.临床骨科解剖学[M].天津:天津科学技术出版社,1991: 707-734.
[11]王启华,孙博.临床解剖学丛书—四肢分册[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,1998: 246-258.
[12]Akahane T, Fujioka F, Shiozawa R. A transepiphyseal fracture of the proximal femur combined with a fracture of the mid-shaft of ipsilateral femur in a child: a case report and literature review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006;126(5):330-334.
[13]Morsy HA. Complications of fracture of the neck of the femur in children. A long-term follow-up study. Injury. 2001;32(1): 45-51.
[14]Mirdad T. Operative treatment of femoral shaft fractures in children: a nine-year experience in a Saudi Arabian population. Injury. 2000;31(10):769-771.
[15]Flynn JM, Wong KL, Yeh GL, et al. Displaced fractures of the hip in children. Management by early operation and immobilisation in a hip spica cast. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002; 84(1):108-112.
[16]Hedin H, Hjorth K, Rehnberg L, et al. External fixation of displaced femoral shaft fractures in children: a consecutive study of 98 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2003;17(4):250-256.
[17]Cheng JC, Tang N. Decompression and stable internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in children can affect the outcome. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;19(3):338-343.
[18]Yeranosian M, Horneff JG, Baldwin K, et al. Factors affecting the outcome of fractures of the femoral neck in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95-B (1):135-142.
[19]Eberl R, Singer G, Ferlic P, et al. Post-traumatic coxa vara in children following screw fixation of the femoral neck. Acta Orthop. 2010;81(4):442-445.
[20]Pape HC, Krettek C, Friedrich A, et al. Long-term outcome in children with fractures of the proximal femur after high-energy trauma. J Trauma. 1999;46(1):58-64.
[21]Plánka L, Chalupová P, Charvátová M, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging for detection of rotational deformities in children with femoral shaft fractures treated by the ESIN method. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2010;77(1):39-42.
[22]Gopinathan NR, Chouhan D, Akkina N, et al. Case report: Bilateral femoral neck fractures in a child and a rare complication of slipped capital epiphysis after internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(10):2941-2945.
[23]Zhang H, Jin L, Li W, et al. Anterior dislocation of the sacroiliac joint with complex fractures of the pelvis and femur in children: a case report. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2013 Mar 22.
[24]Park SS, Noh H, Kam M. Risk factors for overgrowth after flexible intramedullary nailing for fractures of the femoral shaft in children. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(2):254-258.
[25]Bandyopadhyay R, Mukherjee A. Short term complications of titanium elastic nail in the treatment of diaphyseal fracture of the femur in children. Open Orthop J. 2013;7:12-17.
[26]Brousil J, Hunter JB. Femoral fractures in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2013;25(1):52-57.
[27]Bieger R, Ignatius A, Reichel H, et al. Biomechanics of a short stem: In vitro primary stability and stress shielding of a conservative cementless hip stem.J Orthop Res. 2013;31(8): 1180-1186.
[28]Wouters I, Almonroeder T, Dejarlais B, et al. Effects of a movement training program on hip and knee joint frontal plane running mechanics. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2012;7(6): 637-646.
[29]Allen MJ. Advances in total joint replacement in small animals. J Small Anim Pract. 2012;53(9):495-506.
[30]Probst A, Schneider T, Hankemeier S, et al. The prosthesis nail -- a new stable fixation device for periprosthetic fractures and critical fractures of the proximal femur. Unfallchirurg. 2003;106(9):722-731.
[31]Yu YX, Ma JZ, Zhu LB, et al. Failure of internal fixation on displaced femoral neck fractures in adults under fifty-five years old. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(7):542-545.
[32]马元璋,郑祖根,万鹏,等.临床骨内固定学[M].合肥:安徽科学技术出版社,1999.
[33]Khan SK, Khanna A, Parker MJ. Posterior multifragmentation of the femoral neck: does it portend a poor outcome in internally fixed intracapsular hip fractures? Injury. 2009;40(3): 280-282.
[34]Gao K, Gao W, Li F, et al. Treatment of ipsilateral concomitant fractures of proximal extra capsular and distal femur. Injury. 2011;42(7):675-681. Injury. 2011;42(7):675-681.
[35]Bonnaire F, Lein T, Hohaus T,et al. Prosthetic care of proximal femur fractures. Unfallchirurg. 2005;108(5):387-399.
[36]秦步平,王以进,黄圣达,等.三枚双头空心加压钉(DECS)治疗股骨颈骨折的生物力学研究与临床应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2002,10(8):810-812.
[37]康少英,张克亮.旋髂深血管骨瓣移植治疗小儿股骨颈骨折骨不连[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2006,21(3):220.
[38]李坚,唐尚权,付纳新,等.儿童青少年股骨颈colonnaⅡ型骨折的两种内固定方法比较研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008, 23(3):253-254.
