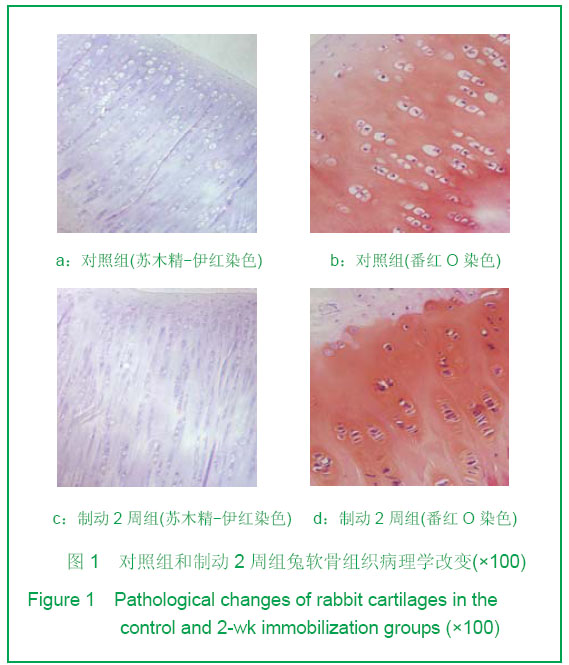
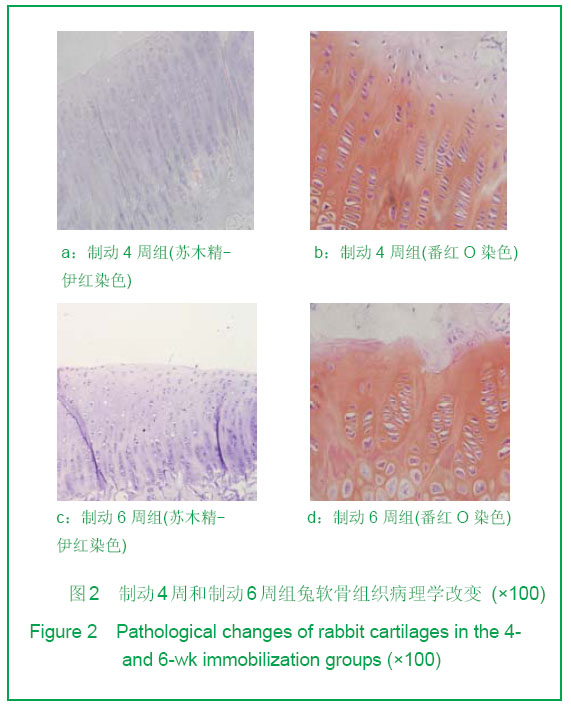
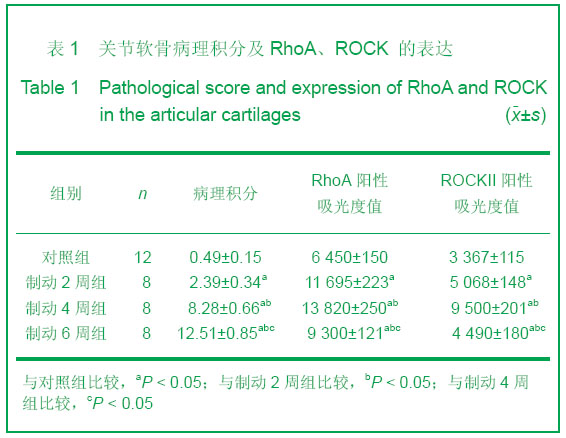
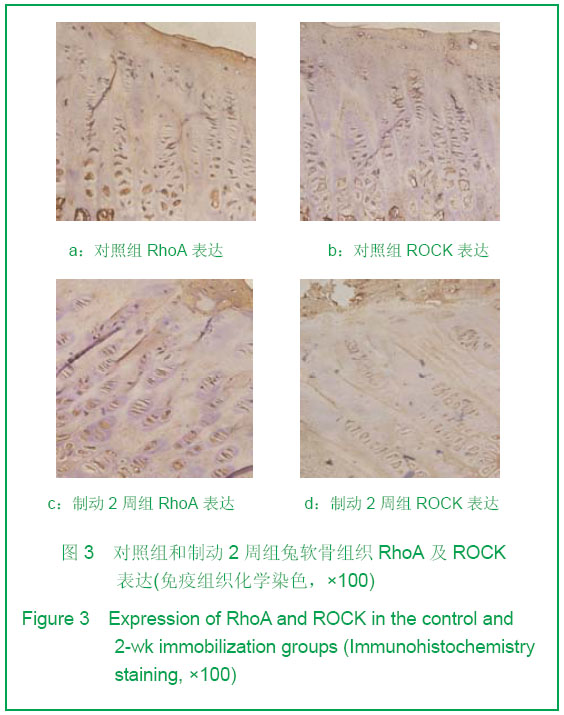
| [1] Durrant LA, Archer CW, Benjamin M,et al. Organisation of the chondrocyte cytoskeleton and its response to changing mechanical conditions in organ culture. J Anat.1999;194 (Pt 3):343-353.[2] Langelier E, Suetterlin R, Hoemann CD, et al. The Chondrocyte Cytoskeleton in Mature Articular Cartilage: Structure and Distribution of Actin, Tubulin, and Vimentin Filaments. J Histochem Cytochem.2000;48(10):1307-1320.[3] Pritzker KP, Gay S, Jimenez SA, et al. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006 ,14(1):13-29.[4] Woods A, Wang G, Beier F. Regulation of chondrocyte differentiation by the actin cytoskeleton and adhesive interactions. J Cell Physiol.2007;213(1): 1-8.[5] Liang J, Feng J, Wu WK,et al. Leptin-Mediated Cytoskeletal Remodeling in Chondrocytes Occurs Via the RhoA/ROCK Pathway. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(3):369-374.[6] Xu K,Ma XL,Zhang Y,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(46):8559-8562.许可,马信龙,张园,等.异常应力条件下关节软骨的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(46):8559-8562.[7] Mankin HJ,Dorfman H,Lippiello L,et al. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971;53(3):523-537.[8] Qiu GX,Wang GS.Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 1987;25(3): 175-177. 邱贵兴,王桂生.兔膝关节制动引起关节软骨退变的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,1987, 25(3):175-177.[9] Chen CW,Wei XC,Yang ZQ,et al.Zhonghua Fengshibingxue Zazhi. 2003;7(6): 332-335. 陈崇伟,卫小春,杨自权,等.伸膝制动骨关节炎动物模型软骨内胶原变化的观察[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2003,7(6): 332-335.[10] Appleton CT, Usmani SE, Mort JS, et al. Rho/ROCK and MEK/ERK activation by transforming growth factor-alpha induces articular cartilagedegradation. Lab Invest. 2010;90(1): 20-30.[11] Haudenschild DR, Chen J,Pang N, et al. Rho Kinase-Dependent Activation of SOX9 in Chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum.2010;62(1):191-200.[12] Kumar D , Lassar AB. The Transcriptional Activity of Sox9 in Chondrocytes Is Regulated by RhoA Signaling and Actin Polymerization. Mol Cell Biol.2009;29(15):4262-4273.[13] Novakofski K, Boehm A, Fortier L.The Small GTPase Rho Mediates Articular Chondrocyte Phenotype and Morphology in Response to Interleukin-1a and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(1):58-64.