• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
骨形态发生蛋白7诱导骨膜细胞碱性磷酸酶的表达
廖家成1,贝抗胜2,连银川1
- 1深圳市龙华人民医院骨外科,广东省深圳市 518109;2韶关市粤北人民医院,广东省韶关市 512025
Bone morphogenetic protein-7 induces the expression of alkaline phosphatase in periosteal cells
Liao Jia-cheng1, Bei Kang-sheng2, Lian Yin-chuan1
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Longhua People’s Hospital, Shenzhen 518109, Guangdong Province, China; 2 Yue Bei People’s Hospital, Shaoguan 512025, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
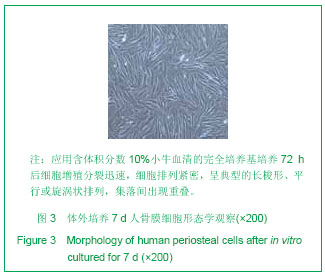
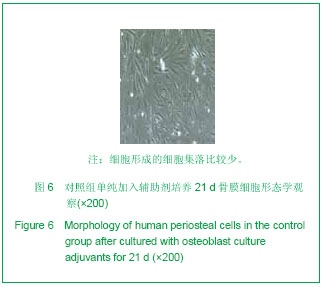
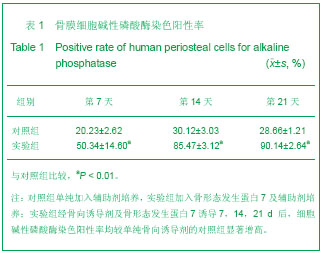
背景:关于骨形态发生蛋白7作为刺激因子诱导细胞成骨的报道目前较少见。 目的:观察骨膜细胞经骨形态发生蛋白7诱导后碱性磷酸酶的表达。 方法:取材于成人胫骨骨膜,常规细胞培养法行骨膜细胞体外培养,分为实验组和对照组,分别加入骨形态发生蛋白7加成骨细胞培养辅助剂和单纯成骨细胞培养辅助剂,相差显微镜观察骨膜细胞形态特征及超微结构。每组分别在第7,14,21天设3个时间点,每个时间点设3个样本,采用碱性磷酸酶试剂盒法检测成骨细胞特异性标志物碱性磷酸酶表达情况。 结果与结论:骨膜细胞经分组培养后,第7天时,实验组和对照组骨膜细胞均有明显增殖,碱性磷酸酶的可被检测出,但量不多,细胞外形为梭形,实验组比对照组检测的碱性磷酸酶数量稍多;第14天时,实验组及对照组骨膜细胞均显著增殖,细胞外形由梭形变为宽梭形,实验组比对照组检测的碱性磷酸酶数量明显增多。第21天时,实验组及对照组骨膜细胞均增殖,其中实验组细胞增殖明显,细胞外形为宽梭形,实验组比对照组检测的碱性磷酸酶数量显著增多。经过统计学分析由骨形态发生蛋白7诱导的骨膜细胞的成骨标志物碱性磷酸酶阳性率明显高于对照组(P < 0.01)。提示骨膜细胞具有良好的成骨和再生能力, 骨形态发生蛋白7能诱导骨膜细胞加强碱性磷酸酶的表达,能诱导骨膜细胞向成骨细胞转化。
中图分类号:




.jpg)