[39]朱通伯,戴克戎.骨科手术学[M].第2版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 1998:790-793.
[40]Quick TJ, Eastwood DM.Pediatric fractures and dislocations of the hip and pelvis.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2005;432:87-96.
[41]周健,卜海富.儿童股骨颈骨折的临床研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,1997,32(3): 235-237.
[42]Mecham N. Pediatric proximal femur fractures--what the trauma nurse should know. J Trauma Nurs. 2003;10(2):52-55.
[43]Togrul E, Bayram H, Gulsen M,et al. Fractures of the femoral neck in children: long-term follow-up in 62 hip fractures. Injury. 2005;36(1):123-130.
[44]Mirdad T. Fractures of the neck of femur in children: an experience at the Aseer Central Hospital, Abha, Saudi Arabia. Injury. 2002;33(9):823-827. |
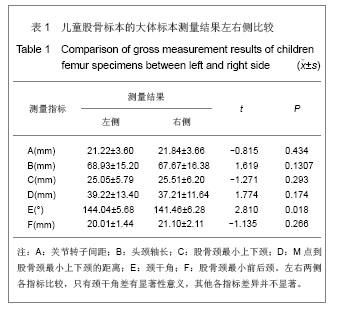
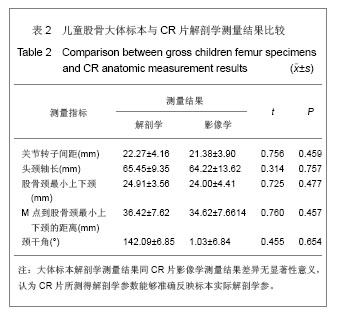
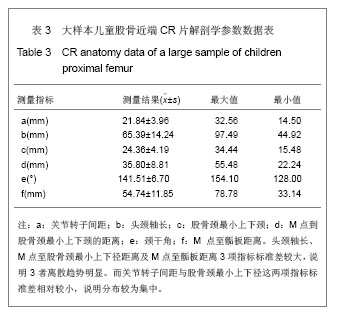
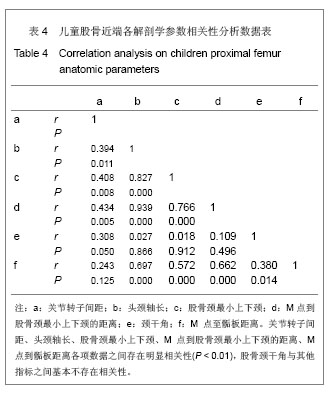
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
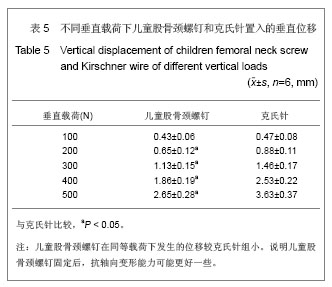
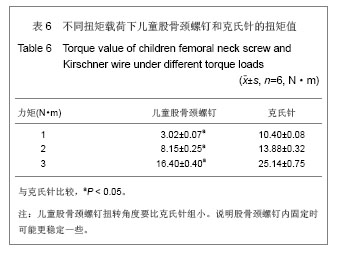
.jpg) 据Ogden[9]的研究表明,无螺纹的细钢针穿过骺板中央,只占骺板的很少范围,即使产生骨骺到干骺端的局部限制,但对整个骺板的生长潜力影响很小,甚至完全没有影响,而有螺纹的钢针固定牢靠,但可发生骺板细胞被压缩而发生骨骺早闭。儿童股骨颈螺钉和儿童鹅头钉、儿童角钢板刃相比,内固定物更加细小,进一步减少了对股骨头血运的影响。可以置入3枚螺钉,3枚螺钉沿股骨颈纵轴方向置入股骨颈,呈倒三角形分布,在空间呈三角形结构,使其在不同平面固定,有较强的抗旋转作用,有利于骨折的愈合。理论上能够恢复骨的正常结构及应力传导,达到对骨折的稳定固定。
据Ogden[9]的研究表明,无螺纹的细钢针穿过骺板中央,只占骺板的很少范围,即使产生骨骺到干骺端的局部限制,但对整个骺板的生长潜力影响很小,甚至完全没有影响,而有螺纹的钢针固定牢靠,但可发生骺板细胞被压缩而发生骨骺早闭。儿童股骨颈螺钉和儿童鹅头钉、儿童角钢板刃相比,内固定物更加细小,进一步减少了对股骨头血运的影响。可以置入3枚螺钉,3枚螺钉沿股骨颈纵轴方向置入股骨颈,呈倒三角形分布,在空间呈三角形结构,使其在不同平面固定,有较强的抗旋转作用,有利于骨折的愈合。理论上能够恢复骨的正常结构及应力传导,达到对骨折的稳定固定。