[14] Koyano Y, Kawamoto T, Kikuchi A, et al. Chondrocyte-derived ezrin-like domain containing protein (CDEP), a rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor, is inducible in chondrocytes by parathyroid hormone and cyclic AMP and has transforming activity in NIH3T3 cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9 Suppl A:S64-8[15] Church V, Nohno T, Linker C,et al. Wnt regulation of chondrocyte differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2002;115(Pt 24): 4809-4818.[16] Haudenschild DR, Chen J,Pang N, et al. Rho Kinase-Dependent Activation of SOX9 in Chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum.2010;62(1):191-200.[17] Haudenschild DR, Nguyen B, Chen J,et al. Rho-Dependent CCL20 Induced by Dynamic Compression of Human Chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum.2008;58(9):2735-2742.[18] Sanz-Ramos P, Mora G, Ripalda-Cemboráin P,et al. Identification of signalling pathways triggered by changes in the mechanical environment in rat chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(8):931-939.[19] Gill KS, Beier F, Goldberg HA. Rho-ROCK signaling differentially regulates chondrocyte spreading on fibronectin and bone sialoprotein. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008;295(1): C38-49. [20] Clark EA, King WG, Brugge JS,et al.Integrin-mediated Signals Regulated by Members of the Rho Family of GTPases. J Cell Biol. 1998;142(2):573-86.[21] Tominaga T, Barber DL.Na–H Exchange Acts Downstream of RhoA to Regulate Integrin-induced Cell Adhesion and Spreading. Mol Biol Cell. 1998;9(8):2287-2303.[22] Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H,et al. Calciumsensitization of smooth musclemediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature. 1997;389(6654):990-994.[23] Wang G, Woods A, Sabari S, et al. RhoA/ROCK Signaling Suppresses Hypertrophic Chondrocyte Differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(13):13205-13214.[24] Matsumoto E, Furumatsu T, Kanazawa T, et al.ROCK inhibitor prevents the dedifferentiation of human articular chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2012;420(1):124-129[25] Takeshita N, Yoshimi E, Hatori C, et al. Alleviating Effects of AS1892802, a Rho Kinase Inhibitor,on Osteoarthritic Disorders in Rodents. J Pharmacol Sci. 2011;115(4):481-489. |