| [1] Athanasiou VT,Papachristou DJ,Panagopoulos A,et al. Histological comparison of autograft,allograft-DBM, xenograft,and synthetic grafts in a trabecular bone defect:an experimental study in rabbits.Med Sci Monit.2010;16(1): 24-31.[2] Develioglu H,Unver Saraydin S,Kartal U.The bone-healing effect of a xenograft in a rat calvarial defect model.Dent Mater J.2009;28(4):396-400.[3] Batista BL,Rodrigues JL,Souza VC,et al.A fast ultrasoundassisted extraction procedure for trace elements determination in hair samples by ICP-MS for forensic analysis. Forensic Sci Int.2009;192(1-3):88-93.[4] Liu CT,Wu CY,Weng YM,et al.Ultrasound-assisted extraction methodology as a tool to improve the antioxidant properties of herbal drug Xiao-chia-hu-tang.J Ethnoph Armacol.2005;99(2): 293-300.[5] Zhang L,Wang X.Hydrophobic ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted extraction of magnolol and honokiol from cortex Magnoliae officinalis.J Sep Sci.2010;33(13): 2035-2038.[6] 肖飞,郑治,王剑龙.新型支架材料磷酸钙骨水泥-聚乳酸聚羟基乙酸二聚体复合物生物相容性的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2006, 23(10):1254-1256.[7] 王明海,冯庆玲,董有海,等.可注射性纳米组织工程骨的生物相容性[J].中华实验外科杂志,2009,26(3):346-348.[8] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局.GB/T 16886.5- 2003.医疗器械生物学评价第5部分:体外细胞毒性试验[S].北京:中国标准出版社, 2003:80-88.[9] 苏保,蒋电明,严永刚,等.氨基酸聚合物/硫酸钙生物工程骨的生物相容性研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2011,33(1):40-44.[10] 李国华,陈吉华.牙科全瓷材料3Y-TZP生物相容性初步评价[J].口腔医学研究,2007,23(1):4-6.[11] Bigham AS,Dehghani SN,Shafiei Z,et al.Xenogenic demineralized bone matrix and fresh autogenous cortical bone effects on experimental bone healing:radiological, histopathological and biomechanical evaluation.J Orthop Traumatol.2008;9(2):73-80. [12] Develioglu H,Sarayd?n S,Kartal U,et al.Evaluation of the Long-Term Results of Rat Cranial Bone Repair Using a Particular Xenograft. J Oral Implantol.2010;36(3):167-173.[13] 兰小勇,周初松,田京,等.海藻酸钙纳米羟基磷灰石胶原复合材料与兔骨髓基质干细胞的体外细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(36):7022-7026.[14] Wingerter S,Tucci M,Bumgardner J,et al.Evaluation of short-term healing following sustained delivery of osteoinductive agents in a rat femur drill defect model.Biomed Sci Instrum.2007;43:188-193.[15] Cool SM,Kenny B,Wu A,et al.Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co- 3-hydroxyvalerate) composite biomaterials for bone tissue regeneration: in vitro performance assessed by osteoblast proliferation,osteoclast adhesion and resorption,and macrophage proinflammatory response.J Biomed Mater Res A.2007;82(3):599-610.[16] Leivo J,Meretoja V,Vippola M,et al.Sol-gel derived aluminosilicate coatings on alumina as substrate for osteoblasts.Acta Biomater.2006;2(6):659-668.[17] Naganawa T,Ishihara Y,Iwata T,et al.In vitro biocompatibility of a new titanium-29niobium-13tantalum-4.6zirconium alloy with osteoblast-like MG63 cells. J Periodontol.2004;75:1701-1707.[18] Liao S,Wang W,Uo M,et al.A three-layerednano-carbonated hydroxyapatite/Co-llagen/PLGA composite membranefor guided tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2005;26(36): 7564-7571.[19] Herath HM,Di Silvio L,Evans JR. Biological evaluation of solid freeformed, hard tissue scaffolds for orthopedic applications.J Appl Biomater Biomech.2010;8(2):89-96. |
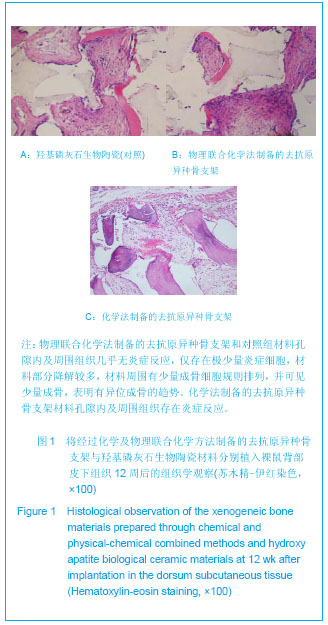


.jpg)