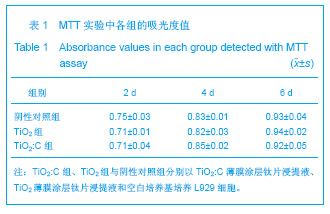
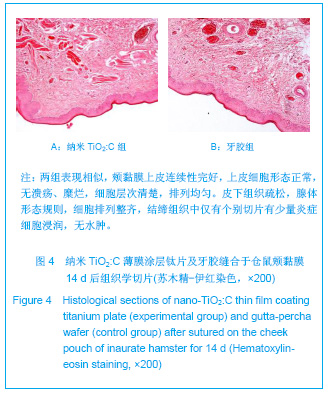
| [1] Lucas D,André A,Lourenço M,et al. Biocompatibility Evaluation of Epiphany/ Resilon Root Canal Filling System in Subcutaneous Tissue of Rats. J Endod.2010;36(1): 110-114. [2] Wang XL,Ma Y,He HM,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(21):4085-4088. 王晓玲,马妍,何惠明,等.不同增稠载体过氧化脲漂白凝胶对口腔黏膜的刺激性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(21): 4085-4088.[3] Williams DF. On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2008;29 (20): 2941-2953.[4] Mai L,Huang C,Wang D,et al.Effect of C doping on the structural and optical properties of sol–gel TiO2 thin films. Appl Surf Sci.2009; 255: 9285-9289.[5] Mai LX,Zhang S,Wang CY,et al.Zhongshan Daxue Xuebao. 2011;50(6):82-87. 麦理想,张晟,王春阳,等.纳米TiO2:C薄膜涂层的构建及对大肠杆菌的抗菌性能研究[J].中山大学学报:自然科学版,2011,50(6): 82-87.[6] ISO 7405:1997.Dentistry-preclinical evaluation of biocompatibi- lity of medical devices used in dentistry-test methods for dental materials. Geneva, 1997.[7] YY/T 0268–2001.牙科学用于口腔的医疗器械生物相容性临床前评价.2002-03–01实施.[8] Allabouch A,Colat-parros J,Salmon R,et al. Biocompatibility of some materials used in dental implantology. Histological study.Colloid Surfaces B.1993;1(5): 323-329.[9] Montanaro L,Campoccia D,Arciola CR. Advancements in molecular epidemiology of implant infections and future perspectives.Biomaterials.2007;28 (34):5155-5168.[10] Vanden Beucken JJ,Walboomers XF,Vos MR,et al.Cyto-and histocompatibility of multilayered DNA-coatings on titanium.J Biomed Mater Res A.2006;77(1): 202-211.[11] Yourtee MD,Tong PY,Rose LA,et al.The Effect of Spiroorthocarbonate Volume Modifier Co-monomers on the In Vitro Toxicology of Trial Non-shrinking Dental Epoxy Co-polymers. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol.2009; 86(3):347.[12] Richardson R,Miller JA,Reichera WM. Polyimides as biomaterials Preliminary biocompatibility testing. Biomaterials. 1993;14(1):627. [13] Zou ZW,Shi FJ,Huang ZH,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(38):7149-7152. 邹兆伟,史福军,黄宗海,等.纳米载银磷酸锆抗菌聚氨酯的细胞毒性检测[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(38): 7149-7152.[14] Wang XY,Wang YL.Beijing Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng. 2007; 26(2):95-98. 王喜云,王远亮.生物材料的生物学评价方法研究进展[J].北京生物医学工程,2007,26(2):95-98. [15] Thonemann B,Schmalz G,Hiller KA,et al.Responses of L929 mouse fibroblasts, primary and immortalized bovine dental papilla-derived cell lines to dental resin components. Dent Mater.2002;18(4):318-323.[16] Weyermann J,Lochmann D,Zimmer A. A practical note on the use of cytotoxicity assays.Int J Pharm.2005;288(2): 369-376.[17] Wang X, Xia Y, Liu L,et al. Comparison of MTT assay, flow cytometry and RT-PCR in the evaluation of cytotoxicity of five prosthodontic materials. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2010; 95(2):357-364.[18] Gorbet MB,Sefton MV.Biomaterial-associated thrombosis: roles of coagulation factors, complement, platelets and leukocytes. Biomaterials.2004; 25(26): 5681 -5703. [19] Yan LD,Wang C,Du EP,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(3):479-474. 阎立丹,王晨,杜文鹏,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯/二氧化硅纳米义齿树脂材料遗传毒性的小鼠骨髓微核试验评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(3):479-474. |