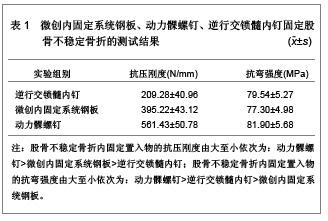
| [1] Krieg JC. Proximal tibial fractures: current treatment, results, and problems. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A2-10.[2] Schandelmaier P, Partenheimer A, Koenemann B, et al. Distal femoral fractures and LISS stabilization. Injury. 2001;32 Suppl 3:SC55-63.[3] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-1-10. https://www.cnki.net[4] 谭相齐,张文祥,季祝永,等.AO微创内固定系统治疗股骨远端骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2010,16(6):450-452.[5] 俞鹤松,周国万.LISS钢板内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效分析[J].现代实用医学,2011,23(11):1236-1237.[6] 张林华,卜海富,周健,等.LISS钢板在治疗股骨远端骨折中的应用[J].安徽医药,2010,14(2):188-189.[7] 徐小平,倪卫东,高仕长,等.LISS钢板治疗老年股骨远端骨折[J].西部医学,2011,23(8):1431-1433.[8] 艾拜都拉•吐拉甫.动力髁螺钉(DCS)在股骨髁间骨折内固定的临床应用[J].新疆医学,2011,41(11):57-58.[9] 叶建华,姜建飞,金志先,等.中西医结合内固定治疗股骨远端骨折30例临床研究[J].生物医学工程学进展,2010,31(2):95-97.[10] 李晓华,廖劲松.动力髁螺钉内固定结合中药熏洗治疗股骨远端骨折58例临床观察[J].中医药导报,2010,16(6):64-65.[11] 王云华,方长昆.动力髁螺钉治疗股骨远端骨折临床分析[J].实用临床医学,2010,11(9):37-39.[12] 孙铁,卢军,李云龙,等.股骨逆向交锁钉在股骨远端骨折中的应用体会[J].中国实用医药,2011,6(4):115-116.[13] 宋锁行.股骨逆行交锁髓内钉治疗股骨远端骨折[J].临床医药实践,2012,21(4):316-318.[14] 李俊青.股骨逆行交锁髓内钉治疗股骨远端骨折疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2011,4(12):106-107.[15] 郑熔昭,罗张进,蒙显章.逆行交锁髓内钉治疗股骨远端骨折63例[J].广西医科大学学报,2010,27(4):629-630.[16] 郝晓.微创内固定系统与动力髁螺钉内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效比较[J].中国医药导报,2011,8(6):162-163.[17] 马继征.微创内固定系统(LISS)与动力髁螺钉固定治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效分析[J].河南外科学杂志,2012,18(2):44-45.[18] 田琨.MIPO技术治疗股骨远端骨折:动力髁螺钉与LISS钢板的比较[J].江西中医药,2010,41(11):42-45.[19] 戎毅.微创内固定系统(LISS)与动力髁螺钉内固定治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效比较[J].中国实用医药,2011,6(16):78-79.[20] 徐存立,孙爱华.LISS及GSH内固定系统治疗股骨远端骨折的疗效分析[J].中国社区医师(医学专业),2012,14(16):148-149.[21] 徐龙伟,季卫平,李浩,等.逆行交锁髓内钉与微创内固定系统内固定治疗股骨远端A3型骨折的随机对比研究[J].浙江创伤外科, 2010,15(6):745-746.[22] 孙邦建,何磊,赵松涛.GSH和DCS治疗股骨远端骨折疗效分析[J].河北医药,2010,32(14):1917-1918.[23] 邱桂斌,温进杰,周春晖,等.不同内固定材料在成人股骨远端骨折手术治疗中的应用观察[J].山东医药,2010,50(34):74-75.[24] 刘德美.逆行交锁髓内钉与动力髁螺钉治疗股骨远端骨折的临床分析[J].中国当代医药,2012,19(7):43-44.[25] 李大伟.股骨远端A型及C型骨折不同内固定方式的疗效比较[J].河北联合大学学报(医学版),2012,14(2):226-227.[26] 孙庆华,赵东,杨龙彪,等.股骨远端骨折不同内固定方法的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(12):1064-1066.[27] Firoozbakhsh K, Behzadi K, DeCoster TA, et al. Mechanics of retrograde nail versus plate fixation for supracondylar femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(2):152-157.[28] Mize RD. Surgical management of complex fractures of the distal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(240):77-86.[29] 张秋林,王家林,王秋根,等.动力髁螺钉治疗股骨远端骨折[J].第二军医大学学报,2001,22(10):938.[30] 任高宏,沈开金,林昂如.股骨远端骨折的治疗现状与进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(4):246-247.[31] Zlowodzki M, Williamson S, Cole PA, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the less invasive stabilization system, angled blade plate, and retrogradeintramedullary nail for the internal fixation of distal femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18(8):494-502.[32] Kregor PJ, Stannard J, Zlowodzki M, et al. Distal femoral fracture fixation utilizing the Less Invasive Stabilization System (L.I.S.S.): the technique and early results. Injury. 2001;32 Suppl 3:SC32-47.[33] Cole PA, Zlowodzki M, Kregor PJ. Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS) for fractures of the proximal tibia: indications, surgical technique andpreliminary results of the UMC Clinical Trial. Injury. 2003;34 Suppl 1:A16-29.[34] Schütz M, Müller M, Regazzoni P, et al. Use of the less invasive stabilization system (LISS) in patients with distal femoral (AO33) fractures: a prospectivemulticenter study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(2):102-108. |